NASA eyes Typhoon Prapiroon's U-turn
2012-10-11
Typhoon Prapiroon is making a U-turn in the Philippine Sea, changing direction from northwest to northeast. NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of the typhoon as it began turning. Visible satellite imagery revealed its most powerful thunderstorms south and east of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Prapiroon on Oct. 10 at 0435 UTC (12:35 a.m. EDT) and captured a visible image of the storm. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument was able to get a visible image of the typhoon, because it was 1:35 p.m. local Asia/Tokyo ...
Suomi NPP satellite sees auroras over North America
2012-10-11
Overnight on October 4-5, 2012, a mass of energetic particles from the atmosphere of the Sun were flung out into space, a phenomenon known as a coronal mass ejection. Three days later, the storm from the Sun stirred up the magnetic field around Earth and produced gorgeous displays of northern lights. NASA satellites track such storms from their origin to their crossing of interplanetary space to their arrival in the atmosphere of Earth.
Using the "day-night band" (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership ...
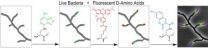
Filming bacterial life in multicolor as a new diagnostic and antibiotic discovery tool
2012-10-11
An international team of scientists led by Indiana University chemist Michael S. VanNieuwenhze and biologist Yves Brun has discovered a revolutionary new method for coloring the cell wall of bacterial cells to determine how they grow, in turn providing a new, much-needed tool for the development of new antibiotics.
Discovery of the new method is expected to broadly impact both basic and applied research tied to understanding, controlling or preventing bacterial cell growth in specific environments, said the two scientists in IU Bloomington's College of Arts and Sciences. ...
Choreography of submerged whale lunges revealed
2012-10-11
Returning briefly to the surface for great lungfuls of air, the underwater lifestyles of whales had been a complete mystery until a small group of pioneers from various global institutions – including Malene Simon, Mark Johnson and Peter Madsen – began attaching data-logging tags to these enigmatic creatures. Knowing that Jeremy Goldbogen and colleagues had successful tagged blue, fin and humpback whales to reveal how they lunge through giant shoals of krill, Simon and her colleagues headed off to Greenland where they tagged five humpback whales to discover how the animals ...
Soft-shelled turtles urinate through mouth
2012-10-11
Chinese soft-shelled turtles are exquisitely adapted to their aquatic lifestyle, sitting contentedly on the bottom of brackish muddy swamps or snorkelling at the surface to breath. According to Y. K. Ip from the National University of Singapore, they even immerse their heads in puddles when their swampy homes dry up: which intrigued Ip and his colleagues. Why do these air-breathing turtles submerge their heads when they mainly depend on their lungs to breathe and are unlikely to breathe in water? Given that some fish excrete waste nitrogen as urea – in addition to ammonia ...
Techniques used to infer pathways of protein evolution found unreliable
2012-10-11
A key assumption that biologists have relied on widely over the past quarter-century in studying the evolution of protein molecules is "highly questionable," according to an article published in the November issue of BioScience.
The article, by Shozo Yokoyama, a vision researcher at Emory University, summarizes experimental work that involved creating and measuring the properties of dozens of reconstructed ancestral versions of visual pigments found in the eyes of vertebrates, including humans, as well as deliberately altered variants. Yokoyama concludes that the studies ...
How food marketers can help consumers eat better while improving their bottom line!
2012-10-11
Food marketers are masters at getting people to crave and consume the foods that they promote. In this study authors Dr. Brian Wansink, co-director of the Cornell University Center for Behavioral Economics in Child Nutrition and Professor of Marketing and Dr. Pierre Chandon, professor of Marketing at the leading French graduate school of business, INSEAD challenge popular assumptions that link food marketing and obesity. Their findings presented last weekend at the Association for Consumer Research Conference in Vancouver, Canada point to ways in which smart food marketers ...
Prospective Alzheimer's drug builds new brain cell connections
2012-10-11
PULLMAN, Wash.—Washington State University researchers have developed a new drug candidate that dramatically improves the cognitive function of rats with Alzheimer's-like mental impairment.
Their compound, which is intended to repair brain damage that has already occurred, is a significant departure from current Alzheimer's treatments, which either slow the process of cell death or inhibit cholinesterase, an enzyme believed to break down a key neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory development.
Such drugs, says Joe Harding, a professor in WSU's College of Veterinary ...
The Marshmallow Study revisited
2012-10-11
For the past four decades, the "marshmallow test" has served as a classic experimental measure of children's self-control: will a preschooler eat one of the fluffy white confections now or hold out for two later?
Now a new study demonstrates that being able to delay gratification is influenced as much by the environment as by innate ability. Children who experienced reliable interactions immediately before the marshmallow task waited on average four times longer—12 versus three minutes—than youngsters in similar but unreliable situations.
"Our results definitely ...
Michelle Salater, CEO of Sumer, LLC, to Host New Podcast Show for Entrepreneurs to Hear Business Confessions
2012-10-11
Michelle Salater will host an extension of her business blog, Copy Doodle, in a new radio show that will focus on helping businesses grow and become more profitable.
Business Confessional Talk Radio: Where Entrepreneurs Gather and Experts Tell All is featured on the Entrepreneur Podcast Network, a platform that condenses advice, information, and inspiration into one space.
Geared toward an audience of entrepreneurs in different stages of their businesses, this show will invite innovative and successful business owners to answer questions and discuss the recipe for ...
Promising Pop Newcomer Courtney Rau Releases "Thanks, But No Thanks" On ITunes
2012-10-11
This new singer is continuing to make impressive music that showcases her keen sense of sound and style and natural talent. Following the successes of her previous single, Courtney has now released her highly anticipated single "Thanks, But No Thanks" on iTunes.
An energetic tune with an empowering tone, Courtney's latest release, "Thanks, But No Thanks," charges the listener, leaving them wanting more. It has a melody that makes it an easy one to play again and again, enlivening and uplifting with its catchy beat and great sense of energy. Now available ...
Lighthouse for the Blind-Saint Louis Wins Contract to Provide Disaster Response Emergency Supplies to U.S. Navy
2012-10-11
The Lighthouse for the Blind-St. Louis, a not-for-profit manufacturing and packaging organization with a dedicated social service mission, has been awarded a contract to provide supplies for use by U.S. Navy Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear and Explosives (CBRNE) disaster response groups.
Under the contract awarded by the federal AbilityOne program, the Lighthouse will utilize employees who are blind in fulfillment operations to pack orders for many types of personal protective equipment and ship these essential supplies to more than 65 U.S. Navy sites around ...
The Best Place Online For All Your Body Detoxification Needs! Our Goal Is To Help You Meet Your Goal At Bodydetoxshop.com
2012-10-11
Best Selection of Detox Teas and Herbal Body Wraps to cleanse your body! Bit.ly/V1F7BU
People who want to have an effective body detoxification program will be very happy to note that http://www.bodydetoxshop.com is now online and ready to serve them. This website has a wide product inventory that caters to all detoxification and weight loss needs. It does not matter what kind of detoxification program or weight loss program you are following. Rest assured, bodydetoxshop.com has the products you need.
Bodydetoxshop.com carries all the leading brands for body detoxification ...
Go Skate Expands Company to Cover 2,500 Public Skate Parks with Lesson Programs
2012-10-11
Go Skate Skateboard School is based in San Diego and has taught skateboard lessons at over 1300 locations in United States for the past three years. In October 2012, Go Skate has expanded to cover all of the country's over 2500 skate parks.
Go Skate's owner, Rob Dunfey says, "We used to get calls all the time from people who would love to learn to skate, but we didn't have a location in their area. Now, they can learn how to skate."
It is now possible to get a skateboard lesson at any public U.S. skate park year-round. Dunfey also adds, "It didn't ...
MusicDishTV Presents Southern Rock Music Video "Everyside" By Eliot Wayne
2012-10-11
Eliot Wayne puts on a guitar clinic in his new powerful southern rock track 'Everyside'. The smooth country vocals blend perfectly with the chugging of Wayne's heavy rock telecaster. The video is great within it's simplicity, as it has Wayne playing the entire song from his patio. Not being distracted by anything else on the screen, the viewer is able to truly focus on the raw emotion displayed by Eliot Wayne. The song's about falling in love, and his lyrics are so moving and so powerful. But let's not forget the awesome guitar lines! When Eliot Wayne goes into a guitar ...
McDill Associates Wins a 2012 American Graphic Design Award
2012-10-11
Design and marketing agency McDill Associates has added another award to its list of noteworthy honors. The agency, now in its 34th year, recently won a 2012 American Graphic Design Award for its Laptop Lunches Bento-Ware packaging for Obentec, Inc.
The packaging recognized by AGDA was designed for an innovative product line of waste-free packing for any meal or snack. The packaging design incorporated original illustrations and key messages developed to broaden the appeal of the nationally distributed line. A messaging and positioning exercise defined the direction. ...
Lee Enterprises Consulting Group Adds Military Expert
2012-10-11
Alternative and renewable energy consulting group, Lee Enterprises of Little Rock, Ark., is pleased to announce the addition of Scott Greenfield to its team of biofuels consultants. Greenfield received a B.A. in Biology from the University of Texas at Austin and a Master's in Business Administration from the University of California, Berkeley. A former Naval Officer, Greenfield has over 22 years of experience working with the Navy as well as in the government and private sectors, most recently working in Special Projects for the Naval Special Warfare Command in the study ...
Breath Tests for Alcohol Are Not Perfect
2012-10-11
In 2011 the state of Washington began changing over the machines its law enforcement officers use to determine the blood alcohol content of people suspected of driving drunk. Commonly referred to as Breathalyzers, these machines use a breath test to measure how much alcohol is in a person's system. If a person is arrested on suspicion of driving under the influence of alcohol, the Breathalyzer results may be used by prosecutors in a DUI case.
How Breathalyzers Work
After a person ingests alcohol, the alcohol enters the bloodstream from the stomach without undergoing ...
Driver Field Sobriety Tests Used in Washington DUI Cases
2012-10-11
When a driver in Washington is pulled over on suspicion of drunk driving, in addition to a breath test, the law enforcement officer may administer a series of driver field sobriety tests. These tests are used to attempt to determine whether a driver is impaired by alcohol, but the officer must ask and the driver must consent to the field tests before they can be performed. The following is a brief overview of the three standardized tests used in field sobriety testing.
Horizontal Gaze Nystagmus
An officer administers a horizontal gaze nystagmus test, commonly called ...
The Price of Safety: Feds Relax Train Accident Prevention Standards
2012-10-11
When a train approaches a railroad crossing, barriers and sounds are supposed to warn crossing traffic. Despite the warning, though, train accidents continue to occur at crossings and along other portions of the rail network in Texas. To help prevent the risk of train accidents, the federal government required railroad companies to outfit their tracks with certain collision-avoidance technology; however, the requirement was recently relaxed due to cost concerns, which may have a detrimental impact on public safety.
Train Crash Prompts Greater Safety Controls
In 2008, ...
Truck Accidents: A Look at Factors that Cause Rear-End Collisions
2012-10-11
Plenty of commercial truck traffic flows through the Dallas-Fort Worth area every day. Unfortunately, because of the high number of 18-wheelers and other heavy trucks, folks in Arlington are no stranger to trucking accidents involving serious injury. One of the worst types of these truck accidents is rear-end collisions.
Truck Accident Statistics
According to the U.S. Department of Transportation, each year about 400,000 motor vehicle crashes involve large trucks in the United States, and rear-end crashes account for 18 percent of those crashes.
Rear-end crashes ...
Driver Charged with DUI in Collision With Bicyclists in Utah
2012-10-11
Recently a 23-year old motorist ran into two bicyclists who were riding on the side of the Van Winkle Expressway in Murray, Utah, sending one of the bicyclists to the hospital with serious head injuries. The other bicyclist was less seriously hurt, receiving only minor injuries. The driver has been arrested on suspicion of driving under the influence. If convicted, the driver could face serious penalties under Utah's DUI and vehicular assault laws.
Drunk Driving in Utah
Under Utah law, a drunk driving charge can be pursued if the driver was operating a motor vehicle ...
Sophisticated Drug Tunnels Discovered in Arizona
2012-10-11
For years secret tunnels along the United States border with Mexico have been built to smuggle drugs, but recently the tunnels have become more sophisticated. In July 2012, four drug smuggling tunnels were discovered within a week of one another: two in California and two in Arizona, with one of the Arizona tunnels being the most advanced tunnel yet discovered. Authorities believe the growing sophistication of the passages may be explained in part by support from Mexican drug cartels.
In the middle of July, Arizona state police discovered a 240-yard tunnel running from ...
Meriweather Pleads to Lesser Charge in Virginia DUI Case
2012-10-11
Popular NFL player Brandon Meriweather of the Washington Redskins is able to move on after a DUI charge earlier this year. After pleading no contest to a reduced charge of reckless driving, Meriweather's case was resolved when he paid a fine, court fees, and received a suspended 180-day jail sentence, avoiding worse penalties that follow a Virginia DUI conviction.
Arrested for Suspected DUI
On April 26, 2012, the two-time Pro Bowler was pulled over by an Arlington County, Virginia police officer around 3:00 a.m. after the officer clocked him driving 73 mph in a 55 ...
Your Life Wishes Require a Will by a Qualified Estate Planning Attorney
2012-10-11
A sluggish economy has incentivized people to do their own home repairs, cook for themselves more and perform other tasks that in a more vibrant economy might not be necessary. Unfortunately, as part this trend, many individuals are using cookie-cutter, out-of-the-box wills and will programs to plan for their heirs and beneficiaries when they pass away.
Rarely do these DIY wills provide anything like what you intend.
Attorney-drafted wills are not just for millionaires concerned about federal and state estate taxes. Estate taxes are commonly referred to as an inheritance ...
[1] ... [5823]
[5824]
[5825]
[5826]
[5827]
[5828]
[5829]
[5830]
5831
[5832]
[5833]
[5834]
[5835]
[5836]
[5837]
[5838]
[5839]
... [8810]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.