Roman military camp dating back to conquest of Gaul throws light on part of world history
2012-09-14
In the vicinity of Hermeskeil, a small town some 30 kilometers southeast of the city of Trier in the Hunsrueck region in the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate, archaeologists from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have confirmed the location of the oldest Roman military fortification known in Germany to date. These findings shed new light on the Roman conquest of Gaul. The camp was presumably built during Julius Caesars' Gallic War in the late 50s B.C. Nearby lies a late Celtic settlement with monumental fortifications known as the "Hunnenring" or "Circle ...
Learning faster with neurodegenerative disease
2012-09-14
People who bear the genetic mutation for Huntington's disease learn faster than healthy people. The more pronounced the mutation was, the more quickly they learned. This is reported by researchers from the Ruhr-Universität Bochum and from Dortmund in the journal Current Biology. The team has thus demonstrated for the first time that neurodegenerative diseases can go hand in hand with increased learning efficiency. "It is possible that the same mechanisms that lead to the degenerative changes in the central nervous system also cause the considerably better learning efficiency" ...
Whole-genome scan helps select best treatment for childhood cancer
2012-09-14
A whole-genome scan to identify large-scale chromosomal damage can help doctors choose the best treatment option for children with neuroblastoma, one of the most common types of childhood cancer, finds an international collaboration jointly led by The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
The researchers called for all children diagnosed with neuroblastoma worldwide to have a whole-genome scan as a standard part of their treatment.
Neuroblastoma, a cancer of the developing nervous system, is sometimes very treatable but other forms are highly aggressive, making the ...
New test to crack down on sporting drugs-cheat test
2012-09-14
Scientists from three UK universities have developed a new test to catch drugs-cheats in sport.
Over the last 10 years, the GH-2004 team, which is based the University of Southampton, has been developing a test for Growth Hormone misuse in sport with funding from the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and US Anti-Doping Agency and with support from UK Anti-Doping.
The test, developed by scientists at the University of Southampton, King's College London and University of Kent at Canterbury, is based on the measurement of two proteins in the blood, insulin-like growth factor-I ...
Researchers find our inner reptile hearts
2012-09-14
Since the early 1900s, scientists have been wondering how birds and mammals could have developed almost identical conduction systems independently of each other when their common ancestor was a cold-blooded reptile with a sponge-like inner heart that has virtually no conduction bundles.
The studies show that it is simply the spongy inner tissue in the foetal heart that gets stretched out to become a fine network of conductive tissue in adult birds and mammals. And this knowledge can be put to use in the future.
### END ...
Environment: Speaking the same language on noise exposure
2012-09-14
Quantifying noise exposure will be significantly easier thanks to a new set of common noise assessment methods published today. Comparable data on noise exposure in Europe is a prerequisite to set up EU policies to reduce noise pollution, a growing health and economic concern all over Europe. The new methods – known as Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU) – were drawn up by the European Commission's in-house science service, the Joint Research Centre. They assess noise from road, rail and air traffic and from industry, and will provide consistent and comparable ...
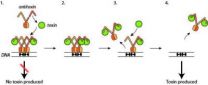
X-rays reveal the self-defence mechanisms of bacteria
2012-09-14
Many pathogenic bacteria are able to go into a dormant state by producing persister cells that are not susceptible to conventional antibiotics. This causes serious problems in the treatment of life-threatening diseases such as tuberculosis, where the presence of persister cells often leads to a resurgence of infection following medical treatment.
At the molecular level, the formation of persister cells is due to the presence of toxins that are produced by the bacteria themselves, and which enable them to enter the dormant state. During this hibernation period, the bacteria ...
Radar measurements of highest precision
2012-09-14
This press release is available in German.
Precise determination of distances is of increasing importance in fabrication technology, for instance, when actuating robots, producing micromechanical components, or controlling machine tools. Frequently, glass scales, inductive sensors, or laser measurement systems are used for distance measurements. Glass scales are very precise and reach micrometer precision. However, they are too inflexible and expensive for daily use. Inductive sensors measuring distances with a coil, magnetic field, and movement work in a contact-free ...
Passive smoking also affects neurodevelopment in babies
2012-09-14
A new study shows that newborns that have been exposed to nicotine from both active and passive smoking mothers show poor physiological, sensory, motor and attention responses.
Smoking during pregnancy has been linked to many different problems in infants like learning difficulties, attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity and even obesity.
However, although the paediatric and obstetric disorders linked to tobacco during this stage are well defined, the effects on neonatal behaviour have not yet been studied in depth.
A new study headed by experts at the ...
New insights on cell competition
2012-09-14
Scientists from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) describe how natural selection also occurs at the cellular level, and how our body's tissues and organs strive to retain the best cells in their ranks in order to fend off disease processes. These results appear this week in the new issue of Cell Reports. The research, carried out in the CNIO, is led by Eduardo Moreno, who is currently working at the University of Bern in Switzerland.
Recent studies suggest that natural selection described by Charles Darwin also occurs at the cellular level, as our body's ...
Trade unions still fail to lure women leaders, study finds
2012-09-14
There is little doubt that Frances O'Grady has made history as the first woman to be elected General Secretary of the Trades Union Congress in September 2012. A recent study from Queen Mary, University of London casts some light on the level of O'Grady's achievement in the wider union landscape.
This cross-national study found that in both the UK and the US, women still have fewer top positions in trade unions despite growth in overall female membership.
The paper, Lift as You Rise: Union Women's Leadership Talk, discusses the lack of women at union leadership level, ...
Getting (drugs) under your skin
2012-09-14
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Using ultrasound waves, MIT engineers have found a way to enhance the permeability of skin to drugs, making transdermal drug delivery more efficient. This technology could pave the way for noninvasive drug delivery or needle-free vaccinations, according to the researchers.
"This could be used for topical drugs such as steroids — cortisol, for example — systemic drugs and proteins such as insulin, as well as antigens for vaccination, among many other things," says Carl Schoellhammer, an MIT graduate student in chemical engineering and one of the lead authors ...
Surgery more profound effect than anesthesia on brain pathology, cognition in Alzheimer's mice
2012-09-14
PHILADELPHIA — A syndrome called "post-operative cognitive decline" has been coined to refer to the commonly reported loss of cognitive abilities, usually in older adults, in the days to weeks after surgery. In fact, some patients time the onset of their Alzheimer's disease symptoms from a surgical procedure. Exactly how the trio of anesthesia, surgery, and dementia interact is clinically inconclusive, yet of great concern to patients, their families and physicians.
A year ago, researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania reported ...
45 percent of layoff victims, despite anger, would return to former employer
2012-09-14
With an 8.1 percent August unemployment rate and 12.5 million Americans out of work, a new Temple University study examines a neglected area of research: how the unemployment process impacts the willingness of those laid off to endorse or return to their previous employer.
The study of predominantly highly paid, college-educated professionals who are unemployed finds that 45 percent of layoff victims would return to work for their former employer – despite anger over being terminated. The research also emphasizes the importance of fair and transparent layoff decisions, ...
Dr. Chiaravalloti of Kessler Foundation comments on trends in rehabilitation research in MS
2012-09-14
September 12, 2012. West Orange, NJ. Nancy Chiaravalloti, PhD, an expert in cognitive rehabilitation research, authored two commentaries on trends in multiple sclerosis (MS) research. Dr. Chiaravalloti is director of Neuropsychology & Neuroscience Research at Kessler Foundation. She was recently appointed director of Traumatic Brain Injury Research at the Foundation and also is principal investigator of the Northern New Jersey TBI System, a NIDRR-funded model system. Dr. Chiaravalloti is also an associate professor at UMDNJ-New Jersey Medical School.
Her editorial, ...
China's nuclear dilemma
2012-09-14
Los Angeles, CA (September 14, 2012) – An expert assessment of China's nuclear weapons strategy highlights the risk of escalation to nuclear war from a conflict beginning with conventional weapons, due to the unusual structure of the nation's military. The new study, previously only available in Chinese, appears in the latest edition of The Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, published by SAGE. The authors believe that this is the first comprehensive non-governmental study on how China's nuclear-war plan was developed.
John W. Lewis and Xue Litai, of Stanford University's ...
Probing matters of the heart
2012-09-14
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — The fate of an embryonic stem cell, which has the potential to become any type of body cell, is determined by a complex interaction of genes, proteins that bind DNA, and molecules that modify those genes and proteins.
In a new paper, biologists from MIT and the University of California at San Francisco have outlined how those interactions direct the development of stem cells into mature heart cells. The study, the first to follow heart-cell differentiation over time in such detail, could help scientists better understand how particular mutations can ...
Simple tool may help evaluate risk for violence among patients with mental illness
2012-09-14
Mental health professionals, who often are tasked with evaluating and managing the risk of violence by their patients, may benefit from a simple tool to more accurately make a risk assessment, according to a recent study conducted at the University of California, San Francisco.
The research, led by psychiatrist Alan Teo, MD, when he was a UCSF medical resident, examined how accurate psychiatrists were at evaluating risk of violence by acutely ill patients admitted to psychiatric units.
The first part of the study showed that inexperienced psychiatric residents performed ...
'Memristors' based on transparent electronics offer technology of the future
2012-09-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The transparent electronics that were pioneered at Oregon State University may find one of their newest applications as a next-generation replacement for some uses of non-volatile flash memory, a multi-billion dollar technology nearing its limit of small size and information storage capacity.
Researchers at OSU have confirmed that zinc tin oxide, an inexpensive and environmentally benign compound, has significant potential for use in this field, and could provide a new, transparent technology where computer memory is based on resistance, instead of an ...
Kidney society describes ways to eliminate wasteful tests and procedures
2012-09-14
Washington, DC (September 13, 2012) — Earlier this year, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN), the world's leading kidney organization, joined other groups in a campaign to help health care professionals and patients avoid wasteful and sometimes harmful medical interventions. A new article in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (CJASN) outlines the ASN's top five recommendations for the campaign and the rationale behind them. Following these recommendations would lower costs and lead to better care for patients with kidney disease.
Unnecessary ...
Looking at you: Face genes identified
2012-09-14
Monozygotic twins have almost identical faces and siblings usually have more similar faces than unrelated people, implying that genes play a major role in the appearance of the human face. However, almost nothing is known about the genes responsible for facial morphology in humans.
This study, carried out on behalf of the International Visible Trait Genetics (VisiGen) Consortium, used head magnetic resonance images together with portrait photographs to map facial landmarks, from which facial distances were estimated. The researchers then applied a genome-wide association ...
New analysis in Science tells how world eradicated deadliest cattle plague
2012-09-14
NAIROBI, KENYA (13 September 2012)—A new analysis published today in Science traces the recent global eradication of the deadliest of cattle diseases, crediting not only the development of a new, heat-resistant vaccine, but also the insight of local African herders, who guided scientists in deciding which animals to immunize and when. The study provides new insights into how the successful battle against rinderpest in Africa, the last stronghold of the disease, might be applied to similar diseases that today ravage the livestock populations on which the livelihoods of one ...
Genes render some rice species sterile
2012-09-14
Researchers have identified a set of three genes that are responsible for hybrid sterility in rice, or the inability of many hybrid rice species to pass their genes on to the next generation. These findings inform a model that suggests how such hybrid sterility is maintained across rice species, and they may lead to the genetic improvement of rice as a food stock.
The research is published in the 14 September issue of the journal Science, which is published by AAAS, the nonprofit science society.
When two different species mate, like a horse and a donkey, their hybrid ...
How fast can ice sheets respond to climate change?
2012-09-14
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- A new Arctic study in the journal Science is helping to unravel an important mystery surrounding climate change: How quickly glaciers can melt and grow in response to shifts in temperature.
According to the new research, glaciers on Canada's Baffin Island expanded rapidly during a brief cold snap about 8,200 years ago. The discovery adds to a growing body of evidence showing that ice sheets reacted rapidly in the past to cooling or warming, raising concerns that they could do so again as the Earth heats up.
"One of the questions scientists have been ...
How early social deprivation impairs long-term cognitive function
2012-09-14
Boston, Sept. 13, 2012-- A growing body of research shows that children who suffer severe neglect and social isolation have cognitive and social impairments as adults. A study from Boston Children's Hospital shows, for the first time, how these functional impairments arise: Social isolation during early life prevents the cells that make up the brain's white matter from maturing and producing the right amount of myelin, the fatty "insulation" on nerve fibers that helps them transmit long-distance messages within the brain.
The study also identifies a molecular pathway ...
[1] ... [6001]
[6002]
[6003]
[6004]
[6005]
[6006]
[6007]
[6008]
6009
[6010]
[6011]
[6012]
[6013]
[6014]
[6015]
[6016]
[6017]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.