Study finds long Covid patients feel pressure to prove their illness is real
2025-03-27
People living with Long Covid often feel dismissed, disbelieved and unsupported by their healthcare providers, according to a new study from the University of Surrey.
The study, which was published in the Journal of Health Psychology, looked at how patients with Long Covid experience their illness. The study found that many patients feel they have to prove their illness is physical to be taken seriously and, as a result, often reject psychological support, fearing it implies their symptoms are "all in the mind".
Professor ...
Smartwatches may help control diabetes through exercise
2025-03-27
Wearable mobile health technology could help people with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) to stick to exercise regimes that help them to keep the condition under control, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied the behaviour of recently-diagnosed T2D patients in Canada and the UK as they followed a home-based physical activity programme – some of whom wore a smartwatch paired with a health app on their smartphone.
They discovered that MOTIVATE-T2D participants were more likely to start and maintain purposeful exercise at if they had the support of wearable technology- the study successfully recruited 125 participants with an 82% ...
Fossils: Ancient parasitic ‘Venus flytrap’ wasp preserved in amber
2025-03-27
An extinct lineage of parasitic wasps dating from the mid-Cretaceous period and preserved in amber may have used their Venus flytrap-like abdomen to capture and immobilise their prey. Research, published in BMC Biology, finds that the specimens of Sirenobethylus charybdis — named for the sea monster in Greek mythology which swallowed and disgorged water three times a day — date from almost 99 million years ago and may represent a new family of insects.
The morphology of S. charybdis indicates the wasps were ...
New species revealed after 25 years of study on ‘inside out’ fossil – and named after discoverer’s mum
2025-03-27
A new species of fossil from 444 million years ago that has perfectly preserved insides has been affectionately named ‘Sue’ after its discoverer’s mum.
The result of 25 years of work by a University of Leicester palaeontologist and published in the journal Palaeontology, the study details a new species of multisegmented fossil and is now officially named as Keurbos susanae.
Lead author Professor Sarah Gabbott from the School of Geography, Geology and the Environment said: “‘Sue’ is an inside-out, legless, headless wonder. Remarkably her insides are a mineralised ...
THE LANCET HIV: Proposed cuts to foreign aid could result in millions of HIV deaths and soaring rates of global HIV infections, new modelling study estimates
2025-03-27
New modelling analysis suggests that proposed funding cuts by major donor countries to foreign aid could undo decades of progress made to end HIV/AIDS as a public health threat and new infections and deaths could surge back to levels not seen since the early 2000s.
The study estimates there could be between 4.4 million to 10.8 million additional new HIV infections by 2030 in low-and-middle income countries (LMICs) and between 770,000 to 2.9 million HIV-related deaths in children and adults by 2030.
The greatest impact from potential funding ...
Study reveals association between dietary sodium consumption and both general and abdominal obesity
2025-03-26
New research to be presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025, Malaga, Spain, 11-14 May) shows an association between the amount of sodium consumed in the diet and the risk of both general and abdominal obesity. The study is by Annika Santalahti, Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland, and colleagues.
General obesity is a person’s obesity status as measured by their body mass index (BMI), with WHO international guidelines stating a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more means a person is living with obesity. Abdominal obesity is where fat accumulates around the abdomen and internal organs there, leading ...
Study finds knowledge of genetics and genomic medicine crucial for mental health providers to deliver informed, personalized care
2025-03-26
San Diego—March 26, 2025– In a manuscript published today in the American Journal of Psychiatry titled Psychiatric Genetics in Clinical Practice: Essential Knowledge for Mental Health Professionals, authors provide updated guidelines on what mental health professionals should know about the latest advances in genetics and how genetics can inform clinical psychiatric practice.
Key findings highlight the importance of understanding the genetic architecture of psychiatric disorders, the potential applications of genetic information in risk assessment, diagnosis, treatment selection, and patient education, ...
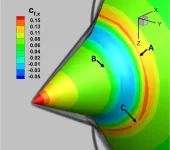
Hypersonic simulation in 3D exposes new disturbances
2025-03-26
At hypersonic speeds, complexities occur when the gases interact with the surface of the vehicle such as boundary layers and shock waves. Researchers in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in The Grainger College of Engineering, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign were able to observe new disturbances in simulations conducted for the first time in 3D.
Fully 3D simulations require a great deal of processing power, making the work expensive to compute. Two things made it possible for Deborah Levin and her Ph.D. student Irmak Taylan Karpuzcu to conduct the research: Time on Frontera, the National Science Foundation-funded leadership-class computer system at the Texas ...
Your neighborhood may affect your risk of dementia
2025-03-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4:00 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 26, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS — People living in more disadvantaged neighborhoods may be more likely to develop dementia than people living in neighborhoods with fewer disadvantages, according to a study published on March 26, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that neighborhood factors cause dementia; it only shows an association.
Neighborhood status was determined by factors such as income, employment, education and disability.
“Our findings show that the community in which you live influences your risk of developing dementia,” ...
Early signs of heart problems linked to smaller brain volumes
2025-03-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4:00 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 26, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS — People who have early signs of heart problems may also have changes in brain health that can be early signs of dementia, such as loss of brain volume, according to a meta-analysis published on March 26, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The meta-analysis does not prove that early heart problems cause loss of brain cells; it only shows an association.
“This review shows that better ...
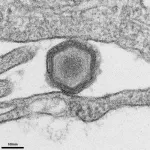
Research finds potential “molecular mimics” behind COVID-induced autoimmune disease
2025-03-26
COVID infection has been linked to higher risk of autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes. But why the virus might cause the body’s immune system to go haywire remains unknown, making it difficult to develop therapies to avoid autoimmunity. One hypothesis is that viral “molecular mimics” that resemble the body’s own proteins trigger an immune response against the virus—and healthy tissues get caught in the crossfire.
Now, with advanced data analysis and machine learning, scientists have identified a set of COVID-derived ...
Pennington Biomedical researchers identify neurons in brain that regulate energy levels and body temperature
2025-03-26
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
March 26, 2025
BATON ROUGE – Scientists at Pennington Biomedical Research Center have gained greater clarity in the brain regions and neurons that control metabolism, body temperature and energy use. Featured in the February edition of the journal Metabolism, Dr. Heike Münzberg-Gruening and a team of researchers discovered which chemicals influence the signals that control how much energy the body uses. In “Leptin Receptor Neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus require distinct neuronal subsets for thermogenesis and weight loss,” researchers laid out the pathways, chemicals, neurons ...
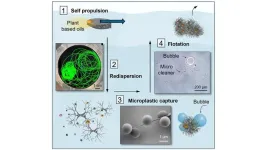
Cleaning microplastics
2025-03-26
In a new paper, researchers at North Carolina State University show proof of concept for a system that, in a single cycle, actively removes microplastics from water.
The findings, described in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, hold the potential for advances in cleansing oceans and other bodies of water of tiny plastics that may harm human health and the environment.
“The idea behind this work is: Can we make the cleaning materials in the form of soft particles that self-disperse in water, capture microplastics as they sink, and then return to the surface with the captured microplastic contaminants?” said Orlin Velev, the S. Frank and Doris Culberson Distinguished ...
MD Anderson names Jeffrey E. Lee, M.D., Chief Medical Executive
2025-03-26
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced that Jeffrey E. Lee, M.D., an internationally regarded leader in the field of oncology, has been appointed chief medical executive (CME) effective April 1.
Prior to his appointment, Lee served as CME ad interim, demonstrating strength as a leader committed to advancing the institution’s efforts in research, patient care, prevention and education. Assuming the role of CME is the culmination of Lee’s 34-year tenure at the institution, where he has made substantial contributions in the field ...
Sensor technology uses nature’s blueprint and machinery to monitor metabolism in body
2025-03-26
Life’s essential functions are powered by a set of compounds called metabolites, which are involved in every natural process including producing energy, regulating cell activity and keeping the body’s systems in balance. Tracking these molecules offers a window into the onset and status of many diseases, overall health, response to treatment and the intricate workings of biological systems.
However, today’s metabolite sensing methods fall short. Most rely on resource-intensive lab tests that give only brief snapshots from isolated samples. The few sensors that can track metabolites continuously are largely limited to detecting blood sugar.
An interdisciplinary ...
Chan Zuckerberg Initiative announces new biohub to develop breakthrough imaging technologies to observe cells in action
2025-03-26
REDWOOD CITY, Calif. (March 26, 2025) — The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced a new grand challenge to develop groundbreaking imaging technologies to transform how scientists observe, measure and understand living cells and organisms. CZI’s two powerhouse institutes, CZ Biohub San Francisco and CZ Institute for Advanced Biological Imaging, will leverage their complementary expertise to form a new Biohub unmatched in the field of life science imaging research. They will combine their teams at a new science campus in Redwood City, Calif., adjacent to CZI ...
Encryption breakthrough lays groundwork for privacy-preserving AI models
2025-03-26
In an era where data privacy concerns loom large, a new approach in artificial intelligence (AI) could reshape how sensitive information is processed.
Researchers Austin Ebel and Karthik Garimella, Ph.D students, and Assistant Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Brandon Reagen have introduced Orion, a novel framework that brings fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) to deep learning — allowing AI models to practically and efficiently operate directly on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first.
The implications of this advancement, ...
Top global award for young technologists goes to researcher who advanced AI with high-performance computers
2025-03-26
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today named Torsten Hoefler, a Professor at ETH Zurich, the recipient of the 2024 ACM Prize in Computing for fundamental contributions to high-performance computing and the ongoing AI revolution. Hoefler developed many of the core capabilities of modern supercomputers and defined key aspects of the algorithms for distributing AI models on them.
The ACM Prize in Computing recognizes early-to-mid-career computer scientists whose research contributions have fundamental impact and broad implications. ...
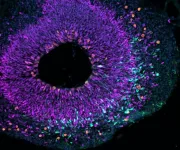
How did the large brain evolve?
2025-03-26
The results of the study show that the two genes act in a finely tuned interplay: one ensures that the progenitor cells of the brain multiply more, while the other causes these cells to transform into a different type of progenitor cell - the cells that later form the nerve cells of the brain. In the course of evolution, this interplay has led to the human brain being unique in its size and complexity.
The newly gained insights not only provide a deeper understanding of the evolutionary development of our brain but could also help to better comprehend how certain developmental disorders or diseases of the brain arise. ‘Our findings deepen the fundamental ...
Rare disease drug nitisinone makes human blood deadly to mosquitoes
2025-03-26
In the fight against malaria, controlling the mosquito population is crucial.
Several methods are currently used to reduce mosquito numbers and malaria risk. One of these includes the antiparasitic medication ivermectin. When mosquitoes ingest blood containing ivermectin, it shortens the insect’s lifespan and helps decrease the spread of malaria.
However, ivermectin has its own issues. Not only is it environmentally toxic, but also, when it is overused to treat people and animals with worm ...
Mini rolling robot takes virtual biopsies
2025-03-26
Embargoed: Not for Release Until 2pm U.S. Eastern Time (6pm GMT) Wednesday, 26 March 2025
With images and videos
A tiny magnetic robot which can take 3D scans from deep within the body, that could revolutionise early cancer detection, has been developed by researchers.
The team, led by engineers from the University of Leeds, say this is the first time it has been possible to generate high-resolution three-dimensional ultrasound images taken from a probe deep inside the gastrointestinal ...
Researchers design tools to develop vaccines more efficiently for African swine fever virus (ASFV)
2025-03-26
Rockville, Maryland—March 26, 2024—Researchers from the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI), the Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI), and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) have developed a reverse genetics system for African swine fever virus (ASFV). This new system will aid researchers in developing vaccines and in studying the pathogenesis and biology of ASFV, a highly contagious, deadly viral disease affecting domesticated and wild pigs, especially prevalent in Africa, Europe, Asia, and the Caribbean. A recent study estimates if ASFV reached the United States it could result ...
How survivors spanned the globe after Earth’s biggest mass extinction
2025-03-26
Scientists don’t call it the “Great Dying” for nothing. About 252 million years ago, upward of 80% of all marine species vanished during the end-Permian mass extinction – the most extreme event of its kind in Earth’s history.
What followed was a mysterious, multimillion-year span that could be called the “Great Dulling,” when marine animal communities looked remarkably alike all over the planet, from the equator to the poles. Researchers have long sought an explanation for this so-called taxonomic homogenization – a scene that played out after other mass extinctions over the past ...
Even in egalitarian Sweden, a "culture of silence" may prevent university staff and students from reporting sexual harassment
2025-03-26
Even in egalitarian Sweden, a "culture of silence" may prevent university staff and students from reporting sexual harassment, with just an 8.1% reporting rate for students who had experienced either rape or attempted rape.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4bW0elh
Article title: What determines the ‘culture of silence’? Disclosing and reporting sexual harassment among university employees and students at a large Swedish public university
Author countries: Sweden
Funding: This work was funded by the Swedish Research Council, ...
Data from the Healthy Minds Study of 140 college campuses in the US suggests that religiousness may be protective against symptoms of depression in students, although less so in sexual minorities
2025-03-26
Data from the Healthy Minds Study of 140 college campuses in the US suggests that religiousness may be protective against symptoms of depression in students, although less so in sexual minorities.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/3XwiyM6
Article Title: Religiousness, sexual orientation, and depression among emerging adults in U.S. higher education: Findings from the Healthy Minds Study
Author Countries: Spain, United Kingdom, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
[1] ... [613]
[614]
[615]
[616]
[617]
[618]
[619]
[620]
621
[622]
[623]
[624]
[625]
[626]
[627]
[628]
[629]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.