Recent study in mice provides key insights on the impact of excessive sucrose consumption in specific organs
2025-03-21
Researchers at the Advanced Research Unit on Metabolism, Development & Aging (ARUMDA), in the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR, Mumbai and TIFR Hyderabad), have unveiled a comprehensive understanding of the harmful effects of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) on human health, using a preclinical mouse model that closely mimics human consumption patterns. The study, published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, sheds light on how chronic sucrose-water intake (10%) alters key physiological, molecular, and metabolic processes across various organs, driving ...
A less toxic way to manufacture daily goods
2025-03-21
Diisocyanates are used in the preparation of all polyurethanes, ranging from the foams used in shoe soles to the thermoplastics used in cell phone cases. Aromatic diisocyanates, which give polyurethane foams their structure, are commonly prepared on the megaton scale in highly secure facilities due to the use of phosgene, a highly reactive and toxic chemical reagent. Michael Burkart’s lab at UC San Diego recently reported the preparation of fully bio-based aromatic diisocyanates from a simple monosaccharide, D-galactose. This new route avoids the use of transition metals, gaseous reagents or any high-pressure/temperature reactions. As an application, the team demonstrates ...
Nearly half of depression diagnoses could be considered treatment-resistant
2025-03-21
Almost half of patients diagnosed with depression classify as being ‘treatment-resistant’ as new research suggests that many don’t respond to multiple antidepressant options.
The new study, published in the British Journal of Psychiatry was led by academics from the University of Birmingham and Birmingham and Solihull Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust. The study found that 48% of patients whose electronic healthcare records reported a diagnosis of depression had tried at least two antidepressants, and 37% had tried four or more different options.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is ...
Deadly bacteria developed the ability to produce antimicrobials and wiped-out competitors
2025-03-21
A drug-resistant type of bacteria that has adapted to health care settings evolved in the past several years to weaponize an antimicrobial genetic tool, eliminating its cousins and replacing them as the dominate strain. University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists made the discovery when combing through local hospital data – and then confirmed that it was a global phenomenon.
The finding, published today in Nature Microbiology, may be the impetus for new approaches in developing therapeutics against some of the world’s deadliest bacteria. It also validates a new use for a system developed at Pitt and UPMC that couples genomic sequencing ...
Device enables direct communication among multiple quantum processors
2025-03-21
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems that would be impossible for the most powerful classical supercomputer to crack.
Just like a classical computer has separate, yet interconnected, components that must work together, such as a memory chip and a CPU on a motherboard, a quantum computer will need to communicate quantum information between multiple processors.
Current architectures used to interconnect superconducting quantum processors are “point-to-point” in connectivity, meaning they require a series of transfers between network nodes, with compounding error rates.
On the way ...
Nanotech-induced cooling improves crop yields in arid climates
2025-03-21
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have developed and combined a new nanoplastic and biodegradable mulch to passively cool greenhouses in hot, arid climates like those in the Middle East. Applying their technology, they lowered temperatures of miniature greenhouses by 25 degrees Celsius and increased crop yields of Chinese cabbage by nearly 200%. The study can be read in Nexus.
The nanoplastic consists of polyethylene, the most widely produced plastic in the world, infused with nanoparticles consisting of the molecule cesium tungsten oxide. These nanoparticles absorb ...
Home sweet home: some great hammerhead sharks stick to the perfect neighborhood in the Bahamas instead of migrating
2025-03-21
New research shows that some great hammerhead sharks are homebodies. Scientists studying great hammerheads around Andros in the Bahamas shark sanctuary have found that while some individuals migrate, others prefer to stay at home — potentially because their environment provides them with everything they need. This information could help protect the critically endangered species.
“The global population of great hammerheads is thought to have reduced by more than 80% over the last three generations, and genomic ...
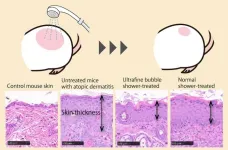
Bubbly idea: Ultrafine bubble showers suppress atopic dermatitis
2025-03-21
Bubble baths might be soothing soaks, but bubble showers could be the next thing in keeping the skin clean.
An Osaka Metropolitan University-led medical research team found that ultrafine bubble showers might help prevent atopic dermatitis.
Graduate School of Medicine student Ayaki Matsumoto and Associate Professor Hisayoshi Imanishi led the study into using ultrafine bubbles, often used to clean medical equipment, on mice with atopic dermatitis.
The scientists found that in mice with atopic dermatitis due to external factors, inflammation was markedly suppressed when the affected skin ...
Aotearoa once home to elephant seals
2025-03-21
Southern elephant seals are the “canary in the coal mine” for the Southern Ocean, offering insight into how the ecosystem may react to future climate change and human impact, new research shows.
Joint senior author Associate Professor Nic Rawlence, Director of the Otago Palaeogenetics Laboratory, says while elephant seals now only inhabit the subantarctic islands and South America, Aotearoa beaches used to be “heaving” with the colossal animals.
“At the time of human arrival in New Zealand, you would be hard pressed to find room on the beaches, with fur seals on the rocky headlands, prehistoric sealions and elephant seals ...
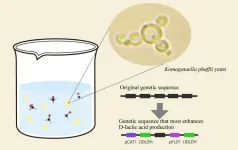
Green recipe: Engineered yeast boosts D-lactic acid production
2025-03-21
Great recipes require the perfect combination of ingredients — biotechnology recipes are no exception.
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have discovered the ideal genetic “recipe” to turn yeast into a tiny yet powerful eco-friendly factory that converts methanol into D-lactic acid, a key compound used in biodegradable plastics and pharmaceuticals. This approach could help reduce reliance on petroleum-based processes and contribute to more sustainable chemical production.
Lactic acid is widely used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and bioplastics. It exists in two forms: L-lactic acid ...
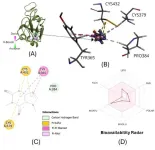
Computational drug discovery: Exploring natural products targeting SARS-CoV-2
2025-03-21
Ikoma, Japan—The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for effective therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2. Although vaccines helped control the spread of the virus, the emergence of new variants continues to challenge global health efforts. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting viral proteins could serve as an effective alternative for controlling the spread of COVID-19 at both individual and community levels.
In this vein, a recent study led by Associate Professor Md. Altaf-Ul-Amin, along with Muhammad Alqaaf, Ahmad Kamal Nasution, Mohammad Bozlul Karim, Mahfujul Islam ...
Almost half of children with complicated appendicitis can recover from surgery at home
2025-03-21
Almost half of children who require surgery for complicated appendicitis can safely complete their recovery at home, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in the Journal of Pediatric Surgery, found more than 40 per cent who received care in the home following a complex appendectomy recovered faster and had fewer complications.
More than 300 patients present with appendicitis to The Royal Children's Hospital (RCH) every year, with about one in three ...
Sensory t-shirt collects patient data and enables shorter postoperative hospital stay
2025-03-21
A t-shirt that monitors a patient’s vitals after urological surgery for cancer could help people return from hospital sooner to recover at home. The device, worn for around two weeks under clothes for three-hour windows each day, enabled patients to feel safer and more reassured than a control group in a pilot study of 70 individuals.
The results are presented this weekend at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress in Madrid.
Telemedicine in medical practice allows patients and clinicians to maintain contact remotely so that care, interventions and monitoring ...
Worse outcomes for men who avoid prostate cancer screening
2025-03-21
Men who consistently avoid prostate cancer screening appointments face a disproportionately higher risk of dying from the disease, finds research identifying a new high-risk group.
An analysis of data from across seven countries from the world’s largest prostate cancer screening study, the European Randomized study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC), is presented this weekend at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress in Madrid.
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer in men in 112 countries, with prevalence expected to double by 2040. If introduced on a national scale, prostate ...
Shrinking Andean glaciers threaten water supply of 90 million people, global policy makers warne
2025-03-21
Shrinking Andean glaciers threaten water supply of 90 million people, global policy makers warned
Shrinking glaciers in the Andes threaten the water supplies of 90 million people
Andean glaciers are thinning by 0.7 metres a year, 35 percent faster than the global average
Climate change is threatening the stability of the Andean glaciers as a water source and the water security of the people who rely on them
Scientists argue we are not doing enough to curb the carbon emissions fueling climate change
Scientists from the University of Sheffield will warn policymakers that the shrinking glaciers of the Andes threaten ...
Women’s earnings fall 10% four years after menopause diagnosis
2025-03-21
Women experience a significant fall in earnings in the years following a menopause diagnosis, with more women stopping work and others working fewer hours, according to a new UCL study published by the Institute for Fiscal Studies.
Economists at UCL, University of Bergen, Stanford University and University of Delaware calculated that women experience a 4.3% reduction in their earnings, on average, in the four years following a menopause diagnosis, with losses deepening to 10% by the fourth year.
This 10% reduction in earnings is approximately half of the estimated 23% loss of earnings experienced by new mothers, also ...
Researchers capture first laser-driven, high-resolution CT scans of dense objects
2025-03-20
A research team led by Colorado State University has achieved a new milestone in 3D X-ray imaging technology. The scientists are the first to capture high-resolution CT scans of the interior of a large, dense object – a gas turbine blade – using a compact, laser-driven X-ray source.
The findings, published this week in Optica, describe the science and engineering behind this new radiographic imaging capability and its potential benefits to a range of industries, from aerospace to additive manufacturing.
The project is a years-long collaboration between researchers at CSU’s Departments ...
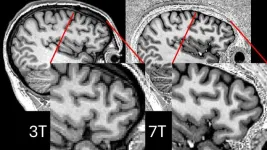
Cambridge team uses powerful new MRI scans to enable life-changing surgery in first for adults with epilepsy
2025-03-20
A new technique has enabled ultra-powerful magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners to identify tiny differences in patients’ brains that cause treatment-resistant epilepsy. In the first study to use this approach, it has allowed doctors at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge, to offer the patients surgery to cure their condition.
Previously, 7T MRI scanners – so called because they operate using a 7 Tesla magnetic field, more than double the strength of previous 3T scanners – have suffered from signal blackspots in crucial parts of the brain. But in research ...
NRL's narrow field imager launches on NASA's PUNCH mission
2025-03-20
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s (NRL) Narrow Field Imager (NFI) was launched into space aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket as a part of NASA’s Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH) mission on March 11 and deployed from Falcon 9 on March 12.
PUNCH is a four-satellite constellation, collecting observations in low Earth orbit. It will conduct global, 3D observations of the inner heliosphere to investigate the solar corona's evolution into the solar wind. The mission is scheduled to conduct science for the next two years, following a 90-day commissioning period.
The NRL-developed NFI, sponsored ...
Galapagos birds exhibit ‘road rage’ due to noise
2025-03-20
A new study has discovered that birds in the Galápagos Islands are changing their behaviour due to traffic noise, with those frequently exposed to vehicles showing heightened levels of aggression.
Published in the journal Animal Behaviour and led by experts from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and the Konrad Lorenz Research Centre at the University of Vienna, the research examined the impact of vehicle noise pollution on Galápagos yellow warblers (Setophaga petechia aureola), a songbird widespread on the archipelago.
The Galápagos Islands, ...
Groundbreaking study finds AI-driven interviews with children may boost accuracy in witness accounts
2025-03-20
Groundbreaking Study Finds AI-Driven Interviews with Children May Boost Accuracy in Witness Accounts
In a first-of-its-kind study published in the journal PLOS ONE, an international team of researchers led by scholars from New York University Shanghai and Åbo Akademi University in Turku, Finland explored the potential of artificial intelligence to assist in sensitive child investigative interviews. The study compared how effectively a Large Language Model (LLM), specifically ChatGPT, and untrained human interviewers were able to interview children about a mock event ...
New framework to measure economic well-being considers new and free goods and services; addition of digital goods boosts growth
2025-03-20
Welfare measurement is among the most fundamental questions in economics. Policymakers and others use gross domestic product (GDP) as a proxy for welfare, but this application does not reflect the benefits of introducing new and free goods and services, such as digital goods, and may result in misunderstanding the economy.
In a new study, researchers developed a framework to measure the welfare contributions of new and free goods and services and quantify their benefits. By applying the framework to several examples (e.g., Facebook, Smartphone cameras), the study found that these goods and services significantly increase welfare.
The study ...
Augmented reality guidance for placing intracranial drains now clinically validated
2025-03-20
March 20, 2025 — Placing an external ventricular drain (EVD) at bedside using augmented reality (AR) guidance is more precise than freehand placement and is associated with fewer reinterventions and complications, according to a clinical pilot study of a novel system. Frederick Van Gestel, MD, a neurosurgery resident at Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel and PhD researcher at Vrije Universiteit Brussel in Brussels, Belgium, and colleagues report first-in-human results in Neurosurgery, the official publication of the Congress ...
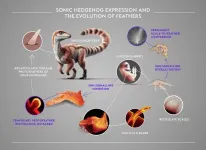
How feathers develop in chickens
2025-03-20
Inhibiting the sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway strongly perturbs feather development in chickens by restricting feather bud outgrowth, invagination and branching, according to a study published March 20th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Rory Cooper and Michel Milinkovitch from the University of Geneva, Switzerland.
Avian feathers are intricate appendages whose forms vary substantially across species and body areas, and between juvenile and adult stages. Understanding both the developmental and evolutionary mechanisms underpinning this morphological diversity has long fascinated biologists. The morphological intricacies ...
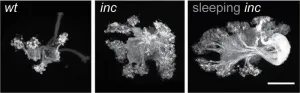
Insomniac fruit fly mutants show enhanced memory despite severe sleep loss
2025-03-20
Fruit fly mutants that have severe sleep deficits perform better at olfactory learning and memory tasks, according to a study published March 20th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Sheng Huang and Stephan Sigrist from Freie Universität Berlin, Germany, and colleagues. The paradox of enhanced memory despite sleep loss could be explained by protein kinase A (PKA) signaling in the mushroom body of the fly brain.
Sleep is a dynamic process conserved from invertebrates to mammals and humans. Although sleep is thought to serve many purposes, it is often studied for its restorative roles, which ...
[1] ... [615]
[616]
[617]
[618]
[619]
[620]
[621]
[622]
623
[624]
[625]
[626]
[627]
[628]
[629]
[630]
[631]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.