Revolutionizing touch: Researchers explore the future of wearable multi-sensory haptic technology
2025-03-25
From virtual reality to rehabilitation and communication, haptic technology has revolutionized the way humans interact with the digital world. While early haptic devices focused on single-sensory cues like vibration-based notifications, modern advancements have paved the way for multisensory haptic devices that integrate various forms of touch-based feedback, including vibration, skin stretch, pressure and temperature. Recently, a team of experts, including Rice University’s Marcia O’Malley and Daniel ...
Disparities in use of MRI to detect prostate cancer
2025-03-25
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths in American men. Further, non-Hispanic Blacks have a higher incidence of prostate cancer and are more likely to die from it than are non-Hispanic whites. A biopsy is recommended if a patient has certain risk factors like age, family history, symptoms and screening test results. When the biopsy sample is taken, physicians use either ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to guide the procedure.
In a new study, researchers at Thomas Jefferson ...
Biology Open smashes the peer review mold
2025-03-25
Academic peer review is notoriously cumbersome. The process assesses the quality of scientific research prior to publication in an academic journal, sometimes delaying publication by many months. The system depends on members of the academic community providing their time and expertise for free. However, finding reviewers can be lengthy and there are no consequences when reviewers produce poor-quality reports lacking constructive feedback. Daniel Gorelick, Editor-in-Chief of the journal Biology Open believed that there could an alternative. ‘My vision is a ...
Scientists unlock frogs’ antibacterial secrets to combat superbugs
2025-03-25
Frogs have thrived for hundreds of millions of years, spreading across virtually every corner of the earth, from tropical jungles to subarctic forests. Throughout their evolution, they have developed remarkable defenses — including previously unreported antibiotics — against the hordes of bacteria that thrive in their moist environments. Variants of these compounds may one day protect humans from drug-resistant pathogens.
In a new paper in Trends in Biotechnology (Cell Press), Cesar de la Fuente, Presidential Associate Professor in Bioengineering and in Chemical and Biomolecular ...
Making foie gras without force-feeding
2025-03-25
WASHINGTON, March 25, 2025 — Foie gras is a unique delicacy made from the liver of a duck or goose. While it can be an acquired taste, the buttery, fatty dish is an indulgent cuisine prized in many parts of the world.
Foie gras is distinct from regular fowl liver thanks to its high fat content, which is traditionally achieved by force-feeding the ducks and geese beyond their normal diets. Researcher Thomas Vilgis is a lover of foie gras, but he wondered if there was a more ethical way to enjoy the dish.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, Vilgis, as well as researchers from Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research and the University of Southern Denmark, created a process to ...
The best butter for a vegan shortbread
2025-03-25
WASHINGTON, March 25, 2025 – Butter is a key ingredient in many baked goods, but for those who are lactose intolerant, finding a good alternative can be a challenge. Vegan butters can sometimes have the wrong consistency, or produce bakes that are not quite right, leaving bakers frustrated or unwilling to try dairy-free alternatives.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Strathclyde examined the properties of several vegan or dairy-free butter alternatives inside one of the region’s most well-known snacks: Scottish shortbread.
“We have a Ph.D. student in the group who is a vegan, and he turns all of our baking habits upside down,” ...
Recovery potential in patients after cardiac arrest who die after limitations or withdrawal of life support.
2025-03-25
About The Study: In this cohort study of comatose patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest, most who died after withdrawal of life-sustaining therapy were considered by experts to have had recovery potential. These findings suggest that novel solutions to avoiding deaths based on biased prognostication or incomplete information are needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan Elmer, MD, MS, email elmerjp@upmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1714)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
LGBTQ+ inclusive policies, nurse job outcomes, and quality of care in hospitals.
2025-03-25
About The Study: Nurses in hospitals with high lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer or questioning, and other sexual and gender minority (LGBTQ+) inclusion reported more favorable job outcomes and care quality in this cross-sectional study. Hospitals should understand that implementing LGBTQ+ inclusive policies goes beyond compliance or diversity; it is essential for improving the work climate, enhancing staff well-being, and optimizing care delivery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hyunmin Yu, PhD, email hyuy@nursing.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
C. diff uses toxic compound to fuel growth advantage
2025-03-25
The pathogen C. diff — the most common cause of health care-associated infectious diarrhea — can use a compound that kills the human gut’s resident microbes to survive and grow, giving it a competitive advantage in the infected gut.
A team led by investigators at Vanderbilt University Medical Center has discovered how C. diff (Clostridioides difficile) converts the poisonous compound 4-thiouracil, which could come from foods like broccoli, into a usable nutrient. Their findings, published March 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, increase ...
Nation of Lifesavers™ takes CPR education to Japan
2025-03-25
DALLAS, March 25, 2025 — Understanding how to properly respond in a cardiac emergency when seconds matter is critical to everyone, everywhere. That is why the American Heart Association, devoted to changing the future to a world of healthier lives for all, and its Nation of Lifesavers™ national ambassador and Buffalo Bills safety, Damar Hamlin, are expanding the Chasing M’s Foundation cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) tour to Tokyo during March 27-30. This work is supporting the American Heart Association’s impact goal to improve survival rates of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest[1].
“Our national Nation ...
ACS study finds nearly four million pre-mature lung cancer deaths in U.S. averted and 76 million years of lives gained due to tobacco control
2025-03-25
New research led by American Cancer Society (ACS) researchers estimates more than 3.8 million lung cancer deaths were averted and a little over 76 million years of life gained in the United States during 1970-2022 due to substantial reductions in smoking prevalence driven by tobacco control. The study is published today in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
“The substantial estimated numbers of averted lung cancer deaths and person-years of life gained highlight the remarkable effect of progress ...
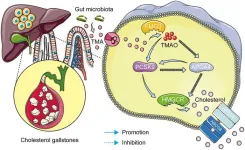
PCSK9 and APOA4: the dynamic duo in TMAO-induced cholesterol metabolism and cholelithiasis
2025-03-25
Background and Aims
Cholesterol synthesis and gallstone formation are promoted by trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a derivative of trimethylamine, which is a metabolite of gut microbiota. However, the underlying mechanisms of TMAO-induced lithogenesis remain incompletely understood. This study aimed to explore the specific molecular mechanisms through which TMAO promotes gallstone formation.
Methods
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were used to compare serum concentrations of TMAO, apolipoprotein A4 (APOA4), and ...
Gas injection setup in new fusion system is guided by public-private research
2025-03-25
When the plasma inside a fusion system starts to misbehave, it needs to be quickly cooled to prevent damage to the device. Researchers at Commonwealth Fusion Systems believe the best bet is a massive gas injection: essentially, a well-timed, rapid blast of cooling gas inside their fusion system, which is known as SPARC. But how many gas valves does it take to quickly tame a plasma that is hotter than the sun? The team has to strike the perfect balance: with too few valves, some parts of SPARC might overheat. With too many, valuable space inside the ...
Offering paid time off dramatically cuts odds of employees quitting their jobs
2025-03-25
About 4.5 million workers in the United States quit their jobs in 2022, continuing a trend that began after the 2007 Great Recession. Despite better labor conditions and the pandemic’s decline, many adults are still less willing to return to work compared to previous recessions, making it harder for companies to attract and retain top talent. Moreover, voluntary turnover – when an employee quits their job as opposed to being fired or laid off – costs U.S. businesses more than $1 trillion each year.
Beyond recruitment and training expenses, turnover disrupts operations, damages customer relationships, and often leads to further departures. Replacing an employee ...
City of Hope opens phase 1 clinical trial aiming to one day transform rectal cancer into a disease treatable with radiation therapy to avoid potential long-term side effects of surgery
2025-03-25
LOS ANGELES — City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. with its National Medical Center named top 5 in the nation for cancer by U.S. News & World Report, has opened a phase 1 trial seeking to one day transform rectal cancer from a mostly radiation-resistant disease to one that can be cured using radiation and chemotherapy.
“Many cancers are cured through radiation therapy alone or radiation in combination with chemotherapy, including — but not limited to — prostate, head and ...
Maternal deaths from cardiovascular causes on the rise in U.S.
2025-03-25
The rate of maternal mortality related to cardiovascular causes more than doubled between 1999 and 2022 in the United States, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
The finding is concerning, especially as the U.S. has the highest overall rate of maternal mortality among all developed countries, researchers said. Since cardiovascular problems are a leading cause of death around the time of pregnancy and childbirth, the new findings shed light on the drivers behind recent trends and draw attention to particularly high rates of mortality seen among ...
New evidence links microplastics with chronic disease
2025-03-25
Tiny fragments of plastic have become ubiquitous in our environment and our bodies. Higher exposure to these microplastics, which can be inadvertently consumed or inhaled, is associated with a heightened prevalence of chronic noncommunicable diseases, according to new research being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
Researchers said the new findings add to a small but growing body of evidence that microplastic pollution represents an emerging health threat. In terms of its relationship with stroke risk, for example, microplastics concentration ...
Movement matters: mobility linked to better outcomes for patients with heart failure
2025-03-25
Compared with those who spent most of their time in a single room, people with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) who were able to travel outside of their home without assistance were significantly less likely to be hospitalized or die within a year, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25). The findings underscore the value of supporting holistic care and encouraging people with heart failure to maintain an active lifestyle and engage with others ...
Growing body of evidence links HPV with heart disease
2025-03-25
In addition to causing several types of cancer, human papillomavirus (HPV) appears to bring a significantly increased risk of heart disease and coronary artery disease, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
Evidence that HPV is linked with heart disease has begun to emerge only recently. This new study is the first to assess the association by pooling data from several global studies, totaling nearly 250,000 patients. Its findings bolster the evidence that a significant relationship exists ...
Pork similar to poultry and legumes on key sustainability and agricultural resource indicators
2025-03-25
A new peer-reviewed studyi* published in Frontiers in Nutrition provides compelling evidence that pork can play a beneficial role in sustainable diets. The research, conducted by scientists at William & Mary, modeled the environmental and economic impacts of substituting various protein sources with pork in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults.
The findings suggest that pork performs similarly to poultry, seafood, eggs and legumes across key sustainability and agricultural resource indicators with a ± 1% change in land use, fertilizer nutrient use and pesticide use.
Modeled ...
These electronics-free robots can walk right off the 3D-printer
2025-03-25
Imagine a robot that can walk, without electronics, and only with the addition of a cartridge of compressed gas, right off the 3D-printer. It can also be printed in one go, from one material.
That is exactly what roboticists have achieved in robots developed by the Bioinspired Robotics Laboratory at the University of California San Diego. They describe their work in an advanced online publication in the journal Advanced Intelligent Systems.
To achieve this feat, researchers aimed to use the simplest technology available: a desktop ...
Dr. Vikaas Sohal of The University of California, San Francisco receives a $130,000 SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) grant to explore therapeutic strategies for reversing cognitive deficits in SYNGAP1-relat
2025-03-25
Mill Valley, CA – March 25, 2025 – The SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) dba Cure SYNGAP1 501(c)(3) announced a $130,000 grant to Dr. Vikaas Sohal at The Regents of The University of California, San Francisco. The grant supports research into new therapies for reversing cognitive deficits in SYNGAP1-related disorders (SRD) by enhancing key brain functions.
Dr. Sohal’s research focuses on cognitive flexibility—the ability to adapt behavior in response to environmental changes—a ...
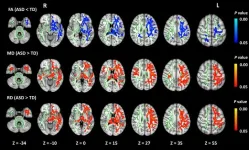
Decoding autism through neuroimaging: how alterations in brain connectivity shape symptoms
2025-03-25
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a growing global concern, affecting approximately 2.8% of children in the United States and 0.7% in China. ASD is characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication difficulties, and repetitive behaviors, making early diagnosis critical for improving outcomes. However, current diagnostic methods rely primarily on behavioral observations, which may delay early interventions. Despite ongoing research, the structural and functional brain differences between children with ASD and typically developing (TD) children remain poorly understood.
Now, in a recent study published in NeuroImage and made available online on February ...
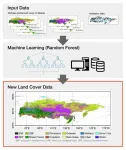
Refining Siberia’s land cover data: A leap forward for climate science
2025-03-25
Siberia, a province located in Russia, is a significant geographical region playing a crucial role in the world’s carbon cycle. With its vast forests, wetlands, and permafrost regions (permanently frozen grounds), Siberia stores a considerable amount of carbon on a global scale. But climate change is rapidly altering Siberia’s landscape, shifting its vegetative distribution and accelerating the permafrost thaw. Classifying land cover is essential to predict future climatic changes, but accumulating land cover data in regions like ...
The evolution of low-temperature adapted enzymes
2025-03-25
Life has evolved over billions of years, adapting to the changing environment. Similarly, enzymes—proteins that speed up biochemical reactions (catalysis) in cells—have adapted to the habitats of their host organisms. Each enzyme has an optimal temperature range where its functionality is at its peak. For humans, this is around normal body temperature (37 °C). Deviating from this range causes enzyme activity to slow down and eventually stop. However, some organisms, like bacteria, thrive in extreme environments, such as hot springs or freezing polar waters. These extremophiles have enzymes adapted to function in harsh conditions.
For ...
[1] ... [609]
[610]
[611]
[612]
[613]
[614]
[615]
[616]
617
[618]
[619]
[620]
[621]
[622]
[623]
[624]
[625]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.