New study sheds light on how bacteria ‘vaccinate’ themselves with genetic material from dormant viruses
2025-03-21
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Key Takeaways:
Bacteria get invaded by viruses called phages.
Scientists are studying how bacteria use CRISPR to defend themselves from phages, which will inform new phage-based treatments for bacterial infections that are resistant to antibiotics.
Bacteria seize genetic material from weakened, dormant phages and use it to form a biological “memory” of the invader that their offspring inherit and use for anti-phage defense.
Like people, bacteria get invaded by viruses. In bacteria, the viral invaders are called bacteriophages, ...
Four advances that could change tuberculosis treatment
2025-03-21
As of early 2025, tuberculosis cases are increasing in the U.S. This disease, often shortened to TB, causes significant lung damage and, if not treated, is almost always lethal. World TB Day on March 24 raises awareness about the disease and commemorates Robert Koch’s discovery of the source bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. More than a century later, scientists continue refining TB diagnosis methods and treatment strategies, some of which are in these four ACS journal articles. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
Fluorescence ...
Obesity Action Coalition & The Obesity Society send letter to FDA on behalf of more than 20 leading organizations & providers urging enforcement of compounding regulations
2025-03-21
March 19, 2025 — Today, the Obesity Action Coalition (OAC) and The Obesity Society (TOS) sent a letter to the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA), along with more than 20 leading organizations and providers across the healthcare continuum, urging the agency to enforce federal regulations around compounding following the recent resolution of GLP-1 medicine shortages. Among the signatories include: the Alliance for Women’s Health & Prevention, the Association of Black Cardiologists, the National Hispanic Medical Association and the National Consumers League.
The letter follows recent announcements from the FDA that Eli Lilly’s ...
New Microbiology Society policy briefing on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in wastewater
2025-03-21
AMR occurs when disease-causing bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites (pathogens) are no longer affected by the medicines that have been developed to target them. Drug-resistant pathogens can cause infections that are difficult or impossible to treat; they increase the risk of disease spread and can lead to severe illness, disability and death.
Wastewater is commonly contaminated with antimicrobial resistant micro-organisms and antimicrobial compounds. Upon entering our environment, such as rivers and seas, contaminated wastewater therefore serves as a pathway for, and major contributor to, the spread of AMR in the UK and ...
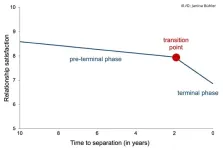
Transition point in romantic relationships signals the beginning of their end
2025-03-21
The end of a romantic relationship usually does not come out of the blue but is indicated one or two years before the breakup. As the results of a psychological study have demonstrated, the terminal stage of a relationship consists of two phases. First, there is a gradual decline in relationship satisfaction, reaching a transition point one to two years before the dissolution of the relationship. "From this transition point onwards, there is a rapid deterioration in relationship satisfaction. Couples in question then move towards separation," said Professor ...
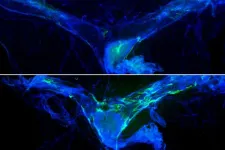
Scientists witness living plant cells generate cellulose and form cell walls for the first time
2025-03-21
In a groundbreaking study on the synthesis of cellulose – a major constituent of all plant cell walls – a team of Rutgers University-New Brunswick researchers has captured images of the microscopic process of cell-wall building continuously over 24 hours with living plant cells, providing critical insights that may lead to the development of more robust plants for increased food and lower-cost biofuels production.
The discovery, published in the journal Science Advances, reveals a dynamic process never seen before and may provide practical applications for everyday products derived from plants including ...
Mount Sinai-led team identifies cellular mechanisms that may lead to onset of inflammatory bowel disease
2025-03-21
A research team led by Mount Sinai has uncovered mechanisms of abnormal immune cell function that may lead to Crohn’s disease, according to findings published in Science Immunology on March 21. The researchers said their discovery provides better understanding of disease development and could inform the development and design of new therapies to prevent inflammation before it starts in the chronic disorder.
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and symptoms can include abdominal ...
SNU-GU researchers jointly develop a liquid robot capable of transformation, separation, and fusion like living cells
2025-03-21
A liquid robot capable of transforming, separating, and fusing freely like living cells has been developed.
Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that a joint research team led by Professor Ho-Young Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Jeong-Yun Sun from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Keunhwan Park from the Department of Mechanical, Smart, and Industrial Engineering at Gachon University has successfully developed a next-generation ...
Climate warming and heatwaves accelerate global lake deoxygenation, study reveals
2025-03-21
Freshwater ecosystems require adequate oxygen levels to sustain aerobic life and maintain healthy biological communities. However, both long-term climate warming and the increasing frequency and intensity of short-term heatwaves are significantly reducing surface dissolved oxygen (DO) levels in lakes worldwide, according to a new study published in Science Advances.
Led by Prof. SHI Kun and Prof. ZHANG Yunlin from the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with researchers from the Nanjing University and the UK’s ...
Unlocking dopamine’s hidden role: Protective modification of Tau revealed
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 19, 2025: The research group led by Prof. Wang Chu from the College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering at Peking University published a research article entitled “Quantitative Chemoproteomics Reveals Dopamine’s Protective Modification of Tau” in Nature Chemical Biology (DOI:10.1038/s41589-025-01849-9). Using a novel quantitative chemoproteomic strategy, the team uncovered a protective role of dopamine (DA) in regulating the function of the microtubule-associated protein Tau. This discovery deepens our understanding of dopamine’s physiological and pathological roles in the human brain.
Why it matters:
1. Dopamine, ...
New drug therapy combination shows promise for advanced melanoma patients
2025-03-21
A federally funded research team led by Sheri Holmen, PhD, investigator at Huntsman Cancer Institute and professor in the Department of Surgery at the University of Utah (the U), is testing a new combination drug therapy that could both treat and prevent melanoma metastasis, or spreading from its original site, to the brain.
“Once melanoma has spread to the brain, it’s very hard to treat. Metastasis to the brain is one of the main causes of death from melanoma,” says Holmen. “We wanted to find a solution to an unmet clinical need for those patients who had no other treatment options ...
Nature’s warriors: How rice plants detect and defend against viral invaders
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 20, 2025: A groundbreaking study led by Li Yi, professor at the School of Life Sciences, was published in Nature on March 12, titled “Perception of viral infections and initiation of antiviral defence in rice”, uncovering a molecular mechanism by which rice cells perceive viral infections and initiate antiviral response, which significantly contributes to understanding of virus-host interactions for further disease resistance breeding.
Why it matters:
Viruses affecting rice, a staple food for more than half of the world population, pose ...
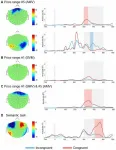
How the brain responds to prices: Scientists discover neural marker for price perception
2025-03-21
Russian scientists have discovered how the brain makes purchasing decisions. Using electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), researchers found that the brain responds almost instantly when a product's price deviates from expectations. This response engages brain regions involved in evaluating rewards and learning from past decisions. Thus, perceiving a product's value is not merely a conscious choice but also a function of automatic cognitive mechanisms. The results have been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
Every day, people are faced with prices of food, technology, and services. Sometimes, a product seems overpriced, ...
Boosting brain’s waste removal system improves memory in old mice
2025-03-21
As aging bodies decline, the brain loses the ability to cleanse itself of waste, a scenario that scientists think could be contributing to neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, among others. Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have found a way around that problem by targeting the network of vessels that drain waste from the brain. Rejuvenating those vessels, they have shown, improves memory in old mice.
The study, published online March 21 in the journal Cell, lays the groundwork to develop therapies for age-related cognitive decline that overcome ...
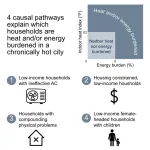
New study sheds light on risks from residential heat and energy burdens in Miami
2025-03-21
A new study on indoor extreme heat connects these two burdens to reveal how the co-occurrence of escalating energy bills and dangerously hot homes in Miami-Dade County exacerbates health and well-being risks for vulnerable households across months of the year.
“Our findings help us understand which types of households are struggling with high indoor heat and high energy bills in a place like Miami, which is hot for many months of the year,” said Lynée Turek-Hankins, the lead author of the study that was conducted during her doctoral studies at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Abess Center for Ecosystem ...
Racial and ethnic inequalities in actual vs nearest delivery hospitals
2025-03-21
About The Study: This cohort study found that American Indian and Black individuals delivered at lower-quality hospitals than white individuals. The disparity in care between Black and white birthing individuals would have been reduced if individuals had delivered at their nearest hospital.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nansi S. Boghossian, PhD, email nboghoss@email.sc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1404)
Editor’s ...
State earned income tax credits and firearm suicides
2025-03-21
About The Study: In this cohort study, the presence and generosity of state refundable earned income tax credits were associated with a decrease in firearm suicide rates, supporting the growing body of literature highlighting the importance of antipoverty policies for reducing firearm suicide.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole Asa, MPH, email nasa3@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1398)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
VR study reveals how pain and fear weaken sense of body ownership
2025-03-21
A study from Hiroshima University found that when people were told to imagine their virtual bodies in pain, their brains resisted the illusion of ownership. Their findings could provide insights into why some people may struggle with feeling connected to their own bodies, particularly in contexts involving depersonalization or negative physical states.
The sense of body ownership—the feeling that our body belongs to us—is crucial in distinguishing ourselves from objects and responding to threats. Researchers study it using techniques like the rubber hand illusion (RHI) and full-body illusion (FBI), in which an individual is somehow ...
Quantum leap: Graphene unlocks orbital hybridization
2025-03-21
Peking University, March 19, 2025: A research team led by Professor Sun Qing-Feng in colloboration with Professor He Lin’s research group from Beijing Normal University has achieved orbital hybridization in graphene-based artificial atoms for the first time. Their findings, entitled “Orbital hybridization in graphene-based artificial atoms” was published in Nature (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08620-z). This work marks a significant milestone in the field of quantum physics and materials science, bridging the gap between artificial and real atomic behaviors.
Why it matters:
1. Quantum dots, often called artificial atoms, can mimic atomic orbitals but have not yet ...
How black holes could nurture life
2025-03-21
At the center of most large galaxies, including our own Milky Way, sits a supermassive black hole. Interstellar gas periodically falls into the orbit of these bottomless pits, switching the black hole into active galactic nucleus (AGN)-mode, blasting high-energy radiation across the galaxy.
It's not an environment you'd expect a plant or animal to thrive in. But in a surprising new study in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers at Dartmouth and the University of Exeter show that AGN radiation can have a paradoxically nurturing effect on life. Rather ...
Dr. Amit Bar-Or, penn medicine neuroimmunologist, awarded the 2025 John Dystel prize for multiple sclerosis research
2025-03-21
Amit Bar-Or, MD, a distinguished researcher and neurologist at Penn Medicine, is the winner of the 2025 John Dystel Prize for Multiple Sclerosis Research, awarded jointly by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society and the American Academy of Neurology. He is being honored for advancing our knowledge of neuroimmunology, precision medicine, and biomarkers in MS. Dr. Bar-Or will deliver the Dystel Prize lecture and receive his award at the American Academy of Neurology 2025 Annual Meeting in San Diego, California on April 8, 2025.
“Dr. Bar-Or has been a key player in shaping the evolving conceptual framework of MS, including how the ...
Recent study in mice provides key insights on the impact of excessive sucrose consumption in specific organs
2025-03-21
Researchers at the Advanced Research Unit on Metabolism, Development & Aging (ARUMDA), in the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR, Mumbai and TIFR Hyderabad), have unveiled a comprehensive understanding of the harmful effects of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) on human health, using a preclinical mouse model that closely mimics human consumption patterns. The study, published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, sheds light on how chronic sucrose-water intake (10%) alters key physiological, molecular, and metabolic processes across various organs, driving ...
A less toxic way to manufacture daily goods
2025-03-21
Diisocyanates are used in the preparation of all polyurethanes, ranging from the foams used in shoe soles to the thermoplastics used in cell phone cases. Aromatic diisocyanates, which give polyurethane foams their structure, are commonly prepared on the megaton scale in highly secure facilities due to the use of phosgene, a highly reactive and toxic chemical reagent. Michael Burkart’s lab at UC San Diego recently reported the preparation of fully bio-based aromatic diisocyanates from a simple monosaccharide, D-galactose. This new route avoids the use of transition metals, gaseous reagents or any high-pressure/temperature reactions. As an application, the team demonstrates ...
Nearly half of depression diagnoses could be considered treatment-resistant
2025-03-21
Almost half of patients diagnosed with depression classify as being ‘treatment-resistant’ as new research suggests that many don’t respond to multiple antidepressant options.
The new study, published in the British Journal of Psychiatry was led by academics from the University of Birmingham and Birmingham and Solihull Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust. The study found that 48% of patients whose electronic healthcare records reported a diagnosis of depression had tried at least two antidepressants, and 37% had tried four or more different options.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is ...
Deadly bacteria developed the ability to produce antimicrobials and wiped-out competitors
2025-03-21
A drug-resistant type of bacteria that has adapted to health care settings evolved in the past several years to weaponize an antimicrobial genetic tool, eliminating its cousins and replacing them as the dominate strain. University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists made the discovery when combing through local hospital data – and then confirmed that it was a global phenomenon.
The finding, published today in Nature Microbiology, may be the impetus for new approaches in developing therapeutics against some of the world’s deadliest bacteria. It also validates a new use for a system developed at Pitt and UPMC that couples genomic sequencing ...
[1] ... [614]
[615]
[616]
[617]
[618]
[619]
[620]
[621]
622
[623]
[624]
[625]
[626]
[627]
[628]
[629]
[630]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.