New study reveals impact of vermicomposted olive wastes on plant defense and pest control.
2025-03-25
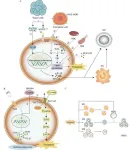
A recent study published in Soil Ecology Letters has elucidated the combined effects of soil amendments and pest attacks on plant-induced defence mechanisms and their impact on the behaviour of biological control agents. The research, conducted by the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and Fundación MEDINA, focused on the utilisation of vermicomposted olive mill waste as a soil amendment and its consequence on the tri-trophic interactions between olive trees (Olea europaea), ...
An extension of process calculus for asynchronous communications between agents with epistemic states
2025-03-25
It plays a central role in intelligent agent systems to model agents’ epistemic states and their changes. Asynchrony plays a key role in distributed systems, in which the messages transmitted may not be received instantly by the agents. Epistemic interaction behaviors can change agents’ epistemic states, while the latter will affect the former. So far, the literature mainly focuses on formalizing the change of epistemic state after receiving information.
To model epistemic interactions between ...
Researchers achieve de novo biosynthesis of plant lignans using synthetic yeast consortia
2025-03-25
Lignans are low molecular weight polyphenolic compounds with important antitumor and antiviral properties. However, their low amounts in medicinal plants and complex structures make sustainable production through plant extraction and chemical synthesis challenging, limiting their availability to meet market demand.
In a study published in Nature Chemical Biology, a research group led by Prof. ZHOU Yongjin from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with Prof. ZHANG Lei ...
Ferroptosis contributes to immunosuppression
2025-03-25
Iron-dependent ferroptosis, a non-apoptotic cell death mechanism, is gaining attention for its role in immune suppression. Ferroptosis, driven by excessive lipid peroxides and iron-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS), differs from other cell death forms in its immunogenicity. It involves the regulation of the cystine/glutamate transport system xc−, with glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) preventing toxic lipid peroxide accumulation. Ferroptosis-related factors are implicated in various diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Macrophages, crucial for immune response, are affected by ferroptosis. ...
Study confirms accuracy of blood test for early Alzheimer’s detection in Asian populations
2025-03-25
A study in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, a leading journal in dementia research, has demonstrated the high accuracy of plasma p-tau217 as a blood-based biomarker for detecting abnormal brain beta-amyloid (Aβ) pathology, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). More significantly, the study validates its effectiveness even in individuals with cerebrovascular disease (CeVD), which is highly prevalent in Asian populations. This finding can enhance early diagnosis, improve patient risk stratification, and facilitate better clinical management of AD in diverse populations.
The ...
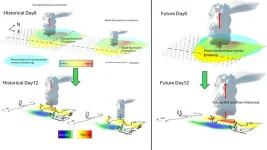
Cloud band movement influences wet spells during Indian monsoon
2025-03-25
The monsoon rains have long remained the lifeblood of India, providing the lion’s share of the water used for drinking and irrigation. The yearly arrival of the rains, which quenches the thirst of the harsh summers, is caused by the movement of cloud bands from the equator towards the north.
A recent study from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has shown that contrary to previous understanding, the strength of the cloud band plays a key role in its movement as well as the density of rains that the Indian subcontinent receives during the wet spells of the monsoon.
India receives 80% ...
Two USC innovators honored by the National Academy of Inventors for unlocking the power of the immune system
2025-03-25
Two researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC have been elected as senior members of the National Academy of Inventors (NAI), an organization that recognizes inventors holding US patents and promotes academic technology and innovation to benefit society.
The newly elected senior members are Preet Chaudhary, MD, PhD, professor of medicine and the Ronald H. Bloom Family Chair in Lymphoma Research, and Michael Selsted, MD, PhD, professor of pathology.
“Professors Chaudhary and Selsted are nationally known for their entrepreneurial research, and I’m thrilled to see them acknowledged with this ...
Increased use of chest x-rays linked to earlier lung cancer diagnosis and improved survival
2025-03-25
● Records of more than 170,000 lung cancer patients combined with chest x-ray rates from 7,400 GP practices were analysed in the new research led by the University of Sheffield
● The study, published in the British Journal of General Practice, shows link between the frequency of chest x-rays and earlier diagnosis and improved survival
● Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths globally
A groundbreaking study has revealed a significant link between the frequency of chest x-ray referrals from GPs ...
From economic struggles to culture wars: New study reveals how GDP influences polarization around the globe
2025-03-25
Polarisation in lower-income countries largely flows from economic and material issues, while social topics and identity-related debates are the most polarising subjects in richer nations, new research reveals.
The study from City St George’s, University of London analysed 40 years of global data to explore how modernisation influences ideological divides, shedding light on the factors driving ideological polarisation across different nations around the world.
As political divisions deepen in many countries, the study clarifies the complex, multifaceted implications ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop affordable sensing system to restore sense of touch in minimally invasive surgery
2025-03-24
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 24, 2025: Researchers from NYU Abu Dhabi’s Advanced Microfluidics and Microdevices Laboratory (AMMLab) have developed an innovative sensing system that restores the missing tactile feedback in minimally invasive surgery (MIS), enhancing precision, ease of use, and safety. The new "off-the-jaw" system integrates force and angle sensors into the handle of laparoscopic tools, providing surgeons with real-time measurements of grasping forces and insights into tissue stiffness and thickness.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) involves small incisions, reducing ...
Rapid and accurate diagnosis of urinary tract infections using targeted next-generation sequencing: A multicenter comparative study with metagenomic sequencing and traditional culture methods
2025-03-24
BACKGROUND
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) rank among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally. Traditional urine culture methods have significant limitations in detection time and sensitivity, prompting the need to evaluate targeted next-generation sequencing (tNGS) as a potential diagnostic tool.
METHODS
The study included a discovery cohort of 400 suspected UTI patients (202 analyzed) and a validation cohort of 200 patients (110 analyzed). The study assessed detection time, concordance rates, ability to identify polymicrobial infections, and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Both clear and turbid ...
Black infants and children consistently have double the risk for death compared to Whites
2025-03-24
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 24 March 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the ...
March/April Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2025-03-24
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study Approach: In this cluster ...
Shared decision making among primary care clinic staff and family involvement improves follow-up for chronic patients
2025-03-24
Original Research
Background and Goal: Regular follow-up visits are critical for managing chronic conditions, yet some primary care clinics achieve higher visit regularity than others. This study aimed to identify specific strategies used by high-performing clinics to promote consistent follow-up visits for adults with chronic conditions.
Study Approach: This qualitative study used semi-structured interviews with 15 primary care physicians, 12 nurses, 15 administrative staff, and 4 pharmacists from 12 clinics—half with high temporal regularity (patients attending follow-ups consistently) and half with low temporal regularity, identifying strategies that helped high–temporal ...
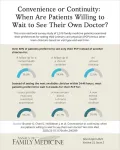
Over half of patients prefer their own doctor and will wait longer for an appointment
2025-03-24
Original Research
Background and Goal: This study focuses on how primary care patients balance the trade-off between continuity of care and access to timely appointments. It examines whether patients prefer to wait longer to see their own primary care physician (PCP) or prefer to see another clinician for faster care.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from a cross-sectional online survey of adult primary care patients in Michigan. Patients were presented with scenarios in the survey for different visit types—annual checkups, chronic and mental health follow-ups, ...
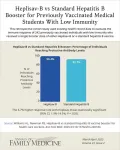
Newer hepatitis B vaccine shows promise as booster for health care workers
2025-03-24
Research Brief
Background and Goal: Health care workers are at higher risk of hepatitis B infection due to occupational exposure to blood and body fluids. They are considered protected if they have a hepatitis B surface antigen antibody (anti-HBs) titer of ≥10 mIU/mL after completing a full vaccination series. This study compared the effectiveness of Heplisav-B, a new hepatitis vaccine, vs. standard hepatitis B vaccines as a booster in previously vaccinated individuals.
Study Approach: Researchers ...
Family-based lifestyle intervention improves weight management and cardiovascular health among high-risk patients
2025-03-24
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study ...
Long-term inhaled corticosteroid use for COPD linked to serious long-term health risks
2025-03-24
Background and Goal: Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are commonly prescribed for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but not recommended as first-line treatment unless patients have asthma/COPD overlap or frequent exacerbations. This study examined whether long-term ICS use (more than two years) increases the risk of serious health conditions compared with short-term use (less than 4 months).
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed electronic health records from over 20 million patients, focusing on individuals aged 45 and ...
Ambulatory antibiotic use in France showed significant decline during the COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-24
Research Brief
Background and Goal: The COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown measures in France affected health care access and prescribing patterns, leading to significant changes in outpatient (ambulatory) antibiotic use. This study examined how systemic antibiotic use in France changed from 2020 to 2022 compared to expected trends.
Study Approach: Researchers used nationwide health insurance data covering 67 million people to track monthly antibiotic prescriptions from January 2010 to March 2022. ...
Many patients with chlamydia and gonorrhea are not receiving CDC-recommended treatment in primary care
2025-03-24
Original Research
Background and Goal: Prompt treatment of chlamydia and gonorrhea following a confirmed diagnosis is essential to prevent complications and reduce transmission. Adherence to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) treatment guidelines in primary care settings remains a concern. This study aimed to quantify the overall treatment rate for chlamydia and gonorrhea and identify factors associated with treatment delays and disparities.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed electronic health record data from the PRIME registry, which includes information ...
“About me” care card tool can improve care planning and cognitive health management
2025-03-24
Original Research
Background and Goal: Existing tools for cognitive impairment focus primarily on clinical diagnosis but do not support discussions that address patients’ personal fears, goals, and social needs.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted a feasibility study using a community and user-centered design approach to develop and test the “About Me” Care Card, a tool developed based on shared decision-making principles. An environmental scan identified gaps in existing cognitive care tools, and a global steering committee made up of health care professionals, patient advocacy groups, ...
Chi, Advincula named Materials Research Society Fellows
2025-03-24
Miaofang Chi and Rigoberto “Gobet” Advincula, both researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, have been elected as Class of 2025 Fellows of the Materials Research Society, or MRS. Chi also holds a joint appointment at Duke University, and Advincula is jointly appointed at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
The society, which has more than 13,000 members from 90 countries, selects Fellows for their distinguished accomplishments and outstanding contributions ...
Expectant and new fathers seek more support to improve maternal health
2025-03-24
PHILADELPHIA (March 24, 2025) – A new Penn Nursing study reveals that expectant and new fathers, particularly Black American fathers, express a significant need for more resources and support to better assist mothers during pregnancy and childbirth. The research, published in BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, highlights a gap in tailored information and resources for fathers within healthcare and social service systems.
Researchers conducted focus groups with eighty new fathers across the United States, with the majority (86%) being Black American, to understand ...
5,700-year storm archive shows rise in tropical storms and hurricanes in the Caribbean
2025-03-24
FRANKFURT. In the shallow waters of the Lighthouse Reef Atoll, located 80 kilometers off the coast of the small Central American country of Belize, the seabed suddenly drops steeply. Resembling a dark blue eye surrounded by coral reefs, the “Great Blue Hole” is a 125-meter-deep underwater cave with a diameter of 300 meters, which originated thousands of years ago from a karst cave located on a limestone island. During the last ice age, the cave’s roof collapsed. As ice sheets melted and global sea level started to rise, the cave ...
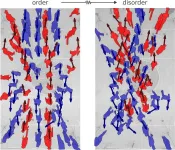
The secret behind pedestrian crossings – and why some spiral into chaos
2025-03-24
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL MONDAY, MARCH 24, 2025 (3:00 PM U.S. Eastern time)
Pedestrian crossings generally showcase the best in pedestrian behaviour, with people naturally forming orderly lanes as they cross the road, smoothly passing those coming from the opposite direction without any bumps or scrapes. Sometimes, however, the flow gets chaotic, with individuals weaving through the crowd on their own haphazard paths to the other side.
Now, an international team of mathematicians, co-led by Professor Tim Rogers at the University of Bath in the UK and Dr Karol Bacik at MIT in ...
[1] ... [611]
[612]
[613]
[614]
[615]
[616]
[617]
[618]
619
[620]
[621]
[622]
[623]
[624]
[625]
[626]
[627]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.