AI food scanner turns phone photos into nutritional analysis
2025-03-18
Snap a photo of your meal, and artificial intelligence instantly tells you its calorie count, fat content, and nutritional value — no more food diaries or guesswork.
This futuristic scenario is now much closer to reality, thanks to an AI system developed by NYU Tandon School of Engineering researchers that promises a new tool for the millions of people who want to manage their weight, diabetes and other diet-related health conditions.
The technology, detailed in a paper presented at the 6th ...
Looking for donors? Start with where they live
2025-03-18
AUSTIN, Texas -- While nonprofit organizations are growing, their donations are shrinking. The number of nonprofits registered with the Internal Revenue Service grew 25% from 2013 to 2023. But during the past year, both money raised and donor counts have dropped 3%.
Their main challenge is low response rates for fundraising solicitations, says Vijay Mahajan, professor of marketing at Texas McCombs. In turn, a major reason is lack of quality data on donors, which makes it harder to successfully target their appeals.
Nonprofits tend to keep data on active donors, such as how much ...
Mastery of language could predict longevity
2025-03-18
Everyone ages, but, sometimes, people outlive all predictions. Previous research has uncovered an unlikely factor related to longevity: intelligence (Bäckman & MacDonald, 2006; Bosworth & Siegler, 2002).
However, intelligence isn’t a simple characteristic. There are many traits that contribute to it that can be tested—from memory to mathematical logic. In a 2024 Clinical Psychological Science study, Paolo Ghisletta of the University of Geneva linked longevity specifically to one of those traits: verbal fluency, the measure of one’s vocabulary and ability to use ...
Threatened by warming waters, brook trout may be able to adapt to hotter weather
2025-03-18
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Brook trout may have a genetic trick up their scales when it comes to adapting, with limitations, to heatwaves that threaten their existence. Scientists have known for years that brook trout — an iconic coldwater fish species native to streams and lakes in the eastern United States and Canada — are extremely vulnerable to warming temperatures, with more than half of their habitats characterized as highly sensitive and highly vulnerable to such changes by U.S. Forest Service researchers in 2010. Now, a novel study led by researchers ...
AI ring tracks spelled words in American Sign Language
2025-03-18
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led research team has developed an artificial intelligence-powered ring equipped with micro-sonar technology that can continuously and in real time track fingerspelling in American Sign Language (ASL).
In its current form, SpellRing could be used to enter text into computers or smartphones via fingerspelling, which is used in ASL to spell out words without corresponding signs, such as proper nouns, names and technical terms. With further development, the device – believed to be the first of its kind – could revolutionize ASL translation by continuously tracking entire signed words and sentences.
“Many other technologies that recognize ...
What’s behind the ‘pop and slosh’ when opening a swing-top bottle of beer?
2025-03-18
WASHINGTON, March 18, 2025 — In a fun experiment, Max Koch, a researcher at the University of Göttingen in Germany — who also happens to be passionate about homebrewing — decided to use a high-speed camera to capture what occurs while opening a swing-top bottle of homebrew.
When Robert Mettin, who leads the Ultrasound and Cavitation group at the university’s Third Institute of Physics, Biophysics, suggested that Koch should submit the findings to the special “kitchen flows” issue of Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Koch and his colleagues chose to ...
Adherence to annual lung cancer screening and rates of cancer diagnosis
2025-03-18
About The Study: In this multicenter cohort study of adults undergoing lung cancer screening, screening adherence was associated with increased overall and early-stage lung cancer detection rates; however, adherence decreased annually after baseline screening, suggesting that it is an important lung cancer screening quality metric.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Roger Y. Kim, M.D., M.S.C.E., email roger.kim@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Geographic access to cancer care and treatment and outcomes of early-stage non–small cell lung cancer
2025-03-18
About The Study: In this cohort study, geographic access to cancer care was associated with guideline-recommended treatment for early-stage non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and outcomes, particularly in socially marginalized patients, underscoring the importance of ensuring appropriate geographic allocations of cancer care resources and addressing travel barriers to health care to improve NSCLC treatment, prognosis, and equity.
Corresponding authors: To contact the corresponding ...
Trauma surgeons propose ‘precision transfusion’ approach to pre-hospital care
2025-03-18
When someone is traumatically injured, giving them blood products before they arrive at the hospital – such as at the scene or during emergency transport – can improve their likelihood of survival and recovery. But patients with certain traumatic injuries have better outcomes when administered specific blood components.
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and UPMC scientist-surgeons announced today in Cell Reports Medicine that giving plasma that has been separated from other parts of donated blood improves outcomes in patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) or shock, whereas giving unseparated or “whole” ...
New artificial intelligence tool accelerates disease treatments
2025-03-18
University of Virginia School of Medicine scientists have created a computational tool to accelerate the development of new disease treatments. The tool goes beyond current artificial intelligence (AI) approaches by identifying not just which patient populations may benefit but also how the drugs work inside cells.
The researchers have demonstrated the tool’s potential by identifying a promising candidate to prevent heart failure, a leading cause of death in the United States and around the world.
The new AI tool called LogiRx, can predict how drugs will affect biological processes in the body, helping scientists understand the effects the drugs will have ...
CCA appoints expert panel on enhancing national research infrastructure
2025-03-18
Canada’s research infrastructure is essential to the future of science and innovation, economic prosperity, and well-being throughout the country. At the request of Innovation, Science, and Economic Development Canada, the CCA has formed an expert panel to support the federal government in optimizing Canada’s research infrastructure—from its national-scale scientific facilities to its digital platforms and collaborative networks—through evidence synthesis and strategic insights. Janet King, Chair of Polar Knowledge Canada’s Board of Directors and Vice-Chair of the Canadian Light Source’s Board of Directors, will serve ...
Rising Stars: PPPL researchers honored in 2024 Physics of Plasmas Early Career Collection
2025-03-18
Celebrating fresh thinking in plasma physics is essential to the continued growth of the field, and this year’s Physics of Plasmas Early Career Collection highlights some of the most promising new voices pushing the boundaries of discovery.
The prestigious collection highlights top papers from all areas of plasma physics research authored by individuals who defended their dissertations within the past five years. This year, three researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) are featured in the Early Career Collection:
Staff Research ...
Add some spice: Curcumin helps treat mycobacterium abscessus
2025-03-18
Highlights:
Mycobacterium abscessus can cause dangerous lung infections.
Treatment usually requires a combination of antibiotics for more than a year.
Researchers in China report that curcumin, found in turmeric, can enhance treatment with bedaquiline, an antimycobacterial.
Animal studies showed that treatment with the combination led to a faster clearance of the infection.
Washington, D.C.—Mycobacterium abscessus is a fast-growing, pathogenic mycobacteria that can cause lung infections, and people who have respiratory conditions or are immunocompromised ...
Coastal guardians pioneer a new way to protect the Florida Keys’ shorelines
2025-03-18
By 2050, sea levels along the United States coast are expected to rise by 0.25 to 0.30 meters, increasing flooding in low-lying areas. Due to its unique geography and infrastructure network, the Florida Keys is particularly at risk of climate hazards such as sea level rise, hurricanes and flooding. Since 2015, the Florida Keys has experienced four hurricanes – Irma (2107), Ian (2022), Helene (2024) and Milton (2024).
Nature-based solutions, such as restoring mangroves and coastal strands, can help mitigate these risks by stabilizing shorelines, improving ecosystems ...
Study shows rise in congenital heart defects in states with restrictive abortion laws
2025-03-18
The incidence of babies born with serious heart defects, known as cyanotic congenital heart disease (CCHD), rose in states that enacted restrictive abortion laws following the U.S. Supreme Court’s 2022 ruling that put abortion laws in the hands of the states, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
The study is the first to look at rates of congenital heart defects since the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ...
Healthy plant-based foods could help people with cardiometabolic disorders live longer
2025-03-18
People with cardiometabolic disorders—such as obesity, diabetes and heart disease—could increase their chances of living longer by adopting a healthy plant-based diet, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
While previous studies have assessed the benefits of plant-based diets in a general population, this new study is the first to focus on their benefits in people with cardiometabolic disorders, which are rising in prevalence worldwide and bring an increased risk of premature death.
“Among populations with cardiometabolic disorders, ...
Cannabis users face substantially higher risk of heart attack
2025-03-18
Marijuana is now legal in many places, but is it safe? Two new studies add to mounting evidence that people who use cannabis are more likely to suffer a heart attack than people who do not use the drug, even among younger and otherwise healthy adults. The findings are from a retrospective study of over 4.6 million people published in JACC Advances and a meta-analysis of 12 previously published studies being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
Marijuana use has risen in the United States, especially in states where it is legal to buy, sell and ...
Lifestyle risks weigh heavier on women’s hearts
2025-03-18
Lifestyle and health factors that are linked with heart disease appear to have a greater impact on cardiovascular risk in women than men, according to a study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session (ACC.25).
While factors such as diet, exercise, smoking and blood pressure have long been linked with heart disease risk, the new study is the first to show that these associations are collectively stronger in women than men. According to the researchers, the ...
Plastic-degrading enzymes from landfills
2025-03-18
Enzymes found in landfills around the world may be able to break down plastic waste. Some 11 billion metric tons of plastic are projected to accumulate in the environment by 2050. Enzymatic and microbial degradation is a promising method of plastic recycling. Landfills, environments where plastics are an abundant resource, are crucibles of bacterial evolution. Liyan Song and colleagues collected plastic biocatalytic enzymes from landfills around the world, using metagenomics and machine learning. Samples came from China, Italy, Canada, Great Britain, Jamaica, and India and included refuse, leachate, sludge, and airborne particles. The authors identified 31,989 possible ...
Feline therapy: Study suggests cats could fill an assistive niche
2025-03-18
PULLMAN, Wash. — For years, therapy dogs have ruled the world of animal-assisted services (AAS), offering stress relief to college students, hospital patients, and those in need of emotional support. But new research suggests that some cats might also have what it takes to join the ranks of therapy animals—bringing their purrs, gentle headbutts, and calm demeanor to the field.
A study in the journal Animals co-authored by Washington State University professor Patricia Pendry, in collaboration with researchers in Belgium, found that therapy cats share specific behavioral traits that may make them well-suited for AAS programs. The research team surveyed ...
Popular cooking cheese made with peas yields same taste and texture
2025-03-18
Creamy, crumbly, mild, or sharp — cheese is a true crowd-pleaser. From everyday meals to gourmet delights, it’s a staple across the Western world. In 2023, the average European enjoyed 20.5 kilograms of cheese.
But it is no secret that, as a dairy product, heavy cheese consumption comes with a significant environmental impact. As such, extensive research is being conducted on how to produce plant-based cheeses. Unfortunately, finding an entirely plant-based cheese that satisfies cheese lovers in terms of both texture and taste has been difficult. And texture in particular has been challenging to get just right.
So, food researchers at the University ...
Dr. Julia Dallman awarded SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) grant for SYNGAP1 research targeting gastro-intestinal treatment development
2025-03-18
Mill Valley, CA – March 18, 2025 – The SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) dba Cure SYNGAP1, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, has awarded a $65,000 grant to Dr. Julia Dallman, Associate Professor of Biology at the University of Miami College of Arts and Sciences, to investigate gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms in SYNGAP1-related disorders (SRD) patients. Leveraging her extensive experience with zebrafish models, Dr. Dallman's research aims to identify therapies that alleviate severe GI issues, such as chronic ...
Benzoporphyrin gold complex: a breakthrough in organic conductive materials
2025-03-18
Unsubstituted π-electronic systems with expanded π-planes are highly desirable for improving charge-carrier transport in organic semiconductors. However, their poor solubility and high crystallinity pose major challenges in processing and assembly, despite their favourable electronic properties. The strategic arrangement of these molecular structures is crucial for achieving high-performance organic semiconductive materials.
In a significant breakthrough, a research team led by Professor Hiromitsu Maeda from Ritsumeikan University, including Associate Professor Yohei Haketa from ...
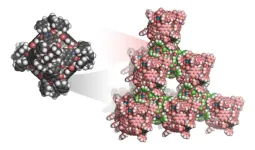
Revolutionary van der Waals open frameworks: a new era in porous materials
2025-03-18
Researchers from Kyoto University have achieved a groundbreaking advancement in materials science by developing the world's first three-dimensional van der Waals open frameworks (WaaFs). This innovation challenges the conventional belief that van der Waals interactions are too weak for open framework materials, demonstrating their potential for stable and highly porous materials.
Published in Nature Chemistry, the study presents a strategy using octahedral metal-organic polyhedra (MOPs) as building blocks to construct WaaFs. These frameworks exhibit high thermal stability, exceptional porosity, and reversible assembly, opening new avenues for applications in gas storage, separation, ...
“Significant proportion” of world’s rural population missing from global estimates, says study
2025-03-18
Global population datasets, crucial for decision-making by governments and institutions, may underestimate rural populations by as much as 53% to 84%, reveals an Aalto University study.
Governments, international bodies and researchers rely on global population data for resource allocation and infrastructure planning to disease epidemiology and disaster risk management. In a new study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Aalto University in Finland show the profound and systematic extent to which these datasets underestimate ...
[1] ... [622]
[623]
[624]
[625]
[626]
[627]
[628]
[629]
630
[631]
[632]
[633]
[634]
[635]
[636]
[637]
[638]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.