Violent supernovae 'triggered at least two Earth extinctions'
2025-03-13
Royal Astronomical Society press release
RAS PR 25/10
Embargoed until 00:01 on Thursday 13 March 2025
At least two mass extinction events in Earth's history were likely caused by the "devastating" effects of nearby supernova explosions, a new study suggests.
Researchers at Keele University say these super-powerful blasts – caused by the death of a massive star – may have previously stripped our planet's atmosphere of its ozone, sparked acid rain and exposed life to harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
They believe a supernova explosion close to Earth could be to blame for both the late Devonian and Ordovician ...
Over 1.2 million medical device side-effect reports not submitted within legal timeframe
2025-03-12
Over 1.2 million medical device adverse event reports were not submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) within the deadline set by federal regulations, finds an analysis of recent data published by The BMJ today.
Of these late reports, more than 400,000 were submitted more than six months after the manufacturer was notified of an adverse event.
The researchers warn that late adverse event reporting may prevent early detection of patient safety concerns.
Most medical devices in the US are approved on the condition that manufacturers report to the FDA when they learn that any of their devices have malfunctioned or may ...
An easy-to-apply gel prevents abdominal adhesions in animals in Stanford Medicine study
2025-03-12
Surgical adhesions — common, sometimes life-threatening complications that arise after open or laparoscopic abdominal surgery — can be prevented in mice and pigs by a gel impregnated with a molecule that blocks a key signaling pathway in the formation of scar tissue.
The gel can be applied as a spray or a wash to the inside of the abdominal cavity immediately after surgery. Over a period of two weeks, the gel releases a small molecule, T-5224, that blocks the activation of adhesion-forming ...
A path to safer, high-energy electric vehicle batteries
2025-03-12
Nickel’s role in the future of electric vehicle batteries is clear: It’s more abundant and easier to obtain than widely used cobalt, and its higher energy density means longer driving distances between charges.
However, nickel is less stable than other materials with respect to cycle life, thermal stability, and safety. Researchers from The University of Texas at Austin and Argonne National Laboratory aim to change that with a new study that dives deep into nickel-based cathodes, one of the two electrodes that facilitate energy storage in batteries.
"High-nickel cathodes ...
openRxiv launch to sustain and expand preprint sharing in life and health sciences
2025-03-12
openRxiv has officially launched as an independent nonprofit to oversee bioRxiv and medRxiv, the world's leading preprint servers for life and health sciences. openRxiv ensures that researchers worldwide can continue to share discoveries rapidly and openly. With a researcher-led governance model, openRxiv strengthens the foundation of preprint sharing, empowering scientists to communicate findings at the speed of discovery.
"We want openRxiv to be a home for all scientists—whether they're early-career researchers, established scholars, or from institutions large and small ...
“Overlooked” scrub typhus may affect 1 in 10 in rural India, and be a leading cause of hospitalisations for fever
2025-03-12
A study of over 32,000 people living in Tamil Nadu, India suggests scrub typhus infection may affect up to 10% of rural populations annually and is a leading yet under-recognised cause of hospitalisations for fever across India.
The study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, was conducted as part of a collaboration between the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) and the Christian Medical College Vellore, India.
Scrub typhus is a potentially life-threatening infection caused by the bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi, which belongs to the rickettsia family. It is spread to humans through the bite of infected larval mites or chiggers. Chiggers are found ...
Vocal changes in birds may predict age-related disorders in people, study finds
2025-03-12
University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds' song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages.
The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird's ...
Spotiphy integrative analysis tool turns spatial RNA sequencing into imager
2025-03-12
Spatial transcriptomics is a cutting-edge technique that characterizes gene expression within sections of tissue, such as heart, skin or liver tissue. These snapshots provide insights into how spatial organization affects cellular functions across the spectrum of biology and disease. Up to now, researchers conducting spatial transcriptomics have had to choose between two options based on their needs: genome-wide coverage or single-cell resolution. To solve this tradeoff, scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and the University of ...
Dynamic acoustics of hand clapping, elucidated
2025-03-12
ITHACA, N.Y. -- In a scene toward the end of the 2006 film, “X-Men: The Last Stand,” a character claps and sends a shock wave that knocks out an opposing army.
Sunny Jung, professor of biological and environmental engineering in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, was intrigued.
“It made me curious about how the wave propagates when we clap our hands,” Jung said.
Jung is senior author of a study, published March 11 in Physical Review Research, that elucidates the complex physical mechanisms and fluid dynamics involved in a handclap, with potential applications in bioacoustics ...
AAN, AES and EFA issue position statement on seizures and driving safety
2025-03-12
MINNEAPOLIS — The American Academy of Neurology (AAN), the American Epilepsy Society (AES) and the Epilepsy Foundation of America (EFA) have issued a consensus position statement on seizures, driver licensure and medical reporting. The position statement is published on March 12, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology (AAN). It was developed with the Ethics, Law, and Humanities Committee, a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological ...
Do brain changes remain after recovery from concussion?
2025-03-12
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4:00 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 12, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS — For college athletes with concussion, brain changes may remain visible in brain scans up to a year after they are cleared to return to play, according to a study published on March 12, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology (AAN).
“Concussion can have long-term effects on brain health, and there is growing evidence that brain recovery may persist months to years, even after symptoms like headache, fatigue and balance problems resolve,” said author Nathan Churchill, PhD, of ...
Want to climb the leadership ladder? Try debate training
2025-03-12
For those looking to climb the corporate ladder in the U.S., here’s an idea you might not have considered: debate training.
According to a new research paper, people who learn the basics of debate are more likely to advance to leadership roles in U.S. organizations, compared to those who do not receive this training. One key reason is that being equipped with debate skills makes people more assertive in the workplace.
“Debate training can promote leadership emergence and advancement by fostering individuals’ assertiveness, which is a key, valued leadership characteristic in U.S. organizations,” says MIT Associate Professor Jackson Lu, one of the scholars ...
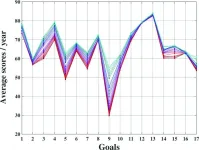
No countries on track to meet all 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals
2025-03-12
A new analysis reveals complex linkages among the United Nations’ (UN’s) 17 Sustainable Development Goals—which include such objectives as gender equality and quality education—and finds that no country is on track to meet all 17 goals by the target year of 2030. Alberto García-Rodríguez of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on March 12, 2025.
In 2015, UN member countries adopted the Sustainable Development ...
Robotics and spinal stimulation restore movement in paralysis
2025-03-12
Spinal cord injuries are life-altering, often leaving individuals with severe mobility impairments. While rehabilitation robotics—devices that guide movement during therapy—have improved training for those with spinal cord injuries, their effectiveness remains limited. Without active muscle engagement, robotic-assisted movement alone does not sufficiently retrain the nervous system.
A team at .NeuroRestore, led by Grégoire Courtine and Jocelyne Bloch, has now developed a system that seemlessly integrates an implanted spinal cord neuroprosthesis with rehabilitation robotics. The researchers’ device delivers well-timed electrical pulses to stimulate ...
China discovers terrestrial "Life oasis" from end-Permian mass extinction period
2025-03-12
A new study reveals that a region in China's Turpan-Hami Basin served as a refugium, or "Life oasis" for terrestrial plants during the end-Permian mass extinction, the most severe biological crisis since the Cambrian period.
The research, published in Science Advances, challenges the widely held view that terrestrial ecosystems suffered the same catastrophic losses as marine environments during this period.
The discovery, led by Prof. LIU Feng from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology (NIGPAS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, provides the first conclusive fossil evidence ...
Poor sleep may fuel conspiracy beliefs, according to new research
2025-03-12
A new study from the University of Nottingham has revealed that poor sleep quality may increase susceptibility to conspiracy beliefs, with depression likely playing a key role in this relationship.
Experts from the University’s School of Psychology examined the link between sleep quality and conspiracy beliefs in two studies involving over 1,000 participants. Their findings, published in the Journal of Health Psychology, indicate that individuals with poorer sleep quality over the past month were more likely to endorse conspiracy theories, particularly after exposure to conspiratorial content.
Conspiracy theories claim that powerful, secretive ...
Adolescent boys who experience violence have up to 8 times the odds of perpetrating physical and sexual intimate partner violence that same day, per South African study collecting real-time data over
2025-03-12
Adolescent boys who experience violence have up to 8 times the odds of perpetrating physical and sexual intimate partner violence that same day, per South African study collecting real-time data over mobile phones
Article URL: https://plos.io/4brsDzz
Article title: Measuring real-time violence exposure and its impact on intimate partner violence perpetration among adolescents
Author countries: US, South Africa
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health under Award R01MH119878. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors ...
Critically endangered hawksbill turtles migrate up to 1,000km from nesting to foraging grounds in the Western Caribbean, riding with and against ocean currents to congregate in popular feeding hotspot
2025-03-12
Critically endangered hawksbill turtles migrate up to 1,000km from nesting to foraging grounds in the Western Caribbean, riding with and against ocean currents to congregate in popular feeding hotspots
Article URL: https://plos.io/41LfJZK
Article title: Inter-nesting area use, migratory routes, and foraging grounds for hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) in the Western Caribbean
Author countries: US, Honduras, Costa Rica
Funding: Funding for this project was provided by the Boyd Lyon Sea Turtle Fund to QDB, ...
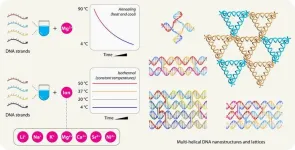
UAlbany researchers unlock new capabilities in DNA nanostructure self-assembly
2025-03-12
ALBANY, N.Y. (March 12, 2025) — University at Albany researchers at the RNA Institute are pioneering new methods for designing and assembling DNA nanostructures, enhancing their potential for real-world applications in medicine, materials science and data storage.
Their latest findings demonstrate a novel ability to assemble these structures without the need for extreme heat and controlled cooling. They also demonstrate successful assembly in unconventional “buffer” substances including nickel. These developments, published today in the journal Science Advances, unlock new possibilities in DNA nanotechnology.
DNA ...
PM2.5 exposure may be associated with increased skin redness in Taiwanese adults, suggesting that air pollution may contribute to skin health issues
2025-03-12
PM2.5 exposure may be associated with increased skin redness in Taiwanese adults, suggesting that air pollution may contribute to skin health issues.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4iDTuuo
Article Title: Association between PM2.5 and skin redness features in Taiwan
Author Countries: Taiwan, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
BD² announces four new sites to join landmark bipolar disorder research and clinical care network
2025-03-12
Today, Breakthrough Discoveries for thriving with Bipolar Disorder (BD²) announced four new national institutions to receive $2.3 million each to join the BD² Integrated Network, a collaborative research and clinical care model that will improve care, interventions, and outcomes for people living with bipolar disorder.
University of Cincinnati/Lindner Center of HOPE, University of California San Diego, The University of Texas at Austin, and The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research join the six inaugural institutions in the network. Working in partnership with clinicians, researchers, and people living ...
Digital Exclusion Increases Risk of Depression Among Older Adults Across 24 Countries
2025-03-12
Older adults who lack internet access are at a significantly higher risk of developing depressive symptoms, especially those with limited familial support or lower income levels, according to a new study published in Health Data Science. Conducted by an international team of researchers, this study analyzed data from five major aging cohort studies covering 24 countries, revealing a strong link between digital exclusion and mental health.
The researchers, led by Dr. Yinzi Jin from Peking University, investigated how digital exclusion—defined as the lack of internet access—affects the mental health of older adults. Using data from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS), ...
Quantum annealing processors achieve computational advantage in simulating problems on quantum entanglement
2025-03-12
Quantum annealing processors outperform classical supercomputers in solving real-world scientific simulations of quantum spin dynamics, researchers report in a new study, achieving results far beyond the capacity of conventional computational methods, which may require impossible time and energy to match. The results provide a challenge to classical computing, where method improvement has in the past tempered claims of quantum advantage. Only in recent years have quantum computers begun to live up to their lofty promises, with quantum processing units (QPUs) with diverse architectures – such as photonic, neutral-atom, and ...
How UV radiation triggers a cellular rescue mission
2025-03-12
How UV Radiation Triggers a Cellular Rescue Mission
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a well-known cause of DNA damage, which can lead to diseases like skin cancer. But how do our cells repair this damage to protect us? Researchers from Sabanci University, Veysel Oğulcan Kaya and Ogün Adebali, have uncovered a fascinating answer: when DNA is damaged by UV light, our cells reorganize their genetic material in 3D space to prioritize repair, in what might be called a “cellular rescue mission.”
A New Look at DNA Repair
DNA, the blueprint of ...
Hepatic stellate cells control liver function and regeneration
2025-03-12
Until now, doctors knew hepatic stellate cells mainly as drivers of liver fibrosis. The actual functions of this cell type have hardly been studied to date. Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), the Mannheim Medical Faculty and Columbia University in New York have now published in the journal Nature that hepatic stellate cells control liver metabolism as well as liver regeneration and size. The results of the study could contribute to new therapeutic approaches for liver diseases.
The liver is a central organ for carbohydrate and protein metabolism as well as for the detoxification ...
[1] ... [625]
[626]
[627]
[628]
[629]
[630]
[631]
[632]
633
[634]
[635]
[636]
[637]
[638]
[639]
[640]
[641]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.