Ethics in patient preferences for AI–drafted responses to electronic messages
2025-03-11
About The Study: In this survey study, participants expressed a mild preference for messages written by artificial intelligence (AI) but had a slightly decreased satisfaction when told AI was involved. Patient experience must be considered along with ethical implementation of AI. Although AI disclosure may slightly reduce satisfaction, disclosure should be maintained to uphold patient autonomy and empowerment.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anand Chowdhury, MD, MMCi, email anand.chowdhury@duke.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Patients’ affinity for AI messages drops if they know the technology was used
2025-03-11
DURHAM, N.C. – In a Duke Health-led survey, patients who were shown messages written either by artificial intelligence (AI) or human clinicians indicated a preference for responses drafted by AI over a human. That preference was diminished, though not erased, when told AI was involved.
The study, publishing March 11 in JAMA Network Open, showed high overall satisfaction with communications written both by AI and humans, despite their preference for AI. This suggests that letting patients know AI was used does not greatly reduce confidence in the message.
“Every health system is grappling with this issue of whether we disclose the use of AI and how,” ...
New ACS led study finds wildfires pose challenges to cancer care
2025-03-11
Due to the physical, psychological, and socioeconomic consequences of a cancer diagnosis and treatment, people with cancer are especially vulnerable during extreme weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires, which are becoming more common and damaging with climate change. A new national study led by American Cancer Society (ACS) and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health researchers finds patients whose facility was impacted by a wildfire disaster during recovery from lung cancer surgery had longer length of stay (LOS) than similar patients treated at the same facility, but at times when no disaster occurred. The findings are out today in the Journal ...
Scientists discover new heavy-metal molecule ‘berkelocene’
2025-03-11
A research team led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has discovered “berkelocene,” the first organometallic molecule to be characterized containing the heavy element berkelium.
Organometallic molecules, which consist of a metal ion surrounded by a carbon-based framework, are relatively common for early actinide elements like uranium (atomic number 92), but they are scarcely known for later actinides like berkelium (atomic number 97).
“This is the first time that evidence for the formation of a chemical bond between berkelium and carbon has been obtained. The discovery provides ...
Repeated esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding
2025-03-11
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt and accurate diagnosis. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy are the primary diagnostic modalities, but initial examinations may sometimes fail to identify the bleeding source. In such cases, repeated endoscopic evaluations can improve detection rates. This review explores the role of repeat EGD and colonoscopy in diagnosing GI bleeding, highlighting the conditions under which they are most beneficial and the challenges associated with their use.
Incidence and Causes of Gastrointestinal ...
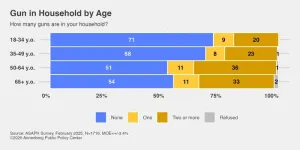
Over 1 in 3 adults in households with guns do not store all in locked locations
2025-03-11
PHILADELPHIA – Since 2017, firearm-related injuries in the United States have been the most common cause of death from injury among children through young adults, ages 1 to 24, surpassing motor vehicle accidents, according to a 2022 study. Access to firearms in one’s home increases the risk of suicide and accidental death.
But over a third of Americans with guns in their homes say they do not store all of them in a locked location (37%), according to the latest health survey from the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania. ...
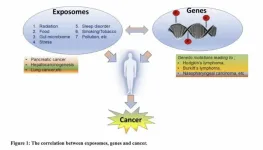
How environmental exposures affect genes and increase cancer risk
2025-03-11
“Environmental exposures may cause genetic damage, lead to mutations in key genes, and/or block the DNA repair mechanisms increasing the risk of cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY – March 11, 2025 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on March 10, 2025, titled “EXPOSOMES and GENES: The duo influencing CANCER initiation and progression.”
In this editorial, Drs. Uzma Saqib, Katherine E. Ricks, Alexander G. Obukhov, and Krishnan Hajela from Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya (DAVV) in Indore, India, discuss how environmental factors, known as exposomes, interact with genes to influence cancer risk. The authors highlight how pollution, diet, ...
Rising CO2 levels: Impacts on crop nutrition and global food supplies
2025-03-11
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex impacts of elevated CO2 levels on food security, plant growth, and crop quality. As the global atmospheric CO2 concentration continues to rise, understanding these effects is crucial for ensuring future food supplies.
On one hand, elevated CO2 can have some positive effects on plants. For C3 plants, it can stimulate photosynthesis, leading to increased dry matter yield and grain production. In legumes, it enhances N2 fixation, which is beneficial for reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers. Additionally, ...
Water movement on surfaces makes more electric charge than expected
2025-03-11
Researchers from RMIT University and the University of Melbourne have discovered that water generates an electrical charge up to 10 times greater than previously understood when it moves across a surface.
The team, led by Dr Joe Berry, Dr Peter Sherrell and Professor Amanda Ellis, observed when a water droplet became stuck on a tiny bump or rough spot, the force built up until it “jumped or slipped” past an obstacle, creating an irreversible charge that had not been reported before.
The new understanding of this “stick-slip” motion of water over a surface paves the way for surface design with controlled electrification, with ...
People with COPD and arthritis have an increased risk of death
2025-03-11
Miami (March 11, 2025) – People with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and arthritis have a higher risk of death than people with arthritis who do not have COPD, according to a new study. The study is published in the January 2025 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the fourth leading cause of death ...
PNAS announces six 2024 Cozzarelli Prize recipients
2025-03-11
WASHINGTON, DC – The Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) has selected six papers published by PNAS in 2024 to receive the Cozzarelli Prize, an award that recognizes outstanding contributions to the scientific disciplines represented by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Papers were chosen from more than 3,200 research articles that appeared in the journal last year and represent the six broadly defined classes under which the NAS is organized. Additionally, the Editorial Board has recognized six papers—one ...
AMS Science Preview: Data deserts, Federal science, malaria prediction
2025-03-11
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form. Below are some recent examples.
JOURNAL ARTICLES
Climate Change Increases Energy Demand and Cost in Texas
Weather, Climate, and Society
Climate change is driving large increases in electricity demand and costs in Texas’ ERCOT market. Compared to a 1950–1980 baseline climate, ERCOT electricity demand in 2023 was 1.9 ...
Microplastics could be fueling antibiotic resistance, Boston University study finds
2025-03-11
Written by Jessica Colarossi
Microplastics—tiny shards of plastic debris—are all over the planet. They have made their way up food chains, accumulated in oceans, clustered in clouds and on mountains, and been found inside our bodies at alarming rates. Scientists have been racing to uncover the unforeseen impacts of so much plastic in and around us.
One possible, and surprising, consequence: more drug-resistant bacteria.
In a startling discovery, a team of Boston University researchers found that bacteria exposed to microplastics became resistant to multiple types of antibiotics commonly used to treat infections. They ...
Microplastics increase antimicrobial resistance
2025-03-11
Washington, D.C.—Microplastics are not just pollutants, but also highly complex materials that facilitate antimicrobial resistance, even without antibiotics, according to a new study. The findings were published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“Addressing plastic pollution isn’t just an environmental issue—it’s a critical public health priority in the fight against drug-resistant infections,” said lead study author Neila Gross, a Ph.D. candidate in the lab of Professor Muhammad ...
Endocrine Society elects Santoro as 2026-2027 President
2025-03-11
WASHINGTON—Endocrine Society members elected Nanette Santoro, M.D., of the University of Colorado School of Medicine in Aurora, Colo., as its 2026-2027 President. She will serve as President-Elect for a year beginning in July 2025 before becoming President in June 2026.
Santoro has served as E. Stewart Taylor Chair of Obstetrics & Gynecology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine since 2010. She is a well-recognized practitioner, dedicated mentor and leading researcher on studies of women with premature and age-appropriate menopause.
She has held many roles with the Endocrine Society, including serving as Vice President of Clinical Science, an author ...
Study explores effects of climatic changes on Christmas Island’s iconic red crabs
2025-03-11
The annual migration of Christmas Island’s red crabs – where millions of creatures cover its beaches as they make their way from land to sea – is a true natural spectacle.
However, little is known about whether and how the species might be impacted under the future environmental conditions created by the changing global climate.
A new study by scientists and graduates at the University of Plymouth has investigated one aspect of how such shifts might affect its earliest development.
Specifically, the research focused on whether lower ...
AI in engineering
2025-03-11
A review explores the role of AI in engineering, assessing the benefits and challenges of the synergy between the two fields. A 2004 DARPA contest pitted AI vehicles against one another in a race on 150 miles of dirt roads. The best-performing vehicle made it less than eight miles of the way. The next year, five vehicles finished a 132-mile course, and today driverless cabs are active in several major cities. Enthusiasts have suggested AI could improve transportation and manufacturing, medicine, consumer goods, and military technology. Rama Chellappa, Guru Madhavan, Ed ...
Dr. Megan Abbott and the University of Colorado awarded $450,000 establishing a Clinical Research Center of Excellence that will also serve as a second site for SYNGAP1 ProMMiS
2025-03-11
Mill Valley, CA – March 11, 2025 – The SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) dba Cure SYNGAP1, a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, has awarded a $450,000 grant to Dr. Megan Abbott and the University of Colorado to establish a Clinical Research Center of Excellence for SYNGAP1-Related Disorders at Children’s Hospital Colorado (CHCO).
This initiative expands the already established Natural History Study to the SYNGAP1 Prospective Multidisciplinary Multisite Study (ProMMiS) while providing specialized care for individuals affected by SYNGAP1-related disorders ...
Empire Discovery Institute appoints Dr. Ronald Newbold as Chief Executive Officer
2025-03-11
Rochester, NY – March 10, 2025 – Empire Discovery Institute (EDI), a leading non-profit drug discovery and development accelerator, is pleased to announce the appointment of Dr. Ronald Newbold as Chief Executive Officer (CEO).
Dr. Newbold, who joined EDI in 2021 as Chief Business Officer, has served as interim CEO since August 2022 and has been instrumental in driving the organization’s growth and success. Under his leadership, EDI has achieved significant milestones, including the growth of the Medicines Discovery ...
Douglas Hanahan, Ph.D., FAACR, honored with the 2025 Pezcoller Foundation-AACR International Award for Extraordinary Achievement in Cancer Research
2025-03-11
CHICAGO – The Pezcoller Foundation-American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) International Award for Extraordinary Achievement in Cancer Research will be presented to Douglas Hanahan, PhD, Fellow of the AACR Academy, during the AACR Annual Meeting 2025, to be held April 25-30 at the McCormick Place Convention Center in Chicago, Illinois.
Hanahan is the Ludwig Distinguished Scholar at the Lausanne Branch of the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research. He is being recognized for his fundamental discoveries in cancer research that have had a far-reaching translational impact. Through the generation and characterization of innovative mouse models, Hanahan defined multistep ...
Mapping DNA's hidden switches: A methylation atlas
2025-03-11
Researchers have developed a comprehensive atlas that maps DNA methylation—a critical chemical modification governing gene activity—across 39 human cell types, revealing a complex landscape of epigenetic regulation. The study identified over 34,000 genomic regions exhibiting distinct ON/OFF methylation patterns at the two copies of the genome we inherited from our parents, a phenomenon known as allele-specific methylation. Some of these methylation changes are caused by genetic differences in genomic sequence of DNA, while others are due to parental imprinting—a ...
Beneficial genetic changes observed in regular blood donors
2025-03-11
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have identified genetic changes in blood stem cells from frequent blood donors that support the production of new, non-cancerous cells.
Understanding the differences in the mutations that accumulate in our blood stem cells as we age is important to understand how and why blood cancers develop and hopefully how to intervene before the onset of clinical symptoms.
As we age, stem cells in the bone marrow naturally accumulate mutations and with this, we see the emergence of clones, which are groups of blood cells ...
New research reveals psychological ‘booster shots’ can strengthen resistance to misinformation over time
2025-03-11
A new study has found that targeted psychological interventions can significantly enhance long-term resistance to misinformation. Dubbed “psychological booster shots,” these interventions improve memory retention and help individuals recognize and resist misleading information more effectively over time.
The study, published in Nature Communications, explores how different approaches, including text-based messages, videos, and online games, can inoculate people against misinformation. The researchers from the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge, Bristol, Potsdam and King’s College London conducted five large-scale experiments with over ...
Arctic sea ice loss drives drier weather over California and wetter over Spain and Portugal
2025-03-11
A study led by researchers from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, has used a novel approach to unravel the influence of the loss of Arctic sea ice on the planet's climate, isolating it from other factors related to climate change.
The study, published in the journal Communications Earth and Environment, shows that on decadal timescales, the loss of Arctic ice favours the climate of the south-west of the United States - and California in particular - becoming drier on average, especially in winter. This phenomenon would also affect ...
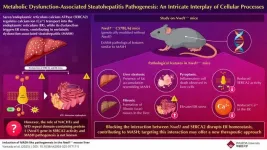
Nwd1 gene deletion triggers MASH-like pathology in mice: a new scientific breakthrough
2025-03-11
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is a liver disease that progresses without symptoms and is associated with significant global public health concerns. It is prevalent in 30% of the population worldwide and poses a risk of advancing to cirrhosis and liver cancer. MASH is marked by lipid droplet accumulation in the liver, progressing from steatosis to inflammation and cell damage, ultimately leading to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. A clear understanding of cellular processes in MASH pathogenesis is essential for developing ...
[1] ... [629]
[630]
[631]
[632]
[633]
[634]
[635]
[636]
637
[638]
[639]
[640]
[641]
[642]
[643]
[644]
[645]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.