Green solvent innovation: high-speed doctor-blading boosts organic solar cell efficiency
2025-03-28
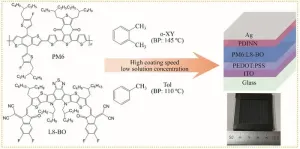
In a recent advancement, researchers have developed a high-speed doctor-blading technique that enhances the efficiency of organic solar cells (OSCs) while using eco-friendly, non-halogenated solvents. This innovative method not only addresses the environmental and scalability challenges of traditional solvents, such as chloroform, but also achieves impressive power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of 18.20% and 17.36% with green solvents like o-xylene and toluene, respectively. With a module efficiency of 16.07%, this breakthrough sets the stage for more sustainable, ...
C-Path announces successful conclusion of the ECOA: getting better together initiative
2025-03-28
TUCSON, Ariz., March 26, 2025 – Critical Path Institute® (C-Path)Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Consortium and Electronic Clinical Outcome Assessment (eCOA) Consortium are pleased to announce the successful conclusion of the eCOA: Getting Better Together Initiative. This initiative, driven by a shared commitment to advancing patient-focused drug development, has culminated in meaningful, lasting changes that will benefit all stakeholders across the eCOA ecosystem.
Beginning in 2019, this C-Path-led collaborative, pre-competitive initiative brought ...
Brain channels ‘stopped in time’ reveal chemical flow that enables learning and thinking
2025-03-28
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In an effort to understand how brain cells exchange chemical messages, scientists say they have successfully used a highly specialized microscope to capture more precise details of how one of the most common signaling molecules, glutamate, opens a channel and allows a flood of charged particles to enter. The finding, which resulted from a study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers, could advance the development of new drugs that block or open such signaling channels to treat conditions as varied as epilepsy and some intellectual disorders.
A report on the experiments, funded by the National ...
PET imaging confirms direct involvement of dopamine in cognitive flexibility
2025-03-28
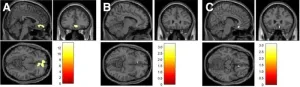
Reston, VA (March 16, 2025)—For the first time, scientists have confirmed a neurobiochemical link between dopamine and cognitive flexibility, according to new research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. PET imaging shows that the brain increases dopamine production when completing cognitively demanding tasks, and that the more dopamine released, the more efficiently the tasks are completed. Armed with this information, physicians may soon be able to develop more precise treatment strategies for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Cognitive flexibility is the ability to adapt one’s thinking and behavior appropriately to ...
Understanding the immune response to a persistent pathogen
2025-03-28
Most humans have long-lived infections in various tissues—including in the nervous system—that typically do not result in disease. The microbes associated with these infections enter a latent stage during which they quietly hide in cells, playing the long game to evade capture and ensure their own survival. But a lack of natural models to study these quiescent stages has led to gaps in scientists’ understanding of how latency contributes to pathogen persistence and whether these stages can be targeted by the immune system.
Now, a team led by University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine researchers ...
GSA conducting April 1 congressional briefing on impact of obesity as we age
2025-03-28
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) invites you to a congressional briefing:
Title: The Impact of Obesity and Opportunity for CMS to Address
When: Tuesday, April 1, from 12 to 1 p.m. ET
Where: Virtual
Click to RSVP
GSA is a professional membership organization committed to promoting the best available interdisciplinary aging research to advance innovations in practice and policy. This is especially key to managing the chronic condition of obesity in health care.
Older people with obesity and overweight require access to proven treatment options and care to improve overall health and reduce other related health care costs. ...
Professor receives pilot funding to conduct study to increase forest farming in Appalachia
2025-03-28
Appalachia is globally recognized as a key supplier of non-timber forest products (NTFPs) with growing demand for its resources. Nearly half of the woodland medicinal species in the global nutraceutical market come from the region, contributing to a multibillion-dollar industry.
Species such as ginseng, slippery elm, and black cohosh are prominent understory sources of medicinal material. Appalachian edible products are also gaining popularity beyond the region. Ramps, a wild Appalachian plant, can sell for more than $20 per pound in places such as New York City.
Spanning 205,000 square miles, Appalachia is home to over ...
New PET radiotracer provides first look at inflammation biomarker in the human brain
2025-03-28
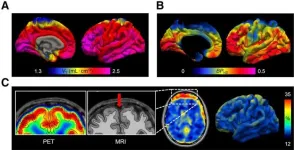
Reston, VA (March 28, 2025)—A novel PET imaging approach can effectively quantify a key enzyme associated with brain inflammation, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The first-in-human study, which imaged the COX-2 enzyme, offers a never-before-seen view of inflammation in the brain, opening the door for COX-2 PET imaging to be used in clinical and research settings for various brain disorders.
COX-2 is an enzyme in the brain that can be markedly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers say that the density of COX-2 in the brain may be a biomarker and effect of inflammation, ...
Genes may influence our enjoyment of music
2025-03-28
Music is central to human emotion and culture. Does our ability to enjoy music have a biological basis? A genetic twin study, published in Nature Communications, shows that music enjoyment is partly heritable. An international team led by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, uncovered genetic factors that influence the degree of music enjoyment, which were partly distinct from genes influencing general enjoyment of rewarding experiences or musical ability.
Music plays an important role in human emotion, social bonding, and cultural expression. As Darwin already noted, music "must ...
Global patterns in seed plant distribution over millions of years
2025-03-28
Why do some plants thrive in specific regions but not in others? A study led by researchers at the University of Göttingen explores the factors shaping plant distributions and how these patterns have changed over millions of years. Analyzing nearly 270,000 seed plant species worldwide, the research highlights the roles of environmental conditions and dispersal barriers in influencing global plant diversity. The results were published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
Using advanced methods that integrate plant distributions with phylogenetic information – meaning data about the evolutionary relationships among plant species – researchers ...
Fatty acids promote immune suppression and therapy resistance in triple negative breast cancer
2025-03-28
HOUSTON – (March 28, 2025) – A new study published in the journal Immunity reveals a mechanism that allows triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) to develop resistance to therapy. Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine showed that lipid accumulation in tumor cells and nearby immune cells promotes immune suppression, but disrupting lipid formulation reverses treatment resistance and the immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Standard-of-care treatment for TNBC includes chemotherapy and immunotherapy. However, some initially responsive tumors still develop recurrences. Researchers studied mouse models and found that TNBC cells that survived treatment accumulated ...
Intermittent fasting increases sex drive in male mice: an approach for low libido in humans?
2025-03-28
Long-term fasting in 24-hour cycles increases the sex drive of male mice by lowering the concentration of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain. This effect is linked to a diet-induced deficiency of the precursor substance tryptophan – an amino acid that must be obtained through food. Researchers from DZNE report on this in the journal Cell Metabolism, together with a Chinese team from Qingdao University and the University of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences. They suggest that similar mechanisms may exist in humans and view fasting as a potential approach for treating unwanted loss of sexual desire.
Fasting ...
Scientists create protein ‘seeds’ that trigger key pathological features of ALS and frontotemporal dementia
2025-03-28
28 March 2024, Leuven, Belgium — Accumulation of a protein called TDP-43 is a key feature of ALS and frontotemporal dementia. In a newly published study, researchers report ‘seeding’ this accumulation through fragments of the culprit protein created in the lab. The findings provide further evidence for a prion-like paradigm wherein protein aggregation occurs in a templated fashion. This breakthrough provides the research field with a powerful way to model and study the mechanisms driving neurodegeneration.
TAR DNA-binding ...
Discrimination-related depression, anxiety pronounced among multiracial, White, Asian populations
2025-03-28
EMBARGOED UNTIL 11 a.m. EST on Friday, March 28, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Discrimination-related Depression, Anxiety Pronounced Among Multiracial, White, Asian Populations
A new study found that more than half of US adults encounter some form of discrimination, and that this mistreatment may fuel higher chances of depression and/or anxiety among specific racial and ethnic groups due to cultural, social, and systemic factors.
A ...
New approach makes one type of clean fuel production 66% more efficient
2025-03-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers have uncovered a more efficient way to turn carbon dioxide into methanol, a type of alcohol that can serve as a cleaner alternative fuel.
In the lab, synthesizing methanol can be extremely difficult, due to the extremely complex reaction pathway needed to select for it. Previous attempts by the same team to manufacture this valuable liquid fuel from carbon dioxide have used a combination of cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPc) molecules and electricity, but this method is inefficient as only about 30% of the carbon dioxide is converted to methanol.
To ...
AI meets oncology: New model personalizes bladder cancer treatment
2025-03-28
Leveraging the power of AI and machine learning technologies, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine developed a more effective model for predicting how patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer will respond to chemotherapy. The model harnesses whole-slide tumor imaging data and gene expression analyses in a way that outperforms previous models using a single data type.
The study, published March 22 in npj Digital Medicine, identifies key genes and tumor characteristics that may determine treatment success. The ability to accurately anticipate ...
New approach could treat anthrax beyond the “point of no return”
2025-03-28
Anthrax, an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis, is often treatable in its early stages. But once the disease has progressed beyond the “point of no return” after just a few days, patients are almost certainly doomed.
In a new Nature Microbiology study, University of Pittsburgh researchers show that a cocktail of growth factors reversed would-be lethal cell damage in mice with anthrax, suggesting that this approach could be adapted for use in patients beyond the brink.
“While only a few people die from anthrax in the United States each year, there is always the concern ...
Those constantly distracted by their phone will just find other ways to procrastinate if it isn’t nearby
2025-03-28
If you just put away your phone to read this, chances are you’re not alone. Our phones are an endless source of distraction, and we interact with them every four to six minutes. This is often driven by habit as well as notifications, leading to a disrupted flow of activity while we’re trying to be productive.
A new study published in Frontiers in Computer Science investigated if placing smartphones just out of our reach while we’re at work influenced device use for activities not related ...
Ottoman Empire’s religious ‘tolerance’ another form of control
2025-03-28
Population surveillance. The carrying of identification while traveling. Add to that the public presence of diverse religions and it sounds like 2025, but this was life in the Ottoman Empire 200 years ago. Yet this seeming tolerance of non-Muslim faiths was in fact tied to the first two aspects, according to research by Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Masayuki Ueno.
The Ottoman Empire lasted from around 1300 until 1922, and at various points in its history ruled present-day Turkey, Egypt, Greece, Hungary, and beyond. In the wake of the 1821 Greek revolt, the Ottoman Empire instituted ...
Smartphone bans alone fail to equip children for healthy use of technology
2025-03-27
Banning smartphone and social media access alone fails to equip children for healthy use of technology, argues a group of international experts in The BMJ today.
They say the focus should shift to a rights based approach, underpinned by age appropriate design and education, that protects children from harm while developing skills to help them participate in a digital society.
Bans on smartphone and social media access have been advocated in many countries to protect children from harm despite ...
Discovery of novel small compounds that delay flowering in plants
2025-03-27
Ikoma, Japan—In an era where climate change threatens food security, scientists worldwide are searching for reliable ways to improve crop production. Extreme weather and shifting seasonal patterns can disrupt traditional agricultural cycles, making technologies that regulate the timing of plant growth invaluable for farmers worldwide.
Plant growth and development are dependent on many factors such as the environment, photoperiod, and genetics. Flowering is an important event in a plant’s life ...
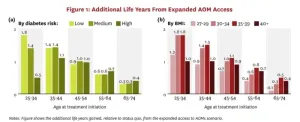
Expanding access to anti-obesity medications delivers 13% return on investment for society
2025-03-27
A new USC Schaeffer Center white paper finds expanded access to anti-obesity medications would lead to significant increases in life expectancy and disease-free years while generating a substantial societal return on investment, even after accounting for treatment costs.
More than 4 in 10 U.S. adults have obesity, which is linked to increased risk of over 200 diseases — including heart disease, diabetes, cancer and dementia — and costs society $260 billion annually to treat. Highly effective new anti-obesity medications can be a powerful tool against chronic disease, but fewer than one-third of health insurers cover them amid concerns about upfront ...
Genetic defense breakthrough: plants repurpose stomatal genes to fend off herbivores
2025-03-27
Ikoma, Japan—Throughout evolution, plants have continuously adapted to survive in changing environments. Apart from complex structural changes, plants have also developed various defense strategies against herbivores, including tougher protective layers, thorns, and chemical deterrents. Delving deeper into the evolution of defense mechanisms, a research team led by Assistant Professor Makoto Shirakawa from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), identified a surprising genetic adaptation in the Brassicales plant order. In these cruciferous ...
David B. Allison, Ph.D., Daniel W. Belsky, Ph.D., and Arlan Richardson, Ph.D., to receive 2025 Scientific Awards of Distinction from the American Federation for Aging Research
2025-03-27
New York, NY — The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR), is pleased to announce the 2025 recipients of three of its annual Scientific Awards of Distinction: David B. Allison, PhD, will receive the Irving S. Wright Award of Distinction; Daniel W. Belsky, PhD, will receive the Vincent Cristofalo Rising Star Award in Aging Research; and Arlan Richardson, PhD, will receive the George M. Martin Lifetime Achievement in Mentoring Award.
The Irving S. Wright Award of Distinction is named in honor of AFAR’s founder and recognizes exceptional contributions to basic ...
Pregnant women advised to avoid mentholated e-cigarettes
2025-03-27
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Vaping during pregnancy is becoming more common, but its impact on early human development is not well understood. A new study by scientists at the University of California, Riverside, now reports that the flavor chemical menthol used in electronic cigarettes could pose risks to a developing baby.
The study, published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, used human embryonic stem cells, or hESCs, to characterize early stages of embryonic development and examined how low concentrations of menthol affect important cellular processes.
The ...
[1] ... [602]
[603]
[604]
[605]
[606]
[607]
[608]
[609]
610
[611]
[612]
[613]
[614]
[615]
[616]
[617]
[618]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.