The hidden superconducting state in NbSe₂: shedding layers, gaining insights
2025-03-31
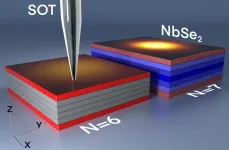
Researchers have discovered an unexpected superconducting transition in extremely thin films of niobium diselenide (NbSe₂). Published in Nature Communications, they found that when these films become thinner than six atomic layers, superconductivity no longer spreads evenly throughout the material, but instead becomes confined to its surface. This discovery challenges previous assumptions and could have important implications for understanding superconductivity and developing advanced quantum technologies.
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have made a surprising discovery about how superconductivity ...
New AI models possible game-changers within protein science and healthcare
2025-03-31
Researchers have developed new AI models that can vastly improve accuracy and discovery within protein science. Potentially, the models will assist the medical sciences in overcoming present challenges within, e.g. personalised medicine, drug discovery, and diagnostics.
In the wake of broadly available AI tools, most technical and natural sciences fields are advancing rapidly. This is particularly true in biotechnology, where AI models power breakthroughs in drug discovery, precision medicine, gene editing, food security, and many other research areas.
One sub-field is proteomics – the study of proteins on a large scale – where ...
Highly accurate blood test diagnoses Alzheimer’s disease, measures extent of dementia
2025-03-31
A newly developed blood test for Alzheimer’s disease not only aids in the diagnosis of the neurodegenerative condition but also indicates how far it has progressed, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Lund University in Sweden.
Several blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease are already clinically available, including two based on technology licensed from WashU. Such tests help doctors diagnose the disease in people with cognitive symptoms, but do not indicate the ...
Mind the seismic gap: Understanding earthquake types in Guerrero, Mexico
2025-03-31
Plate temperature and water release can explain the occurrence of different types of earthquakes in Guerrera, Mexico. The Kobe University simulation study also showed that the shape of the Cocos Plate is responsible for a gap where earthquakes haven’t occurred for more than a century. The results are important for accurate earthquake prediction models in the region.
Where one tectonic plate is pushed down by another, the resulting stress is released in various tectonic events. There are catastrophic megathrust earthquakes, unnoticeable “slow slip events,” and continuous low-frequency “tectonic tremors,” and knowing ...
One hour’s screen use after going to bed increases your risk of insomnia by 59%, scientists find
2025-03-31
Scientists have found another reason to put the phone down: a survey of 45,202 young adults in Norway has discovered that using a screen in bed drives up your risk of insomnia up by 59% and cuts your sleep time by 24 minutes. However, social media was not found to be more disruptive than other screen activities.
“The type of screen activity does not appear to matter as much as the overall time spent using screens in bed,” said Dr Gunnhild Johnsen Hjetland of the Norwegian Institute of Public Health, ...
Canada needs to support health research at home and abroad
2025-03-31
In the face of major changes to federal policy and funding in the United States, Canada should support Canadian researchers with adequate funding to ensure long-term research in health and science, argue authors in two articles published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
“As the US stands on the brink of tearing down its exemplary system for covering the full costs of research, Canada, with its flawed federal system for indirect costs, should heed the recent commissioned science policy report and a chorus of advocacy calling for an enhanced indirect cost system,” writes Dr. William Ghali, vice-president ...
Cannabis use disorder among insured pregnant women in the US between 2015-2020
2025-03-31
Cannabis use has been increasing during pregnancy, according to researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Previous research has observed that past-month cannabis use has more than tripled among pregnant women in the U.S. from 2002-2020 with self-reported cannabis use rising from 1.5 percent to 5.4 percent over the 18 years of tracking data. The findings are published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Medical guidelines recommend that pregnant women abstain from cannabis because of its link to an increased risk of adverse maternal ...
Education system needs overhaul to support school anxiety, psychologists say
2025-03-30
The UK education system must urgently change to be more understanding of school ‘refusers’, as returning to school might not be the right outcome for some children, psychologists say.
While much has been made of school attendance figures in recent months, a group of experts are suggesting not enough attention has been given to the experiences of parents and young people experiencing school distress.
In a new book, What Can We Do When School’s Not Working?, a parent and two ...
Play “humanizes” pediatric care and should be key feature of a child-friendly NHS – report
2025-03-30
Play should be a core feature of children’s healthcare in forthcoming plans for the future of the NHS, according to a new report which argues that play “humanises” the experiences of child patients.
The report, by University of Cambridge academics for the charity Starlight, calls for play, games and playful approaches to be integrated into a ‘holistic’ model of children’s healthcare – one that acknowledges the emotional and psychological dimensions of good health, ...
Stricter oversight needed as financial misconduct drives risk-taking in banking
2025-03-30
Banks facing regulatory sanctions for financial misconduct tend to adopt riskier business practices, according to new research.
The authors warn repeated or systemic misconduct can accelerate risk-taking in ways that weaken both individual institutions and the wider financial system.
Researchers from the University of East Anglia (UEA), the US Department of the Treasury and Bangor University, in the UK, drew on data from nearly 1,000 publicly listed US banks from 1998 to 2023 - a period spanning multiple economic cycles including the 2007–09 ...
Cardiac arrest during long-distance running races
2025-03-30
About The Study: This study found that despite increased participation in U.S. long distance running races, the incidence of cardiac arrest during U.S. marathons and half-marathons remains stable. There has been a marked decline in cardiac arrest mortality, and coronary artery disease was the most common etiology among cases with sufficient cause-related data. Effective emergency action planning with immediate access to defibrillation may explain the improvement in survival.
Corresponding Authors: To ...
Preventable cardiac deaths during marathons are down, Emory study finds
2025-03-30
While more people than ever are running marathons in the U.S., the risk of dying from a heart attack during a run has fallen dramatically in recent years. That’s a key conclusion from a new study by Jonathan Kim, associate professor in the Emory School of Medicine. Kim’s research is a follow-up to a study he published in 2012 – the first investigation into unexpected cardiac arrests during long distance running events.
The new findings, published in JAMA, indicate that while the rate of marathon runners who suffer cardiac arrests remained unchanged, their chance for survival is twice what it was in the ...
New study finds peripheral artery disease often underdiagnosed and undertreated; opportunity to improve treatments, lower death rates
2025-03-30
A new Intermountain Health study finds that peripheral artery disease, a condition that affects more than 10 million Americans over the age of 40, is often underdiagnosed and undertreated, with fewer women getting guideline-directed medical therapy than men.
As a result, combined with this highly debilitating disease, patients with peripheral artery disease have a more than 50 percent chance of dying from the condition.
Peripheral artery disease affects nearly 10 percent of the US population. It occurs when the arteries that carry blood to the legs and arms become narrowed or blocked by plaque ...
Use of antidepressant medication linked to substantial increase in risk of sudden cardiac death
2025-03-30
Vienna, Austria- 30 March 2025
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) refers to an unexpected death of a person, believed to be caused by a heart-related issue. It occurs within one hour of the onset of symptoms in witnessed cases or within 24 hours of the person being last seen alive in unwitnessed cases.
The causes in people under the age of 39 are often a thickening of the heart muscle or an electrical problem with the heart. In older people, SCD is more likely to be caused by a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply the heart.
Previous research has shown1 that patients with psychiatric disorders have an increased all-cause mortality ...
Atrial fibrillation diagnosed in midlife is linked to a 21% increased risk of dementia at any age and a 36% higher risk of early-onset dementia
2025-03-30
Vienna, Austria- 31 March 2025
New research presented at the EHRA 2025, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology, shows that the presence of atrial fibrillation (AF) increases the risk of future dementia by 21% in patients diagnosed with AF under 70 and the risk of early-onset dementia (diagnosed before age 65 years) by 36%. The association was stronger in younger adults and was lost in older adults aged 70 years and over.
“This is the largest European population-based study evaluating the association between AF and dementia,” say the authors that include Dr Julián Rodriguez ...
Mode of death in patients with heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction
2025-03-30
About The Study: Among patients with heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction/heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the Finerenone Trial to Investigate Efficacy and Safety Superior to Placebo in Patients With Heart Failure randomized clinical trial, higher proportions of cardiovascular and overall mortality in those with ejection fraction less than 50% were related principally to higher proportions of sudden death. A clear treatment effect of finerenone on cardiovascular or cause-specific mortality was not identified, although the trial was likely underpowered for these outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Akshay S. Desai, ...
Intravenous ferric carboxymaltose in heart failure with iron deficiency
2025-03-30
About The Study: In patients with heart failure and iron deficiency, ferric carboxymaltose did not significantly reduce the time to first heart failure hospitalization or cardiovascular death in the overall cohort or in patients with a transferrin saturation less than 20%, or reduce the total number of heart failure hospitalizations vs placebo.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Stefan D. Anker, MD, PhD, email s.anker@cachexia.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2025.3833)
Editor’s ...
Artificial intelligence in the prevention of sudden death
2025-03-30
Many cases of sudden cardiac death could be avoided thanks to artificial intelligence. As part of a new study to be published in European Heart Journal, a network of artificial neurons imitating the human brain was developed by researchers from Inserm, Paris Cité University and the Paris public hospitals group (AP-HP), in collaboration with their colleagues in the USA. During the analysis of data from over 240 000 ambulatory electrocardiograms, this algorithm identified patients at risk of a serious arrhythmia that was capable of triggering cardiac arrest within the following 2 weeks in over 70% of cases.
Each ...
Oral semaglutide vastly reduces heart attacks, strokes in people with type 2 diabetes
2025-03-29
Both the injectable and oral forms of semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, have gained recent attention for their effectiveness against weight gain, high blood sugar, and even alcohol cravings.
A new clinical trial, co-led by endocrinologist and diabetes expert John Buse, MD, PhD, and interventional cardiologist Matthew Cavender, MD, MPH, at the UNC School of Medicine has shown that the oral form of semaglutide can significantly reduce cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and/or ...
Prothrombin complex concentrate vs frozen plasma for coagulopathic bleeding in cardiac surgery
2025-03-29
About The Study: In this unblinded randomized clinical trial, prothrombin complex concentrate had superior hemostatic efficacy and safety advantages to frozen plasma among patients requiring coagulation factor replacement for bleeding during cardiac surgery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Keyvan Karkouti, MD, email keyvan.karkouti@uhn.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2025.3501)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Who needs a statin? New study compares prescribing recommendations based on traditional risk factors vs. coronary artery calcium scoring
2025-03-29
A new study by researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City aims to determine the best method to screen and evaluate patients who are at risk of developing coronary heart disease and which patients would benefit from taking a statin medication to lower cholesterol.
Currently, cardiologists determine a patient’s need for a statin based on traditional risk factors, using the Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE), which calculates coronary risk by assessing the risk factors of age, sex, total and HDL cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and whether someone ...
Finerenone and atrial fibrillation in heart failure
2025-03-29
About The Study: The efficacy of finerenone was consistent regardless of atrial fibrillation status in this study. New-onset atrial fibrillation was associated with a substantially higher risk of subsequent outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, John J. V. McMurray, MD, email john.mcmurray@glasgow.ac.uk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2025.0848)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Low coronary artery calcium score is associated with an excellent prognosis regardless of a person’s age, new study finds
2025-03-29
Having a coronary artery calcium (CAC) score of zero has generally been accepted as a marker of a very low risk of having a cardiac event within the next five years. However, age is a strong contributor to coronary risk, with risk increasing markedly as people age.
Whether age-related risk factors diminish the low risk predicted by a zero coronary artery calcium score has been uncertain – until now.
A large new study of more than 40,000 patients from heart researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City finds that a zero coronary artery calcium score continues to be an accurate indicator of a low risk for a coronary ...
Groundbreaking consensus statement on conduction system pacing released: a major milestone in the evolution of pacing therapy
2025-03-29
Vienna, 30 March 2025– The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) has released a groundbreaking consensus statement on conduction system pacing (CSP), marking a significant milestone in the evolution of pacing therapy. The document was officially presented today at the EHRA 2025 congress in Vienna and simultaneously published in EP Europace.
For over 50 years, right ventricular pacing has been a standard treatment for slow heart rhythms. However, in some patients, this approach can lead to reduced heart function and even heart failure. Furthermore, biventricular pacing ...
Nuclear monitoring system suggests landslide cut off internet in west Africa
2025-03-29
Hydroacoustic signals captured by the world’s international nuclear monitoring system suggest an underwater landslide may have broken communications cables and disrupted internet traffic in west African countries for several weeks in March 2024.
Researchers used data collected by hydrophones installed by the International Monitoring System of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO) to determine the location of the possible landslide, placing it along the steep slopes of Trou Sans Fond Canyon offshore of Ivory Coast.
The proposed landslide corresponds with the timing and location of four broken cables in the canyon, according to Vaibhav Vijay Ingale of UC ...
[1] ... [600]
[601]
[602]
[603]
[604]
[605]
[606]
[607]
608
[609]
[610]
[611]
[612]
[613]
[614]
[615]
[616]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.