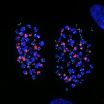
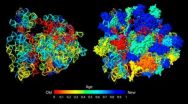
Sending out an SOS: How telomeres incriminate cells that can't divide
2012-03-13
LA JOLLA, CA----The well-being of living cells requires specialized squads of proteins that maintain order. Degraders chew up worn-out proteins, recyclers wrap up damaged organelles, and-most importantly-DNA repair crews restitch anything that resembles a broken chromosome. If repair is impossible, the crew foreman calls in executioners to annihilate a cell. As unsavory as this last bunch sounds, failure to summon them is one aspect of what makes a cancer cell a cancer cell.
A recent study from scientists at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies showed exactly how ...
Gaffney Hotel Lets Guests Earn More Points From Hilton HHonors
2012-03-13
The Hampton Inn Gaffney Hotel is offering a special promotion that lets guests earn more points from Hilton HHonors . Travelers who sign up for the More Points promotion will earn 1,000 Bonus Points per night plus 5,000 Bonus Points for every weekend stay for two nights or more for stays now through March 31, 2012. Special offers and rates are subject to availability; some restrictions may apply.
Among other Gaffney South Carolina hotels, the Hampton Inn Gaffney is a leading place to stay in the area. The property's features and amenities include:
- Free hot breakfast ...
Why do we see the man in the moon?
2012-03-13
There's something poetic about gazing up at the night sky, seeing the familiar face of the "Man in the Moon" who faithfully accompanies us through life. The synchronous rotation of the Moon taking the same amount of time to spin around its own axis as it does to revolve around Earth is what causes the Moon to "lock eyes" with Earth, resulting in one of its hemispheres constantly facing us. But is there a reason why this particular half of the Moon locked with Earth, or was it pure coincidence that it didn't "turn its back" on us?
Through careful analysis and simulations, ...
US citizenship may be determined at random
2012-03-13
The fate of nearly half a million immigrants hoping for U.S. citizenship may have been determined randomly, at least in part, according to a new study by a Michigan State University researcher who found the high-stakes civics test isn't a reliable measure of civics knowledge.
To be awarded citizenship, immigrants must correctly answer six of 10 questions on the verbally administered civics portion of the U.S. Naturalization Test, said Paula Winke, assistant professor of second language studies.
Questions are randomly selected by an immigration officer from a pool of ...
Super 8 Monroe NC Hotel Offers Close Lodging for Guests Attending Top Scholars Day at Wingate University
2012-03-13
Super 8 Monroe NC Hotel offers convenient lodging to students and their parents attending upcoming Top Scholars Days at Wingate University. The events will take place on campus March 17, 2012 and April 21, 2012; reservations are required. Top Scholars Day was created for admitted students to have the opportunity to chat with current students and professors at Wingate University. Attending students may compete for free tuition in the Tweet for Tuition Challenge.
"Situated only 5 miles from the school, our hotel near Wingate University is looking forward to welcoming ...
Researchers discover mechanism in cells that leads to inflammatory diseases
2012-03-13
Los Angeles, March 12, 2012 – Cedars-Sinai researchers have unlocked the mystery of how an inflammatory molecule is produced in the body, a discovery they say could lead to advances in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Type 2 diabetes and numerous other chronic diseases that affect tens of millions of people.
The study, funded by the National Institutes of Health, is published online by the peer-reviewed journal Immunity and will appear in the March print edition.
The researchers identified for the first time the mechanism that leads to the production of the ...
Study of ribosome evolution challenges 'RNA World' hypothesis
2012-03-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In the beginning – of the ribosome, the cell's protein-building workbench – there were ribonucleic acids, the molecules we call RNA that today perform a host of vital functions in cells. And according to a new analysis, even before the ribosome's many working parts were recruited for protein synthesis, proteins also were on the scene and interacting with RNA. This finding challenges a long-held hypothesis about the early evolution of life.
The study appears in the journal PLoS ONE.
The "RNA world" hypothesis, first promoted in 1986 in a paper in the ...
Common North American frog identified as carrier of deadly amphibian disease
2012-03-13
AUDIO:
This is an audio recording of the distinctive "ribbit " call of the Pacific chorus frog (28 seconds long, MP3 file, WAV file available on request).
This noisy frog is a potent...
Click here for more information.
Known for its distinctive "ribbit" call, the noisy Pacific chorus frog is a potent carrier of a deadly amphibian disease, according to new research published today in the journal PLoS ONE. Just how this common North American frog survives chytridiomycosis ...
March/April 2012 Annals of Family Medicine tip sheet
2012-03-13
Four articles in the current issue draw attention to policy initiatives and implications of the rapidly changing U.S. health care environment. Collectively, they examine some of the challenges and opportunities facing the country following the 2010 passage of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act.
Researchers Project Cost of Family Health Insurance Premiums Will Surpass Household Income by 2033
Updating estimates of who will be able to afford health insurance in the future in light of the 2010 Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act that reformed health ...
Diacetylmorphine for opioid addiction cheaper and more effective than methadone
2012-03-13
Using injectable diacetylmorphine — the active ingredient in heroin — to treat chronic opioid addiction is cheaper and more effective than methadone, states an article in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Methadone is the most common treatment for people who are dependent on opioids such as heroin, although research indicates that most people over time go back to using illicit drugs. The North American Opiate Medication Initiative, a randomized controlled trial, indicated that diacetylmorphine is more effective in keeping opioid-dependent people in treatment. ...
Largest ever study of childhood ALL shows improving survival
2012-03-13
A 21,626-person study published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that the five-year survival rate for children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood cancer, improved from 83.7 percent in those diagnosed during the years 1990-1994, to 90.4 percent for those diagnosed in the years 2000-2005.
"The improved survival is due to using existing drugs better, not because of the introduction of new drugs. We're indebted to all the families who choose to join these clinical trials, allowing us to optimize these combinations," ...
Extensive taste loss in mammals
2012-03-13
PHILADELPHIA (March 12, 2012) – Scientists from the Monell Center report that seven of 12 related mammalian species have lost the sense of sweet taste. As each of the sweet-blind species eats only meat, the findings demonstrate that a liking for sweets is frequently lost during the evolution of diet specialization.
Previous research from the Monell team had revealed the remarkable finding that both domestic and wild cats are unable to taste sweet compounds due to defects in a gene that controls structure of the sweet taste receptor.
Cats are obligate carnivores, meaning ...
Medically prescribed heroin more effective, less costly than current methadone treatment
2012-03-13
Medically prescribed heroin is more cost-effective than methadone for treating long-term street heroin users, according to a new study by researchers at Providence Health Care and the University of British Columbia.
The study, published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal (CMAJ), attributed most of the economic benefits to the fact that recipients of medically prescribed heroin (diacetylmorphine) stayed in treatment longer and spent less time in relapse than those receiving methadone. Both results are associated with reduced criminal activity and lower health ...
Major study stops bladder cancer from metastasizing to lungs
2012-03-13
The diagnosis of localized bladder cancer carries an 80 percent five-year survival rate, but once the cancer spreads, the survival rate at even three years is only 20 percent. A major study published today in the Journal of Clinical Investigation not only shows how bladder cancer metastasizes to the lungs but pinpoints a method for stopping this spread.
Specifically, the study shows that versican, a protein involved in cancer cell migration, is a driver of lung metastasis and that high levels of versican are associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer patients. The ...
JCI early table of contents for March 12, 2012
2012-03-13
EDITOR'S PICK
Restoring what's lost: uncovering how liver tissue regenerates
The liver is unique among mammalian organs in its ability to regenerate after significant tissue damage or even partial surgical removal. Laurie DeLeve and her colleagues at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles wanted to better understand which cells are specifically responsible for driving liver regeneration. A specialized cell type, known as liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, has generally been thought to promote regeneration of liver tissue. However, the DeLeve team suspected ...
Craftmark Countertops Points Out that Granite is Still a Bargain
2012-03-13
Granite countertops in Atlanta have a lot of competition these days with the popularity of concrete, recycled glass, soapstone, quartz, and a host of other surfaces gaining ground in the Atlanta countertops market. However, Craftmark Countertops in Atlanta points out that the look and longevity of Atlanta granite countertops is comparable to the other surfaces and often a fraction of the cost.
With its rise in popularity over the last decade, granite is no longer a surface of exclusivity, and so some higher end homes are being built with other more expensive surfaces. ...
Restoring what's lost: Uncovering how liver tissue regenerates
2012-03-13
The liver is unique among mammalian organs in its ability to regenerate after significant tissue damage or even partial surgical removal. Laurie DeLeve and her colleagues at the University of Southern California in Los Angeles wanted to better understand which cells are specifically responsible for driving liver regeneration. A specialized cell type, known as liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, has generally been thought to promote regeneration of liver tissue. However, the DeLeve team suspected that stem cells and progenitor cells, which have the capacity to differentiate ...
Sugar-sweetened drinks linked to increased risk of heart disease in men
2012-03-13
Men who drank a 12-ounce sugar-sweetened beverage a day had a 20 percent higher risk of heart disease compared to men who didn't drink any sugar-sweetened drinks, according to research published in Circulation, an American Heart Association journal.
"This study adds to the growing evidence that sugary beverages are detrimental to cardiovascular health," said Frank B. Hu, M.D., Ph.D., study lead author and professor of nutrition and epidemiology in the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston, Mass. "Certainly, it provides strong justification for reducing sugary beverage ...
Red meat consumption linked to increased risk of total, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality
2012-03-13
Boston, MA -- A new study from Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) researchers has found that red meat consumption is associated with an increased risk of total, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality. The results also showed that substituting other healthy protein sources, such as fish, poultry, nuts, and legumes, was associated with a lower risk of mortality.
The study will be published online in Archives of Internal Medicine on March 12, 2012.
"Our study adds more evidence to the health risks of eating high amounts of red meat, which has been associated with type ...
More red meat consumption appears to be associated with increased risk of death
2012-03-13
CHICAGO – Eating more red meat appears to be associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality and death from cardiovascular disease and cancer, but substituting other foods including fish and poultry for red meat is associated with a lower mortality risk, according to a study published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Meat is a major source of protein and fat in many diets and previous studies suggest that eating meat is associated with increased risk for diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD) and certain cancers, ...
Prescribing opioids for pain after short-stay surgery appears associated with long-term use
2012-03-13
CHICAGO – Prescribing opioids for pain to older patients within seven days of short-stay surgery appears to be associated with long-term analgesic use compared to those patients who did not receive prescriptions for analgesics after surgery, according to a study published in the March 12 issue of Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Patients are frequently prescribed analgesics after ambulatory or short-stay surgery in anticipation of postoperative pain and the most common analgesics prescribed to outpatients are opioids (such as codeine and ...
Statin use appears associated with modest reduction in Parkinson's disease risk
2012-03-13
CHICAGO – Regular use of cholesterol-lowering statin drugs may be associated with a modest reduction in risk for developing Parkinson disease, particularly among younger patients, according to a study in the March issue of Archives of Neurology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Statins are one of the most prescribed classes of drugs in the United States and some researchers have hypothesized that the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating effects of these medications may be neuroprotective. However, statins also may have unfavorable effects on lowering the level of ...
Routine glaucoma screening program may benefit middle-age African-American patients
2012-03-13
CHICAGO – Implementing a routine national glaucoma screening program for middle-age African American patients may be clinically effective; however its potential effect on reducing visual impairment and blindness may be modest, according to a computer-based mathematical model reported in the March issue of Archives of Ophthalmology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
"Primary open-angle glaucoma is a chronic, degenerative disease that affects more than 2.2 million Americans and 1.9 percent of Americans older than 40 years," the authors write as background in the study. ...
Behavioral intervention appears to improve outcomes among socioeconomically disadvantaged patients
2012-03-13
CHICAGO – A behavioral intervention program appears to be associated with modest weight loss and improved blood pressure control in a high-risk, socioeconomically disadvantaged group of obese patients, according to a study published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Obesity is not sufficiently addressed in the U.S. primary care system and socioeconomically disadvantaged patients who seek care at community health centers are particularly affected by the limited availability of obesity treatments, the authors write in their ...
Personal mobile computing increases doctors' efficiency
2012-03-13
Providing personal mobile computers to medical residents increases their efficiency, reduces delays in patient care and enhances continuity of care, according to a "research letter" in the March 12, 2012, issue of the Archives of Internal Medicine.
In November 2010, the University of Chicago Medicine became the first hospital in the country to provide residents with tablet computers on a large scale, supplying iPads to all 115 residents in internal medicine. When surveyed in 2011, more than three out of four of the residents reported that the portable computers allowed ...
[1] ... [6685]
[6686]
[6687]
[6688]
[6689]
[6690]
[6691]
[6692]
6693
[6694]
[6695]
[6696]
[6697]
[6698]
[6699]
[6700]
[6701]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.