A new approach for breaking plastic waste down to monomers
2025-02-20
Researchers have reported a method for breaking down commercial polymers like Plexiglass into monomers, a form more desirable for reuse. This could help alleviate the growing plastic waste stream. Most current plastic recycling methods rely on macroscopic mechanical shredding, cleaning and reprocessing. As a result, the properties degrade relative to the virgin polymer. Chemical decomposition to the original monomer would enable more thorough purification and then repolymerization to restore ideal performance. Here, Hyun Suk Wang and colleagues report the discovery that in dichlorobenzene solvent, violet light irradiation ...
High-performance computing at a crossroads
2025-02-20
High-performance computing (HPC) systems – advanced computing ensembles that harness deliver massive processing power – are used for a range of applications, and the demand for them has increased with the rise of generative artificial intelligence (AI). However, for both traditional uses and to advance the power of AI, technical advances in HPC are greatly needed, say Ewa Deelman and colleagues in a Policy Forum. “With international competition for leadership in computing intensifying, without a renewed commitment, ...
Chemists find greener path to making key industrial chemical
2025-02-20
Scientists have discovered a potentially greener way to produce a crucial industrial chemical used to make many everyday products from plastics and textiles to antifreeze and disinfectants, according to a new study published in Science and co-authored by Tulane University chemical engineer Matthew Montemore.
The breakthrough could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the manufacture of ethylene oxide, which has an estimated $40 billion global market. The current production process requires chlorine, which is toxic and ...
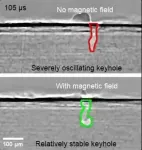
Giant X-ray facility shows that magnets can reduce flaws in 3D printed components
2025-02-20
Safety critical components for aircraft and Formula 1 racing cars could one day be 3D printed via a new technique, developed by researchers at UCL and the University of Greenwich, that substantially reduces imperfections in the manufacturing process.
The technique was developed after the team used advanced X-ray imaging to observe the causes of imperfections that formed in complex 3D printed metal alloy components. If this technique becomes widely deployed it could make a range of these components, from artificial hip joints to aircraft parts, stronger and more durable.
The study, published in Science, observes the forces at play during ...
Cooling materials – Out of the 3D printer
2025-02-20
Rapid, localized heat management is essential for electronic devices and could have applications ranging from wearable materials to burn treatment. While so-called thermoelectric materials convert temperature differences to electrical voltage and vice versa, their efficiency is often limited, and their production is costly and wasteful. In a new paper published in Science, researchers from the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) used a 3D printing technique to fabricate high-performance thermoelectric materials, reducing production costs significantly.
Thermoelectric coolers, also called solid-state ...
New knowledge portal adiposetissue.org enhances obesity and metabolism research with centralized data
2025-02-20
Addressing the Challenge of Dispersed Data
For years, adipose tissue research has generated vast amounts of omics data, but these datasets remained scattered across different repositories, making comprehensive analysis challenging. Adiposetissue.org now brings insights together, integrating transcriptomic and proteomic with clinical data from more than 6,000 individuals, enabling researchers to explore obesity-related changes, weight-loss effects, and cellular mechanisms with unprecedented depth.
“We developed ...
Study suggests new molecular strategy for treating fragile X syndrome
2025-02-20
Building on more than two decades of research, a study by MIT neuroscientists at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory reports a new way to treat pathology and symptoms of fragile X syndrome, the most common genetically-caused autism spectrum disorder. The team showed that augmenting a novel type of neurotransmitter signaling reduced hallmarks of fragile X in mouse models of the disorder.
The new approach described in Cell Reports works by targeting a specific molecular subunit of “NMDA” receptors that they discovered plays a key role in how neurons synthesize ...
Digging into a decades-old hepatitis B mystery suggests a new potential treatment
2025-02-20
In their effort to answer a decades-old biological question about how the hepatitis B virus (HBV) is able to establish infection of liver cells, research led by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), Weill Cornell Medicine, and The Rockefeller University identified a vulnerability that opens the door to new treatments.
The team successfully disrupted the virus’s ability to infect human liver cells in the laboratory using a compound already in clinical trials against cancer — laying the ...
Big birds like emus are technical innovators, according to University of Bristol researchers
2025-02-20
Large birds – our closest relations to dinosaurs - are capable of technical innovation, by solving a physical task to gain access to food.
This is the first time scientists have been able to show that palaeognath birds such as emus and rheas can solve tricky problems.
In the study, published today in Scientific Reports, emus, which have previously been called the ‘world’s dumbest bird’ were able to create one new technique to access food (lining up a hole with a food chamber) and moved the hole in the most efficient direction towards food in 90% of cases. A male rhea ...
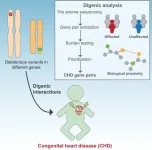
Hidden genetic causes of congenital heart disease identified
2025-02-20
New York, NY [February 20, 2025]—Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and collaborators have identified novel genetic interactions that may contribute to congenital heart disease (CHD), a common birth defect. Details on their findings were reported in the February 20 online issue of The American Journal of Human Genetics [DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2025.01.024].
“Our research reveals the potential for digenic inheritance—where two genes work together to cause disease—expanding our understanding of the genetic underpinnings of congenital heart ...
Semaglutide and nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
2025-02-20
About The Study: The results of this study suggest a modest increase in the risk of nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy among individuals with type 2 diabetes associated with semaglutide use, smaller than that previously reported, and warranting further investigation into the clinical implications of this association.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Cindy X. Cai, MD, MS, email ccai6@jhmi.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.6555)
Editor’s ...
Inequities in the application of behavioral flags for hospitalized pediatric patients
2025-02-20
About The Study: This cohort study found significant inequities in incidence of behavioral flags in the electronic health record among racially and socioeconomically marginalized pediatric patients. This finding was most pronounced for Black or African American patients younger than 8 years, suggesting that this phenomenon may be a response to Black families rather than specific patient behavior.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, April Edwell, MD, MAEd, email April.edwell@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.61079)
Editor’s ...
Paxlovid’s impact on hospitalization and death in COVID-vaccinated older adults far weaker than previously thought
2025-02-20
Paxlovid does not significantly reduce COVID-19 hospitalization and mortality among vaccinated older adults, according to new UCLA-led research.
The study questions the assumption that Paxlovid’s effectiveness in reducing COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths in unvaccinated adults also applies to vaccinated adults. Pfizer’s 2022 clinical trial found reduced COVID-19 hospitalization in unvaccinated middle-aged adults; while a subsequent 2024 clinical trial found no significant reduction in vaccinated middle-aged adults. Since most older Americans have already received two or more COVID-19 vaccines, Paxlovid’s effectiveness on vaccinated ...
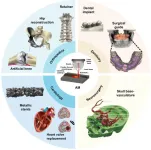
Additive manufacturing of biomedical metals for medical implant fabrication
2025-02-20
Biomedical metal implant materials are widely used in clinical applications, including dental implants, hip replacement, bone plates, and screws. However, traditional manufacturing processes face limitations in meeting customized medical needs, internal structural control, and efficient material utilization. For example, when producing complex-shaped titanium alloy parts using conventional methods, the material consumption ratio is as high as 10:1-20:1, leading to significant material waste.
As a result, ...
Antioxidant-enzyme Interaction in non-communicable diseases
2025-02-20
Introduction
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant defenses, plays a central role in the development of non-communicable diseases (NCDs). These diseases, including cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, neurodegenerative conditions, cancer, and liver and kidney diseases, are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants serve as the body’s primary defense against ROS, maintaining redox homeostasis and preventing cellular damage. However, when ROS levels exceed the capacity of antioxidant defenses, oxidative stress ensues, contributing ...
Turtles change nesting patterns in response to climate change
2025-02-20
New research shows that turtles are responding to climate change by nesting earlier.
Researchers monitoring nesting green and loggerhead turtles in Cyprus have discovered they are returning to their regular nesting spots earlier each year to compensate for rising temperatures.
In sea turtles, temperature determines the biological sex of offspring, with more females born when it is warmer, as well as fewer successful hatchings when it gets too hot.
Turtles also have “natal philopatry”, which means they return to nest in the area where they themselves hatched.
A research team from the University of Exeter and the Society for the Protection of ...
New research links grape consumption to improved muscle health in both men and women
2025-02-20
A new study from Western New England University (WNE) has revealed that long-term grape consumption significantly impacts muscle health, with notable benefits for both men and women. The research, published in the journal Foods, suggests that a diet including grapes can modify gene expression in muscle, potentially offering a new nutritional strategy for maintaining muscle mass and function.
Around 30 million tons of grapes are consumed every year, and their benefits extend beyond nutrition. Grapes have been shown to ...
Both sides of the coin: Lack of consensus on continuing vs. discontinuing opioid medications prescriptions for adults with chronic pain
2025-02-20
INDIANAPOLIS – Chronic pain is complex and difficult to treat. Prescribing opioid pain medications has become controversial but may help some patients.
With the goal of informing clinician practice, a new study explores the harms and benefits of continuing and of discontinuing the long-term prescription of opioid medicines to adults with chronic pain. The authors analyzed the opinions of 28 experts on the harms versus benefits of maintaining, tapering or terminating opioid pain medication prescriptions ...
National Academy of Inventors welcomes 162 emerging inventors
2025-02-20
The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) has announced the 2025 class of Senior Members, comprised of 162 emerging inventors from NAI’s Member Institutions. This year’s class of NAI Senior Members is the largest to date and hails from 64 NAI Member Institutions across the nation. Collectively, they are named inventors on over 1200 U.S. patents.
“To see this program grow year over year is a testament to the dedication our Member Institutions have to fostering innovation on their campuses and supporting their inventive staff ...
Narcissists more likely to feel ostracized
2025-02-20
Narcissists feel ostracized more frequently than their less self-absorbed peers, according to research published by the American Psychological Association. This may stem not only from being shunned due to their personalities but from a tendency to misinterpret ambiguous social signals as exclusion.
“Feeling ostracized is a subjective experience based on the perception of social cues by the individual. Some may be intentionally ostracized, while others may merely believe they are being excluded when that’s not the case,” said lead author Christiane Büttner, PhD, of the University of Basel. “Our findings suggest that ...
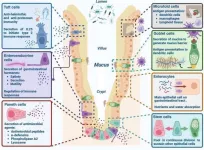
Unfolded protein response: A key regulator of intestinal health and disease
2025-02-20
The intestinal epithelium is a highly dynamic barrier that regulates digestion, absorption, immune responses, and communication between the gut microbiota and the nervous system. To maintain homeostasis, intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) must efficiently manage protein production and secretion, a process tightly controlled by the unfolded protein response (UPR).
New research published in eGastroenterology demonstrates that disruptions in the UPR contribute to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), colorectal cancer, and other gut-related disorders. This highlights potential therapeutic strategies to restore ...
Small amounts of moderate to vigorous physical activity are associated with big reductions in dementia risk
2025-02-20
A little movement could help prevent dementia, even for frail older adults, suggests a new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The researchers found that engaging in as little as 35 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week, compared to zero minutes per week, was associated with a 41% lower risk of developing dementia over an average four-year follow-up period. Even for frail older adults—those at elevated risk of adverse health outcomes—greater activity was associated with lower dementia risks.
The ...
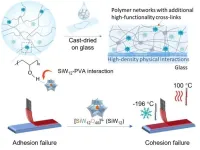
Enhancing adhesive performance of polyvinyl alcohol with sub-nanoscale polyoxotungstate clusters under extreme conditions
2025-02-20
Water-based adhesives face several challenges despite their environmental benefits. One major issue is that achieving high adhesion strength on various substrates, especially in wet or humid conditions, is difficult due to the inherent properties of water-based systems. Additionally, the volatility of water also leads to issues like bubble formation and uneven drying, affecting the adhesive's performance and appearance. Moreover, formulating water-based adhesives with both high solids content and low viscosity is technically demanding, ...
Recognizing the evolution of clinical syndrome spectrum progression in individuals with single large-scale mitochondrial DNA deletion syndromes (SLSMDS))
2025-02-20
Philadelphia, February 20, 2025 – Researchers from the Mitochondrial Medicine Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have better characterized a spectrum of what were classically considered discrete mitochondrial DNA deletion disease syndromes. The findings offer new insights into genetic causes, potential symptoms, and disease progression, and may inform future clinical trial development. The findings were published today in the journal Genetics in Medicine.
Mitochondrial disease refers to a group of disorders that affect the mitochondria, which are tiny compartments present in almost every cell of the body that ...
Another way longer paternity leaves help new parents
2025-02-20
A longer paternity leave after the birth of a child can improve the co-parenting relationship between moms and dads in a key way, a new study finds.
Researchers found that mothers were less likely to discourage fathers’ involvement in parenting if the dads had taken more time off after their child was born.
“When fathers take longer leaves, mothers might take that as a sign that fathers are more interested in being an active parent and be less likely to try to prevent them from participating in child care,” said Reed Donithen, ...
[1] ... [662]
[663]
[664]
[665]
[666]
[667]
[668]
[669]
670
[671]
[672]
[673]
[674]
[675]
[676]
[677]
[678]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.