The best way to market fine wine: Teach and learn or wine and dine?
2011-11-23
Los Angeles, CA (November 22, 2011)) According to new research, wine promoters may want to spend more money on brochures and flyers and less money on wine tastings as they market to novice wine drinkers. A recent study published in Cornell Hospitality Quarterly (a SAGE journal) finds that without teaching about the background and process of wine production, new wine drinkers can be more easily influenced by advertising to make their purchases than their experienced counterparts.
Authors Kathryn A. LaTour, Michael S. LaTour, and Andrew H. Feinstein wrote that while the ...
Mindomo Presenter - The First Real Presentation Mode for Mind Maps
2011-11-23
Expert Software Applications announced today the immediate availability of Mindomo Presenter - a radical new way to present Mind Maps online and offline. The strength of Mind Maps comes from their brain-friendly hierarchical structure. However, that strength is also a weakness when it comes to sharing a mind map.
"A mind map has a single starting point and it has multiple ending points, it has no single path which will guide you trough every idea in a mind map. When creating a mind map there is no way to include a guidance to viewers which would make it easy to ...
Nomorerack.com Offers Incredible Deals Black Friday to Cyber Monday
2011-11-23
Nomorerack (www.nomorerack.com) celebrates the largest shopping day of the year with a huge Black Friday through Cyber Monday Sale. The online discount shopping and daily deal site is taking Black Friday to new heights with a sale that lasts through the weekend and into Cyber Monday, starting at 12:00 AM EST November 25th through the 28th.
Instead of the traditional 8 deals announced each day offering members up to 90% MSRP on today's hottest products, the weekend sale will unveil 90 deals every single day. This Black Friday sale will also feature surprise doorbuster ...
Invaluable Information for UK Expatriates at Europe-Wide Seminars
2011-11-23
The sessions are aimed at informing British expatriates of ways to build and maximum their wealth, and to share vital information regarding new laws for UK citizens overseas.
Invaluable advice and knowledge is to be offered by independent financial experts in several key destinations in Spain, Switzerland, Germany, Luxembourg, France, and Belgium.
deVere Group Director, Mike Coady, says the seminars are part of the Group's global commitment to reaching clients wherever they are in the world. "With the worldwide economic situation as it is, it's more important ...
Evolutionary practices in schools can benefit at-risk students
2011-11-22
BINGHAMTON, NY – Helping at-risk high schoolers succeed in the classroom has always been difficult. Binghamton University Professor David Sloan Wilson thinks that he has a solution: design a school program that draws upon general theories of social behavior.
Wilson, who has studied the evolution of social behavior throughout his career, recently had an opportunity to advise a new program for at-risk 9th and 10th graders in the upstate community of Binghamton, NY. Known as the Regents Academy, the program initiated in the Binghamton City School District was a huge success ...
Research group proposes first system for assessing the odds of life on other worlds
2011-11-22
PULLMAN, Wash. – Within the next few years, the number of planets discovered in orbits around distant stars will likely reach several thousand or more. But even as our list of these newly discovered "exoplanets" grows ever-longer, the search for life beyond our solar system will likely focus much more narrowly on the relatively few of these new worlds which exhibit the most Earth-like of conditions.
For much of the scientific community, the search for alien life has long been dominated by the notion that our own planet serves as the best model of conditions best suited ...
People with early Alzheimer's disease may be more likely to have lower BMI
2011-11-22
ST. PAUL, Minn. – Studies have shown that people who are overweight in middle age are more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease decades later than people at normal weight, yet researchers have also found that people in the earliest stages of Alzheimer's disease are more likely to have a lower body mass index (BMI). A current study examines this relationship between Alzheimer's disease and BMI.
The study, published in the November 22, 2011, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology, examined 506 people with advanced brain imaging ...
Poor recycling of BACE1 enzyme could promote Alzheimer's disease
2011-11-22
Sluggish recycling of a protein-slicing enzyme could promote Alzheimer's disease, according to a study published online on November 21 in The Journal of Cell Biology (www.jcb.org).
Abeta, the toxic protein that accumulates in the brains of Alzheimer's patients, is formed when enzymes cut up its parental protein, known as amyloid precursor protein. One of those enzymes is beta-secretase or BACE1. BACE1 cycles between the Golgi apparatus and the plasma membrane, traveling through endosomes on the way. A protein complex called the retromer helps transport proteins back from ...
YourHomeSupply.com Introduces New Line Of Home Security Cabinet And Door Hardware
2011-11-22
Your Home Supply, a one stop shop for cabinet and door hardware needs, has recently introduced a new range of products that include First Watch Security, a premium line of home security hardware. The new selection of bolts, latches, strike plates, latch guards, drawer, cabinet, mailbox and window locks, door reinforcers as well as patio and replacement knobs is available at the lowest prices with an unmatched quality. The new First Watch Security product not only adds to the security of a home, but also lends a door a new style. Customers can even get custom designed products ...
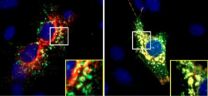
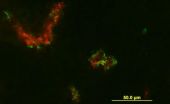
Researchers shrink tumors and minimize side effects using tumor-homing peptide to deliver treatment
2011-11-22
LA JOLLA, Calif., November 21, 2011 – The trouble with most anti-cancer therapies is that they are lethal to most cells in the body, not just cancer cells. As a result, patients experience side effects like nausea, increased susceptibility to infection, and increased risk of developing secondary cancers later in life. Researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham) are developing techniques to deliver cancer drugs directly to tumors, increasing their effectiveness and decreasing collateral damage. In a study published the week of November 21 ...
New breast cancer screening guidelines released
2011-11-22
New breast cancer screening guidelines for women at average risk of breast cancer, published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj110334.pdf, recommend no routine mammography screening for women aged 40-49 and extend the screening interval from every 2 years, which is current clinical practice, to every 2 to 3 years for women aged 50-74. The guidelines also recommend against routine clinical breast exam and breast self-examination in asymptomatic women.
The guidelines, aimed at physicians and policy-makers, ...
DesignPractica Expands eCommerce and Custom CMS Services
2011-11-22
DesignPractica has been creating and maintaining custom websites for small businesses in Greater Vancouver area for several years. Now, in addition to offering WordPress, Django and Google Application Engine websites, DesignPractica will also provide support and development services with all top open-source and hosted eCommerce and CMS systems, such as Magento, Drupal, Volusion, Shopify, Satchmo and others, for small, medium and large businesses in the greater Vancouver region.
DesignPractica has a successful history of helping local manufacturers, farmers, restaurants ...
More than one-quarter of Canadian adults projected to have hypertension in 2012/13
2011-11-22
Hypertension in Canada is increasing, and it is projected that more than one-quarter of Canadian adults will be diagnosed with hypertension by 2012/13, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj101863.pdf. Older women were more likely to be diagnosed with high blood pressure compared with men, and people in the Atlantic provinces had the highest rates of hypertension.
Canadian researchers looked at data on 26 million adults aged 20 years and over between 1998󈟏 and 2007/08 to ...
Families report adverse events in hospitalized children not tracked by health-care providers
2011-11-22
Families of hospitalized children can provide valuable information about adverse events relating to their children's care that complements information documented by health care professionals, states a study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj110393.pdf.
Hospitals in Canada have instituted systems to encourage reporting of adverse events — things that may negatively affect the recovery or health of a patient — in patient care. In pediatrics, it is estimated that 1% of children in hospital ...
NIH researchers identify key proteins of inner ear transduction channel
2011-11-22
National Institutes of Health-funded researchers have identified two proteins that may be the key components of the long-sought after mechanotransduction channel in the inner ear—the place where the mechanical stimulation of sound waves is transformed into electrical signals that the brain recognizes as sound. The findings are published in the Nov. 21 online issue of The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The study used mice in which two genes, TMC1 and TMC2, have been deleted. The researchers revealed a specific functional deficit in the mechanotransduction channels ...
October Issue of Proceedings of the IEEE Presents Most Comprehensive Metamaterials Analysis Ever Assembled
2011-11-22
The future of the metamaterials field shows great promise for achieving exotic new functions according to October's Proceedings of the IEEE, the most highly-cited general-interest journal in electrical engineering and computer science, approaching its 100th year of publication in 2012. Entitled "Metamaterials: Fundamentals and Applications in the Microwave and Optical Regimes," the 16-article issue, written by internationally renowned leaders in the field is packed with innovative research reports on potential new functions and insights that could impact many ...
Implanted neurons, grown in the lab, take charge of brain circuitry
2011-11-22
MADISON -- Among the many hurdles to be cleared before human embryonic stem cells can achieve their therapeutic potential is determining whether or not transplanted cells can functionally integrate into target organs or tissues.
Writing today (Monday, Nov. 21) in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a team of Wisconsin scientists reports that neurons, forged in the lab from blank slate human embryonic stem cells and implanted into the brains of mice, can successfully fuse with the brain's wiring and both send and receive signals.
Neurons are specialized, ...
Boosting the aged immune response to flu virus
2011-11-22
As people age, their immune system becomes less robust. This makes them more susceptible to serious and frequently life-threatening infections with viruses that affect the respiratory tract such as influenza A virus (IAV). Stanley Perlman and colleagues, at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, have now identified a new immune system defect in aged mice that makes them more susceptible than young mice to developing severe clinical disease upon infection with respiratory viruses such as IAV. Importantly, they were able to reverse the defect by inhibiting the immune molecule ...
Conservatoryinfo.co.uk Introduces New Redesigned Website
2011-11-22
For businesses, having a signature look is important for brand awareness; however, when the evolving times call for a major change, Conservatoryinfo.co.uk knows how to do it right. After years of maintaining the same look of their website, Conservatoryinfo.co.uk implements a major redesign to improve its functionality, interface, and overall performance for users and search engines.
The new website provides an easy flow of information combined with appealing graphics that was launched last September 2011. It debuted with new features and built-in SEO elements in accordance ...
BRAF addiction of thyroid cancers makes them therapeutically vulnerable
2011-11-22
Papillary carcinoma is the most common form of thyroid cancer. Approximately one quarter of these carcinomas have mutations in the BRAF gene. The prevalence of such mutations is even greater in high-grade carcinomas, particularly those that are refractory to standard treatment, which is radioactive iodine (RAI). A team of researchers led by James Fagin, at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, has now identified a way to potentially exploit the expression of BRAF by such cancers for therapeutic purposes.
Despite the prevalence of BRAF mutations in papillary ...
Expanding treatment options for Cushing disease
2011-11-22
Cushing disease is a hormone disorder that causes a diverse array of symptoms, including fat accumulation, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, muscle wasting, and ultimately death. It is caused by a tumor in the anterior pituitary gland that results in the secretion of excess amounts of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Treatment options are essentially limited to surgical resection. However, tumors commonly recur, meaning that new treatment options are needed. A team of researchers, led by Shlomo Melmed, at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, has now identified ...
JCI online early table of contents: Nov. 21, 2011
2011-11-22
EDITOR'S PICK: Boosting the aged immune response to flu virus
As people age, their immune system becomes less robust. This makes them more susceptible to serious and frequently life-threatening infections with viruses that affect the respiratory tract such as influenza A virus (IAV). Stanley Perlman and colleagues, at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, have now identified a new immune system defect in aged mice that makes them more susceptible than young mice to developing severe clinical disease upon infection with respiratory viruses such as IAV. Importantly, they were ...
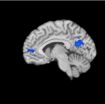
Tuning out: How brains benefit from meditation
2011-11-22
Experienced meditators seem to be able switch off areas of the brain associated with daydreaming as well as psychiatric disorders such as autism and schizophrenia, according to a new brain imaging study by Yale researchers.
Meditation's ability to help people stay focused on the moment has been associated with increased happiness levels, said Judson A. Brewer, assistant professor of psychiatry and lead author of the study published the week of Nov. 21 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Understanding how meditation works will aid investigation into ...
The Best Affiliate Marketing Companies Ranked by topseos.com for November 2011
2011-11-22
topseos.com, the independent authority on search vendors, has released their list of the best affiliate marketing companies for November 2011. An evaluation of affiliate marketing companies has led to the creation of a list of rankings showcasing the top ten affiliate marketing services in the online marketing industry. The process for evaluating the best affiliate marketing services includes the use of a set of evaluation criteria which consists of the five most important aspects of these services.
The Top 10 Affiliate Marketing Companies for November 2011 are:
1) ...
Cancer screening reform needed
2011-11-22
Since the National Cancer Institute developed the first guidelines on mammography screening over thirty years ago, advocacy and professional groups have developed guidelines focused on who should be screened, instead of communicating clearly the risks and benefits of screening, according to a commentary by Michael Edward Stefanek, Ph.D., the associate vice president of collaborative research in the office of the vice president at Indiana University, published online Nov. 21 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Stefanek writes that too much time has been spent ...
[1] ... [6881]
[6882]
[6883]
[6884]
[6885]
[6886]
[6887]
[6888]
6889
[6890]
[6891]
[6892]
[6893]
[6894]
[6895]
[6896]
[6897]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.