Low fertility in Europe -- is there still reason to worry?
2011-06-19
The post-war trend of falling birth rates has been reversed across Europe, according to a new study. However, despite an increasing emphasis on family and fertility policies in Europe, this recent development involves social, cultural and economic factors more than individual policy interventions.
For some decades, couples have been having children later in life. But birth-rates among younger women have stabilised and the long-term trend towards lower fertility rates has been reversed.
Politicians are still left to grapple with problems associated with an ageing population ...
IOF calls for improved strategies to close the treatment gap and reduce future burden of fractures
2011-06-19
It pays to prevent fractures. That's one of the main findings of a landmark report 'Osteoporosis – Burden, Healthcare provision and Opportunities in the European Union' newly published in the journal Archives of Osteoporosis. The study, compiled by the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) in collaboration with the European Federation of the Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA), calculates the future burden of fractures as a consequence of increasing treatment uptake in the five largest European countries as well as Sweden.
Fragility fractures, which ...
US Medicaid drug lists cost more, deliver less
2011-06-19
The U.S. Medicaid program is likely paying far more than necessary for medications and not offering patients the most effective ones available, by ignoring international evidence-based lists of safe and effective medications, according to a new study by researchers at University of California, San Francisco.
The study, which compared the Medicaid program's Preferred Drug Lists in 40 states nationwide against the World Health Organization's 2009 Essential Medicines List, found that the medications that are automatically paid for by the state-run Medicaid programs vary ...
University of Louisville surgeons perform first prosthetic bypass graft with patient's stem cells at point-of-care
2011-06-19
LOUISVILLE, Ky. – The first three patients to undergo an investigational surgical procedure for peripheral vascular disease that involves the patient's own stem cells continue to do well, reports the University of Louisville surgeon who is the principal investigator.
The "TGI-PVG IDE" clinical trial initiated at UofL involves using a patient's own stem cells to line man-made bypass grafts to better the chances at saving the limbs of patients with peripheral artery disease. Charles B. Ross, M.D., chief of the Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapeutics, ...
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope completes first round of cryogenic mirror test
2011-06-19
The first six of 18 segments that will form NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's primary mirror for space observations completed final cryogenic testing this week. The ten week test series included two tests cycles where the mirrors were chilled down to -379 degrees Fahrenheit, then back to ambient temperature to ensure the mirrors respond as expected to the extreme temperatures of space.
A second set of six mirror assemblies will arrive at Marshall in late July to begin testing, and the final set of six will arrive in the fall.
The X-ray and Cryogenic Facility at NASA's ...
How Long Do Breast Implants Last?
2011-06-19
When you are considering breast augmentation it is common to wonder how long the implants will last. Stories abound about leaking implants and implant ruptures, causing some women to seriously consider if this procedure is safe and long lasting. It is important to remember that no medical device can last a lifetime. Like all medical devices, breast implants can, over time, wear down and require replacement.
Why Breast Implants Fail
A majority of breast implants last for ten to 25 years. Some women may enjoy a longer lifespan and others may have to replace their breast ...
System 92E looking more like a developing east Pacific tropical storm
2011-06-19
A low pressure area in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, located off the western coast of Mexico, is still getting organized, and System 92E and the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite spotted heavy rain and strong thunderstorms within.
On Friday, June 17, 2011, System 92E appeared on satellite imagery as a broad area of low pressure that contained showers and thunderstorms. System 92E was located several hundred miles south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec. The gulf is a large area at 16 North and 95 West, which is right where the low pressure area is centered. Many ...
Despite Protocols, Wrong-Site Surgeries Persist
2011-06-19
In an effort to prevent wrong-site and wrong-patient surgeries, the Joint Commission developed the Universal Protocol in 2004. The protocol introduced a series of steps -- preprocedure verification, site marking, and a time out prior to beginning the procedure -- to ensure the correct surgery was being performed on the right person.
New research is finding that despite the introduction of the Universal Protocol, operations performed on the wrong person or wrong body part continue to happen at an alarming level.
Colorado Study
In a study published in the Archives ...
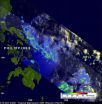
NASA satellite sees Tropical Depression 06W near the Philippines
2011-06-19
The sixth western Pacific tropical cyclone (06W) of 2011 has developed near the Philippines and the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite saw some heavy rainfall in the storm. Tropical Depression 06W was dropping the heaviest rain over the open waters of the Western North Pacific Ocean on June 17 as the storm continues to move toward China.
The TRMM satellite is operated by the Japanese Space Agency and NASA, and continually monitors the tropics and measures rainfall in tropical cyclones. TRMM captured an early morning look at the forming depression on ...
Divorce: After Age 50, The Choices Become More Complex
2011-06-19
A recent Smart Money article warns of financial mistakes made by those older than 50 years of age when they divorce. A divorce at age 50 or beyond is more complex, simply because there are usually more assets at stake and less time to recoup assets after divorce, making the division of marital property more complex.
The story highlights areas where people over or undervalue assets. For instance, retirement accounts are usually a high value asset at this point in most couple's lives, second in value only to their homes.
Don't Forget About the Taxes
What people often ...
Wiretapping: a New Tactic for Prosecutors in White-Collar Cases
2011-06-19
Hedge-Fund Mogul Raj Rajaratnam Sunk by Wiretap Evidence
Last month, a U.S. District Court jury in New York convicted Raj Rajaratnam, co-founder of hedge giant The Galleon Group, of fraud and conspiracy after two and one-half weeks of deliberation. As the principal player in the nation's largest illegal stock-tipping case since Ivan Boesky in the 1980s, Rajaratnam may be compelled to surrender millions in profits gained from his illegal activities. He also faces potentially 25 years in prison when he is sentenced on July 29.
A major player on Wall Street, Rajaratnam ...
Fathers find financial crisis hits family life
2011-06-19
Much coverage of the economic downturn has focussed on its immediate impact, yet it is likely to hold long-term implications for family life. A research study 'Changing Lives and Times' funded by the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) at Cardiff University has explored the impact of the financial crisis on the daily lives and future plans of new fathers, finding that several men were making significant life changes.
New dad William described how he and his wife decided to stick with one child rather than have the three children they originally planned for, because ...
Evaluate Your Financial Picture Before Talking to a Bankruptcy Lawyer
2011-06-19
Bankruptcy is usually one of the last steps a consumer will take when his or her financial situation has hit a critical stage. Along with considering bankruptcy, a debtor also may want to think about making some financial changes.
In a survey conducted by the National Foundation for Credit Counseling, researchers found that a majority of consumers felt frustrated at having to practice unending frugality because of job loss or underemployment. Also contributing to the frustration are the increasing costs of medical supplies and services, food and gasoline, and stagnant ...
Vebnet Announces Partnership with vielife
2011-06-19
Vebnet has enhanced its employee benefits, offering to allow global access to an online health and wellbeing solution, by partnering with employee health solutions specialist vielife.
Employers using Vebnet's reward and flexible benefits technology can now offer their employees a personalised, multi-language and interactive health and well-being service through vielife Online. The service lets employees measure and monitor their sleep, stress, nutrition and physical activity levels and encourages them to make healthier lifestyle choices, while helping employers to improve ...
Macdonald Burlington Appoints New General Manager
2011-06-19
Macdonald Burlington on New Street in Birmingham has appointed 38 year-old Derek McDonagh as General Manager.
His appointment to the 115-bedroom hotel in Birmingham that boasts one of the largest conference facilities in the city reflects the hotel's determination to firmly position itself as the number one choice for corporate, conference and leisure visitors to the UK's second largest city.
Dublin born McDonagh, who assumes responsibility for over 80 staff and conferencing space for up to 500 delegates (Horton Room), said of his appointment: "The Macdonald ...
The National Trust Asks Community to Help Shape Future of North East Farmland
2011-06-19
The National Trust is asking the local community surrounding its Gibside Estate in Tyne & Wear to help decide the future of 150 acres of farmland it has purchased adjoining the 600 acre property.
The charity has invested over half a million pounds to save the pasture and arable land from open cast mining.
The acquisition came on the back of a ground swell of opposition to the mining proposal in the local community where a mine would have been visible for miles around, created noise pollution, vibrations from explosions and high levels of dust.
A mine would ...
Special Offer for the Men and Women of the United States Military at The Inn at Honey Run
2011-06-19
Just in time to celebrate Independence Day, The Inn at Honey Run has announced a special offer as a thank you to the men and women of the United States Military, who have risked their lives in order to keep their country safe and protect the rights and freedom of America. To help celebrate the dedication of military men and women, and to show the heroes much deserved appreciation and gratitude, The Inn at Honey Run is offering a $76.00 rate for Sunday, July 3 thru Sunday, July 10. This special is valid for any room in the main inn.
This special is available to both ...
Drew Lachey, National Performers Headline July 11 Kick Off to 2012 World Choir Games Countdown
2011-06-19
The countdown to the 2012 World Choir Games in Cincinnati USA starts officially on July 11, 2011 with a celebration event at downtown Cincinnati's Fountain Square taking place from 11:30 a.m. - 1:30 p.m. Cincinnati native, Grammy-nominated 98 Degrees member and "Dancing with the Stars" Season 2 winner Drew Lachey will emcee the event, introducing a variety of national musical performers and kick starting a yearlong cultural celebration in Cincinnati USA. 2012 marks the first time ever that the Games have been held in the United States. Visitor information for ...
Healthcare Resources Online Announces Partnership With The Endocrine Society
2011-06-17
Healthcare Resources Online is pleased to announce that they will be the powering engine behind EndoCare Online, The Endocrine Society's new service for its members. EndoCare Online, different from any other healthcare web service available today, is a novel and comprehensive resource delivery model. The service will meet the needs of enhanced patient care for both endocrinology professionals and their patients with a variety of endocrine disorders and other health issues.
EndoCare Online works by connecting The Endocrine Society members to the resources they want, when ...
Splash Dogs, Wiener Dog Races and Amazing Animal Acts Showcase Their Talents at America's Family Pet Expo
2011-06-17
JUMP! The Ultimate Dog Show, Dock diving dogs, doggy makeovers, CFA Cat Show, the world-famous Free Flight Bird Show and Creepy Crawly Critter Show are just a few performances that Washingtonians will experience at America's Family Pet Expo at the Puyallup Fair & Events Center in Puyallup, Wash., Friday-Sunday, July 8-10, 2011.
After 22 successful years in Southern California, the expo expands to Washington to provide a weekend of entertainment, with animal performances, stage shows, shopping and the chance to interact with various breeds of dogs, cats, birds, fish, ...
The Las Vegas Review Journal Lists Award Winning Comedian Don Barnhart's Comedy Show As The Best Of Las Vegas
2011-06-17
Named Best of Las Vegas by the LVRJ, The Don Barnhart Comedy Show features the top headlining comedians that you've seen on Comedy Central, MTV, HBO, Leno, Conan, Letterman, BET including Barnhart himself along with a rotating cast of the next generation of comedy superstars.
Don's goal is to make his show a home for Vegas' growing comedy community and to help showcase their talents and when Barnhart is on the road, he'll feature a special guest headliner to fill in for him making this a true Las Vegas Comedy Club.
The Clarion Hotel (formerly Greek Isles) is located ...
McCormick USA and Woods Equipment Announce Strategic Alliance
2011-06-17
Duluth, Ga. based McCormick USA and Oregon, IL. based Woods Equipment Company announced today that they have formed a strategic partnership to offer Woods-attachments through McCormick USA's nationwide dealer network.
This alliance covers a full line of agriculture and landscape equipment including cutters, finish and zero-turn mowers, front-end loaders, backhoes, snow blowers, and assorted scrapers, discs, rakes, post hole diggers, stump grinders and blades. All equipment covered under this agreement will be McCormick red and branded McCormick by Woods.
"Being ...
Auckland Aces Anaru Kitchen and Bruce Martin make NZ A Cricket Side
2011-06-17
The New Zealand team will assemble in Maroochydore for a training camp on 18 July before transferring to Brisbane on 26 July for the Emerging Player Tournament. The other three teams are Australian Institute of Sport (AIS), and emerging cricket teams of South Africa and India.
This year will see a format change from the traditional competition structure with the teams completing a round of three-day matches to determine the winner.
Previous Emerging Player Tournament's have featured Twenty20 and 50-over matches but the participating nations felt the longer version ...
Access Display Group Sets its Sites on Social Media
2011-06-17
Access Display Group, Inc. (ADG), a leading B2B manufacturer of quick-changing framing systems and display cases, is now using Facebook and Twitter as a way of expanding its online footprint, increasing interaction with its customers, suppliers, and employees.
Established in 1992, ADG designs, manufactures and distributes signage display fixtures and is best known for its patented, multi-purpose "SwingFrames" - swing-open display fixtures with discrete hinge and locking mechanisms. In addition to SwingFrames, ADG manufactures and distributes a range of other ...
Angelique Bates aka 'Alizay' Announces Release of Debut Single 'Can't Fade Me Now' on 18th July 2011.
2011-06-17
Angelique 'Alizay' Bates, a Californian native from Haitian/Native American Indian decent shot to fame in the Nickelodeon's #1 hit, television show, All That, and has since appeared in numerous US TV shows and Hollywood films.
Angelique Bates who also goes by the name of 'Alizay' is a familiar face on the Hollywood red carpet, and also heavily involved in charity work, regularly volunteering for The Red Cross, Feed The Children and also featured in the recent Ashton Kutcher/Demi Moore 'End US Hunger' campaign.
Now, focusing on her music career, Angelique 'Alizay' ...
[1] ... [7200]
[7201]
[7202]
[7203]
[7204]
[7205]
[7206]
[7207]
7208
[7209]
[7210]
[7211]
[7212]
[7213]
[7214]
[7215]
[7216]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.