Nobel Laureates appeal for climate protection
Mainau Declaration 2015
2015-07-03
(Press-News.org) To mark the final day of the 65th Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting, on Friday, 3 July, over 30 Nobel laureates assembled on Mainau Island on Lake Constance signed a declaration on climate change. The "Mainau Declaration 2015 on Climate Change" states "that the nations of the world must take the opportunity at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Paris in December 2015 to take decisive action to limit future global emissions." It is expected that a new international agreement on climate protection will be approved at the 21st UN Climate Conference to succeed the Kyoto Protocol.
Following on from the latest climate policy resolutions adopted by the G7 states and the environment- and climate-oriented encyclical "Laudato si'" issued by Pope Francis, the Nobel laureates' declaration is another urgent warning of the consequences of climate change. "If left unchecked, our ever-increasing demand for food, water, and energy will eventually overwhelm the Earth's ability to satisfy humanity's needs, and will lead to wholesale human tragedy," the declaration continues.
The Mainau Declaration 2015 is the result of an initiative on the part of Nobel Science Laureates who took part in the 65th Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting. The signatories to the declaration have all been awarded Nobel Prizes in physiology or medicine, in physics or in chemistry. Some of the laureates who have not attended the final day of the meeting had already put their names to the declaration earlier at Lindau.
The spokesperson for the initiators is US astrophysicist Brian Schmidt. Having grown up in Montana and Alaska, he studied physics and astronomy at the University of Arizona. In 1993 he was awarded a doctorate at Harvard University for his work on supernovae, the brief but brilliant results of exploding stars. Since 1995 he has been working in Australia at the Australian National University's Mount Stromlo Observatory where he heads one of the two teams which, at the end of the 1990s, were able to determine from their measurements of the brightness of remote supernovae that the rate at which the universe is expanding is accelerating. It was for this discovery that he was awarded the 2011 Nobel Prize for Physics along with Saul Perlmutter and Adam Riess.
This is the first time since 1955 that Nobel laureates use the platform of the Lindau Nobel Laureate Meeting to take a stand on social policy issues. The first Mainau Declaration signed on that occasion by a total of 51 Nobel laureates on the initiative of physics laureate Otto Hahn contained an appeal for the peaceful use of nuclear energy and warned of the dangers inherent in its application for military purposes.
The total of 65 laureates taking part in the 65th Lindau Meeting was the highest number ever assembled here. In addition to the numerous laureates of the medicine, physics or chemistry Nobel Prizes, the speakers also included Indian Nobel Peace Laureate Kailash Satyarthi and Nigerian Nobel Literature Laureate Wole Soyinka. The week-long conference annually provides an opportunity for an inter-generational and an inter-cultural exchange of ideas: Over 650 young scientists from 88 countries successfully passed the multi-stage selection process to take part in this interdisciplinary anniversary meeting. The Lindau Meetings were established in 1951 by Lennart Count Bernadotte af Wisborg and the Lindau city councilors Franz Karl Hein and Gustav Wilhelm Parade. Ever since, the final day of the meeting has traditionally been held on Mainau Island.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-03
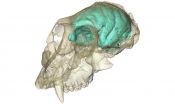
DURHAM, N.C. -- The brain hidden inside the oldest known Old World monkey skull has been visualized for the first time. The creature's tiny but remarkably wrinkled brain supports the idea that brain complexity can evolve before brain size in the primate family tree.
The ancient monkey, known scientifically as Victoriapithecus, first made headlines in 1997 when its fossilized skull was discovered on an island in Kenya's Lake Victoria, where it lived 15 million years ago.
Now, thanks to high-resolution X-ray imaging, researchers have peered inside its cranial cavity ...
2015-07-03
BARCELONA-LUGANO, 3 July 2015 - The phase IIIb CONSIGN study has confirmed the benefit of regorafenib in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), researchers announced at the ESMO 17th World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer 2015 in Barcelona.(1) The safety profile and progression free survival were similar to phase III trial results.
CONSIGN was a prospective, observational study that was initiated to allow patients with mCRC access to regorafenib before marketing authorisation and to assess safety, which was the primary endpoint. The randomised ...
2015-07-03
Spiders travel across water like ships, using their legs as sails and their silk as an anchor, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Evolutionary Biology. The study helps explain how spiders are able to migrate across vast distances and why they are quick to colonise new areas.
Common spiders are frequently observed to fly using a technique called 'ballooning'. This involves using their silk to catch the wind which then lifts them up into the air. Ballooning spiders are estimated to move up to 30 km per day when wind conditions are suitable, helping ...
2015-07-03
Scientists have developed a new technique allowing the bioprinting at ambient temperatures of a strong paste similar to 'play dough' capable of incorporating protein-releasing microspheres.
The scientists demonstrated that the bioprinted material, in the form of a micro-particle paste capable of being injected via a syringe, could sustain stresses and strains similar to cancellous bone - the 'spongy' bone tissue typically found at the end of long bones.
This work, published today (3 July 2015) in the journal Biofabrication, suggests that bioprinting at ambient temperatures ...
2015-07-03
A therapy that replaces the faulty gene responsible for cystic fibrosis in patients' lungs has produced encouraging results in a major UK trial.
One hundred and thirty six patients aged 12 and over received monthly doses of either the therapy or the placebo for one year.
The clinical trial reached its primary endpoint with patients who received therapy having a significant, if modest benefit in lung function compared with those receiving a placebo.
Patients from across England and Scotland participated, and were treated in two centres, Royal Brompton Hospital in ...
2015-07-03
Banded mongooses take extraordinary risks to ensure that they find the right mate.
Female banded mongooses risk their lives to mate with rivals during pack 'warfare' and both males and females have also learned to discriminate between relatives and non-relatives to avoid inbreeding even when mating within their own social group.
Researchers from the University of Exeter and Liverpool John Moores University found that 18% of wild banded mongoose pups are fathered by males from rival packs.
Banded mongooses are found living in stable social groups across Central ...
2015-07-03
For the first time gene therapy for cystic fibrosis has shown a significant benefit in lung function compared with placebo, in a phase 2 randomised trial published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal. The technique replaces the defective gene response for cystic fibrosis by using inhaled molecules of DNA to deliver a normal working copy of the gene to lung cells.
"Patients who received the gene therapy showed a significant, if modest, benefit in tests of lung function compared with the placebo group and there were no safety concerns," said senior author Professor ...
2015-07-02
LAWRENCE -- A new study that is the first to use Social Security Administration's personal income tax data tracking the same individuals over 20 years to measure individual lifetime earnings has confirmed significant long-term economic benefits of college education.
ChangHwan Kim, a University of Kansas researcher, said the research team was also able to account for shortcomings in previous studies by including factors such as gender, race, ethnicity, place of birth and high school performance that would influence a person's lifetime earnings and the probability of college ...
2015-07-02
DALLAS, July 2, 2015 -- An emergency room rapid response plan for children can help diagnose stroke symptoms quickly, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Stroke.
"Just as there are rapid response processes for adults with a possible stroke, there should be a rapid response process for children with a possible stroke that includes expedited evaluation and imaging or rapid transfer to a medical center with pediatric stroke expertise," said Lori Jordan, M.D., Ph.D., study senior author and an assistant professor of pediatrics and neurology ...
2015-07-02
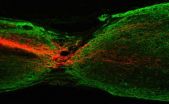
Researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have found a way to stimulate the growth of axons, which may spell the dawn of a new beginning on chronic SCI treatments.
Chronic spinal cord injury (SCI) is a formidable hurdle that prevents a large number of injured axons from crossing the lesion, particularly the corticospinal tract (CST). Patients inflicted with SCI would often suffer a loss of mobility, paralysis, and interferes with activities of daily life dramatically. While physical therapy and rehabilitation would help the patients to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Nobel Laureates appeal for climate protection
Mainau Declaration 2015