(Press-News.org) Cold Spring Harbor, NY – Big Data is everywhere, and we are constantly told that it holds the answers to almost any problem we want to solve. Companies collect information on how we shop, doctors and insurance companies gather our medical test results, and governments compile logs of our phone calls and emails. In each instance, the hope is that critical insights are hidden deep within massive amounts of information, just waiting to be discovered.
But simply having lots of data is not the same as understanding it. Increasingly, new mathematical tools are needed to extract meaning from enormous data sets. In work published online today, two researchers at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) now challenge the most recent advances in this field, using a classic mathematical concept to tackle the outstanding problems in Big Data analysis.
What does it mean to analyze Big Data? A major goal is to find patterns between seemingly unrelated quantities, such as income and cancer rates. Many of the most common statistical tools are only able to detect patterns if the researcher has some expectation about the relationship between the quantities. Part of the lure of Big Data is that it may reveal entirely new, unexpected patterns. Therefore, scientists and researchers have worked to develop statistical methods that will uncover these novel relationships.
In 2011, a distinguished group of researchers from Harvard University published a highly influential paper in the journal Science that advanced just such a tool. But in a paper published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, CSHL Quantitative Biology Fellow Justin Kinney and CSHL Assistant Professor Gurinder "Mickey" Atwal demonstrate that this new tool is critically flawed. "Their statistical tool does not have the mathematical properties that were claimed," says Kinney.
Kinney and Atwal show that the correct tool was hiding in plain sight all along. The solution, they say, is a well known mathematical measure called "mutual information," first described in 1948. It was initially used to quantify the amount of information that could be transmitted electronically through a telephone cable; the concept now underlies the design of the world's telecommunications infrastructure. "What we've found in our work is that this same concept can also be used to find patterns in data," Kinney explains.
Applied to Big Data, mutual information is able to reveal patterns in large lists of numbers. For instance, it can be used to analyze patterns in data sets on the numerous bacterial species that help us digest food. "This particular tool is perfect for finding patterns in studies of the human microbiome, among many other things," Kinney says.
Importantly, mutual information provides a way of identifying all types of patterns within the data without reliance upon any prior assumptions. "Our work shows that mutual information very naturally solves this critical problem in statistics," Kinney says. "This beautiful mathematical concept has the potential to greatly benefit modern data analysis, in biology and in biology and many other important fields.
INFORMATION:
The research described here was supported by the Simons Center for Quantitative Biology at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
"Equitability, mutual information, and the maximal information coefficient" appears online in PNAS on February 17, 2014. The authors are: Justin Block Kinney and Gurinder Singh Atwal. The paper can be obtained online at: http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2014/02/14/1309933111.abstract
About Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Founded in 1890, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has shaped contemporary biomedical research and education with programs in cancer, neuroscience, plant biology and quantitative biology. CSHL is ranked number one in the world by Thomson Reuters for the impact of its research in molecular biology and genetics. The Laboratory has been home to eight Nobel Prize winners. Today, CSHL's multidisciplinary scientific community is more than 600 researchers and technicians strong and its Meetings & Courses program hosts more than 12,000 scientists from around the world each year to its Long Island campus and its China center. For more information, visit http://www.cshl.edu.
Researchers propose a better way to make sense of 'Big Data'
New application of a classic concept challenges the latest statistical tools
2014-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study on methane emissions from natural gas systems indicates new priorities
2014-02-18
A new study published in the journal Science says that the total impact of switching to natural gas depends heavily on leakage of methane (CH4) during the natural gas life cycle, and suggests that more can be done to reduce methane emissions and to improve measurement tools which help inform policy choices.
Published in the February 14 issue of Science, the study, "Methane Leaks from North American Natural Gas Systems," presents a first effort to systematically compare North American emissions estimates at scales ranging from device-level to continental atmospheric studies. ...
Baby hearts need rhythm to develop correctly
2014-02-18
NASHVILLE, Tenn. – To develop correctly, baby hearts need rhythm...even before they have blood to pump.
"We have discovered that mechanical forces are important when making baby hearts," said Mary Kathryn Sewell-Loftin, a Vanderbilt graduate student working with a team of Vanderbilt engineers, scientists and clinicians attempting to grow replacement heart valves from a patient's own cells.
In an article published last month in the journal Biomaterials the team reported that they have taken an important step toward this goal by determining that the mechanical forces ...
Nitrogen-tracking tools for better crops and less pollution
2014-02-18
Stanford, CA— As every gardner knows, nitrogen is crucial for a plant's growth. But nitrogen absorption is inefficient. This means that on the scale of food crops, adding significant levels of nitrogen to the soil through fertilizer presents a number of problems, particularly river and groundwater pollution. As a result, finding a way to improve nitrogen uptake in agricultural products could improve yields and decrease risks to environmental and human health. Nitrogen is primarily taken up from the soil by the roots and assimilated by the plant to become part of DNA, ...
Regenerating orthopedic tissues within the human body
2014-02-18
By combining a synthetic scaffolding material with gene delivery techniques, researchers at Duke University are getting closer to being able to generate replacement cartilage where it's needed in the body.
Performing tissue repair with stem cells typically requires applying copious amounts of growth factor proteins -- a task that is very expensive and becomes challenging once the developing material is implanted within a body. In a new study, however, Duke researchers found a way around this limitation by genetically altering the stem cells to make the necessary growth ...
Research of zebrafish neurons may lead to understanding of birth defects like spina bifida
2014-02-18
COLUMBIA, Mo. – The zebrafish, a tropical freshwater fish similar to a minnow and native to the southeastern Himalayan region, is well established as a key tool for researchers studying human diseases, including brain disorders. Using zebrafish, scientists can determine how individual neurons develop, mature and support basic functions like breathing, swallowing and jaw movement. Researchers at the University of Missouri say that learning about neuronal development and maturation in zebrafish could lead to a better understanding of birth defects such as spina bifida in ...
Prison-based education declined during economic downturn, study finds
2014-02-18
State-level spending on prison education programs declined sharply during the economic downturn, with the sharpest drop occurring in states that incarcerate the most prisoners, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Large states cut spending by an average of 10 percent between the 2009 and 2012 fiscal years, while medium-sized states cut spending by 20 percent, according to the study.
"There has been a dramatic contraction of the prison education system, particularly those programs focused on academic instruction versus vocational training," said Lois Davis, the ...
Miriam Hospital study shows social gaming site effective weight loss tool
2014-02-18
(PROVIDENCE, R.I.) -- Researchers from The Miriam Hospital have found that DietBet, a web-based commercial weight loss program that pairs financial incentives with social influence, delivers significant weight losses. The study and its findings have been published in the current issue of the open access publication JMIR Serious Games.
Tricia Leahey, Ph.D., lead researcher at The Miriam Hospital Weight Control and Diabetes Research Center, sought to examine weight losses associated with the social gaming website and contributing factors to gauge the success of such web-based ...
Rife with hype, exoplanet study needs patience and refinement
2014-02-18
Imagine someone spent months researching new cities to call home using low-resolution images of unidentified skylines. The pictures were taken from several miles away with a camera intended for portraits, and at sunset. From these fuzzy snapshots, that person claims to know the city's air quality, the appearance of its buildings, and how often it rains.
This technique is similar to how scientists often characterize the atmosphere — including the presence of water and oxygen — of planets outside of Earth's solar system, known as exoplanets, according to a review of exoplanet ...
Frequent flyers, bottle gourds crossed the ocean many times
2014-02-18
Bottle gourds traveled the Atlantic Ocean from Africa and were likely domesticated many times in various parts of the New World, according to a team of scientists who studied bottle gourd genetics to show they have an African, not Asian ancestry.
"Beginning in the 1950s we thought that bottle gourds floated across the ocean from Africa," said Logan Kistler, post-doctoral researcher in anthropology, Penn State. "However, a 2005 genetic study of gourds suggested an Asian origin."
Domesticated bottle gourds are ubiquitous around the world in tropical and temperate areas ...
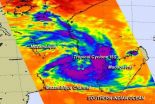
NASA sees Tropical Cyclone 15S form in the Mozambique Channel
2014-02-18
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone 15S as it formed in the Mozambique Channel on Feb. 18 and the AIRS instrument aboard gathered infrared data on its cloud top temperatures and potential.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical cyclone 15S on Feb. 18 at 10:53 a.m. EST. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument captured infrared data on the tropical system that showed the highest cloud tops and strongest thunderstorms were in a band that stretched from the east to the south of the center. Cloud top temperatures were near -63F/-52C, indicating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
[Press-News.org] Researchers propose a better way to make sense of 'Big Data'New application of a classic concept challenges the latest statistical tools