(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
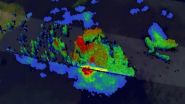
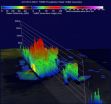
In this TRMM 3-D simulated flyby of System 92B from May 21, some powerful convective storm tops were reaching heights of almost 17 km (about 10.5 miles).
Click here for more information.
NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites captured radar and infrared data on developing tropical low pressure area System 92B as it now makes it way north through the Bay of Bengal.
On May 22 at 00:51 UTC, NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite passed over System 92B as it was dropping heavy rainfall over the Bay of Bengal. TRMM's Precipitation Radar (PR) revealed that rain was falling at the extreme rate of over 191 mm (about 7.5 inches) per hour in powerful convective storms in the center of the Bay of Bengal well to the east of India.
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, TRMM's Precipitation Radar data were also used to construct a simulated 3-D view of 92B's rainfall structure looking toward the east from India. TRMM PR pulled away a veil of clouds and revealed that some powerful convective storm tops were reaching heights of almost 17 km (about 10.5 miles). The extreme rainfall in this area was returning radar reflectivity values of over 53.7 dBZ to the TRMM satellite.
On May 22 at 7:11 UTC/3:11 a.m. EDT, NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 92B and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument captured infrared data on the low's cloud tops. Satellite imagery shows that the low-level circulation center is large and poorly defined with flaring and fragmented deep convection. The data showed two areas where thunderstorms had high cloud tops and very cold temperatures near -63F/-52C. Thunderstorms that high into the troposphere have been found to generate heavy rainfall. The areas of strong thunderstorms were north and west of the center of circulation.
By 08:00 UTC/4 a.m. EDT, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center estimated that System 92B had maximum sustained winds between 25 to 30 knots (28.7 to 34.5 mph/46.3 to 55.5 kph). Metsat satellite imagery indicated that the circulation center is located near 17.0 north latitude and 92.1 east longitude in the Bay of Bengal, about 315 nautical miles south of Chittagong, Bangladesh.
System 92B is moving north at 5 knots (5.7 mph/9.2 kph). Computer models vary on the development of the tropical low pressure area, but do expect it to continue drifting to the north and north-northwest.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that System 92B's potential for the development of a significant tropical cyclone within the next 24 hours remains high.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro/Hal Pierce
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Two NASA Satellites see System 92b headed north in Bay of Bengal
2014-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Antibiotic crisis needs united global response, experts say
2014-05-22
Growing resistance to antibiotics and other drugs demands a coordinated global response on the same scale as efforts to address climate change, experts say.
Without an international commitment to tackle the issue, the world faces a future in which simple infections that have been treatable for decades become deadly diseases, they warn.
Resistance to antibiotics to tackle bacterial infections and antimicrobial drugs used to treat parasites, viruses and fungi is spreading at an alarming rate. Treatment for many infectious diseases is now reliant on just one or two drugs.
Professor ...
Not all diamonds are forever
2014-05-22
Images taken by Rice University scientists show that some diamonds are not forever.
The Rice researchers behind a new study that explains the creation of nanodiamonds in treated coal also show that some microscopic diamonds only last seconds before fading back into less-structured forms of carbon under the impact of an electron beam.
The research by Rice chemist Ed Billups and his colleagues appears in the American Chemical Society's Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Billups and Yanqiu Sun, a former postdoctoral researcher in his lab, witnessed the interesting ...
EuroPCR 2014 examines vascular response and long-term safety of bioresorbable scaffolds
2014-05-22
22 May 2014, Paris, France: At EuroPCR 2014 yesterday, experts discussed the development in evidence for bioresorbable vascular scaffolds, which represent an era of vascular restoration in interventional cardiology. The available data were analysed and participants heard that bioresorbable fixed strut vascular scaffolds are associated with increased acute thrombogenicity due to flow disturbances. This means that patients who are implanted with these devices need to receive ongoing dual antiplatelet therapy. The panellists also pointed out that endothelialisation is further ...
RaDAR guides proteins into the nucleus
2014-05-22
May 22, 2014, New York, NY – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has identified a novel pathway by which proteins are actively and specifically shuttled into the nucleus of a cell. Published online today in Cell, the finding captures a precise molecular barcode that flags proteins for such import and describes the biochemical interaction that drives this critically important process. The discovery could help illuminate the molecular dysfunction that underpins a broad array of ailments, ranging from autoimmune diseases to cancers.
Although small proteins can diffuse passively ...
Wondering about the state of the environment? Just eavesdrop on the bees
2014-05-22
VIDEO:
This shows bees on dandelions.
Click here for more information.
Researchers have devised a simple way to monitor wide swaths of the landscape without breaking a sweat: by listening in on the "conversations" honeybees have with each other. The scientists' analyses of honeybee waggle dances reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on May 22 suggest that costly measures to set aside agricultural lands and let the wildflowers grow can be very beneficial to bees.
"In ...
Blocking pain receptors found to extend lifespan in mammals
2014-05-22
Chronic pain in humans is associated with worse health and a shorter lifespan, but the molecular mechanisms underlying these clinical observations have not been clear. A study published by Cell Press May 22nd in the journal Cell reveals that the activity of a pain receptor called TRPV1 regulates lifespan and metabolic health in mice. The study suggests that pain perception can affect the aging process and reveals novel strategies that could improve metabolic health and longevity in humans.
"The TRPV1 receptor is a major drug target with many known drugs in the clinic ...
Genes discovered linking circadian clock with eating schedule
2014-05-22
LA JOLLA—For most people, the urge to eat a meal or snack comes at a few, predictable times during the waking part of the day. But for those with a rare syndrome, hunger comes at unwanted hours, interrupts sleep and causes overeating.
Now, Salk scientists have discovered a pair of genes that normally keeps eating schedules in sync with daily sleep rhythms, and, when mutated, may play a role in so-called night eating syndrome. In mice with mutations in one of the genes, eating patterns are shifted, leading to unusual mealtimes and weight gain. The results were published ...
New technology may help identify safe alternatives to BPA
2014-05-22
Numerous studies have linked exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) in plastic, receipt paper, toys, and other products with various health problems from poor growth to cancer, and the FDA has been supporting efforts to find and use alternatives. But are these alternatives safer? Researchers reporting in the Cell Press journal Chemistry & Biology have developed new tests that can classify such compounds' activity with great detail and speed. The advance could offer a fast and cost-effective way to identify safe replacements for BPA.
Millions of tons of BPA and related compounds ...
Discovery of how Taxol works could lead to better anticancer drugs
2014-05-22
VIDEO:
This video shows how the constant addition of tubulin bound to GTP provides a cap that prevents the microtubule from falling apart. UC Berkeley scientists found that the hydrolyzation of...
Click here for more information.
University of California, Berkeley, scientists have discovered the extremely subtle effect that the prescription drug Taxol has inside cells that makes it one of the most widely used anticancer agents in the world.
The details, involving the drug's ...
Gene behind unhealthy adipose tissue identified
2014-05-22
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have for the first time identified a gene driving the development of pernicious adipose tissue in humans. The findings imply, which are published in the scientific journal Cell Metabolism, that the gene may constitute a risk factor promoting the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Adipose tissue can expand in two ways: by increasing the size and/or the number of the fat cells. It is well established that subjects with few but large fat cells, so-called hypertrophy, display an increased risk of developing ...