Ocean primed for more El Niño: ANU media release
Salinity and temperature records from corals in a remote Pacific island in Kiribati show the ocean has warmed over the last sixty years and has set up the conditions for stronger El Niño weather events
2014-11-13
(Press-News.org) The ocean is warming steadily and setting up the conditions for stronger El Niño weather events, a new study has shown.
A team of US, Australian, and Canadian researchers sampled corals from a remote island in Kiribati to build a 60-year record of ocean surface temperature and salinity.
"The trend is unmistakeable, the ocean's primed for more El Niño events," says lead-author Dr Jessica Carilli, now based at the University of Massachusetts, Boston.
Team member Dr Helen McGregor from the Research School of Earth Sciences at The Australian National University said the change in El Niño patterns could have a major impact on Australia's weather.
"During an El Niño event warm waters to the north of Australia move eastward, taking their rainfall with them," she said.
"This changes the pattern of Australia's rainfall and droughts significantly."
El Niños occurs irregularly every two to seven years and have often coincided with severe droughts in Queensland and New South Wales. The current conditions show that a weak El Niño has brought warmer and drier conditions to Australia for late 2014.
The team focused on regional differences in sea temperatures that generate the circulating winds known as the Walker Circulation, which drive the trade winds that bring moisture across the Pacific Ocean to the north of Australia.
The island from which the corals were sampled, Butaritari, was chosen for its location at one end of the Walker Circulation.
The team extracted a core from a Porites coral on the outer part of the atoll which showed a clear layer structure that, like tree rings, told the seasonal life story of the coral.
"This coral quietly laid down an excellent record of the ocean conditions at that location," Dr McGregor said.
"It greatly complements direct measurements of the ocean temperatures made by humans throughout the 60 year period, filling in the inconsistencies and gaps."
The team used the amounts of the chemicals strontium, calcium and oxygen in the coral to work out the ocean's salinity and temperature.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-13
HOUSTON - (Nov. 13, 2014) - While feelings of disgust can increase behaviors like lying and cheating, cleanliness can help people return to ethical behavior, according to a recent study by marketing experts at Rice University, Pennsylvania State University and Arizona State University. The study highlights the powerful impact emotions have on individual decision-making.
"As an emotion, disgust is designed as a protection," said Vikas Mittal, the J. Hugh Liedtke Professor of Marketing at Rice's Jones Graduate School of Business. "When people feel disgusted, they tend to ...
2014-11-13
Half a million objects, including debris, satellites, and the International Space Station, orbit the planet in the thermosphere, the largest layer of Earth's atmosphere. To predict the orbits--and potential collisions--of all this stuff, scientists must forecast the weather in the thermosphere.
Researchers who analyzed the role that gravitational effects of the Moon have on the thermosphere found that satellites taking different paths around the planet--circling over the poles, around the equator, or any route in between--will experience different levels of lunar-induced ...
2014-11-13
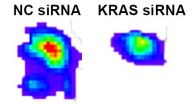
CHAPEL HILL, NC - Researchers from the UNC School of Medicine and colleagues at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a new approach to block the KRAS oncogene, one of the most frequently mutated genes in human cancer. The approach, led by Chad Pecot, MD, an assistant professor of medicine at UNC, offers another route to attack KRAS, which has proven to be an elusive and frustrating target for drug developers.
The new method relies upon a specifically sequenced type of small interfering RNA - or siRNA. The findings, published in the journal ...
2014-11-13
Irvine, Calif., Nov. 13, 2014 -- A new bloodstream infection test created by UC Irvine researchers can speed up diagnosis times with unprecedented accuracy, allowing physicians to treat patients with potentially deadly ailments more promptly and effectively.
The UCI team, led by Weian Zhao, assistant professor of pharmaceutical sciences, developed a new technology called Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection. In as little as 90 minutes, IC 3D can detect bacteria in milliliters of blood with single-cell sensitivity; no cell culture is needed.
The work appears ...
2014-11-13
The Sudbury Basin located in Ontario, Canada is one of the largest known impact craters on Earth, as well as one of the oldest due to its formation more than 1.8 billion years ago. Researchers who took samples from the site and subjected them to a detailed geochemical analysis say that a comet may have hit the area to create the crater.
"Our analysis revealed a chondritic platinum group element signature within the crater's fallback deposits; however, the distribution of these elements within the impact structure and other constraints suggest that the impactor was a comet. ...
2014-11-13
Among overweight and obese adults who had asthma and participated in weight loss programs, more severe asthma, male sex, and improvements in eating behaviors were all linked with better success at losing weight.
The finding that individuals with more severe asthma may have a greater motivation to lose weight suggests that these individuals should be targeted for intervention. Also, gender tailoring of weight loss programs may be useful to enhance weight loss success, said Lisa Wood, senior author of the Respirology study.
INFORMATION: ...
2014-11-13
People can gauge the accuracy of their decisions, even if their decision making performance itself is no better than chance, according to a new study published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
In the study, people who showed chance-level decision making still reported greater confidence about decisions that turned out to be accurate and less confidence about decisions that turned out to be inaccurate. The findings suggest that the participants must have had some unconscious insight into their decision making, even though ...
2014-11-13
Philadelphia, PA (November 13, 2014) -- Patients on dialysis are very vulnerable during emergencies or disasters, but many are unprepared for such situations, according to two studies that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Dialysis patients are highly dependent on technologies to sustain their lives, with ongoing needs for transportation, electricity, and water for the dialysis apparatus. Interruption of these needs by a natural disaster can be devastating.
Naoka Murakami, MD, PhD ...
2014-11-13
TORONTO, Nov. 13, 2014--Canadians with cystic fibrosis are living almost 20 years longer than they did two decades ago, according to a research paper published today.
The median survival age was 49.7 years in 2012, up from 31.9 years in 1990, Dr. Anne Stephenson, a respirologist and research at St. Michael's Hospital wrote in the European Respiratory Journal. Since the paper was written, Dr. Stephenson has updated the median survival age to include Cystic Fibrosis Canada data from 2013 and reported the median age of survival has in fact reached 50.9 years.
In addition, ...
2014-11-13
Scientists from the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles describe a new distinctive fly species of the highly diverse genus Megaselia. The study published in the Biodiversity Data Journal proposes an innovative method for streamlining Megaselia species descriptions to save hours of literature reviews and comparisons.
The new species, M. shadeae, is easily distinguished by a large, central, pigmented and bubble-like wing spot. The description is part of the the Zurquí All Diptera Biodiversity Inventory (ZADBI) project, and represents the first of an incredible ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ocean primed for more El Niño: ANU media release
Salinity and temperature records from corals in a remote Pacific island in Kiribati show the ocean has warmed over the last sixty years and has set up the conditions for stronger El Niño weather events