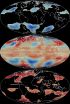
(Press-News.org) BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- It's widely known that the Earth's average temperature has been rising. But research by an Indiana University geographer and colleagues finds that spatial patterns of extreme temperature anomalies -- readings well above or below the mean -- are warming even faster than the overall average.
And trends in extreme heat and cold are important, said Scott M. Robeson, professor of geography in the College of Arts and Sciences at IU Bloomington. They have an outsized impact on water supplies, agricultural productivity and other factors related to human health and well-being.
"Average temperatures don't tell us everything we need to know about climate change," he said. "Arguably, these cold extremes and warm extremes are the most important factors for human society."
Robeson is the lead author of the article "Trends in hemispheric warm and cold anomalies," which will be published in the journal Geophysical Review Letters and is available online. Co-authors are Cort J. Willmott of the University of Delaware and Phil D. Jones of the University of East Anglia.
The researchers analyzed temperature records for the years 1881 to 2013 from HadCRUT4, a widely used data set for land and sea locations compiled by the University of East Anglia and the U.K. Met Office. Using monthly average temperatures at points across the globe, they sorted them into "spatial percentiles," which represent how unusual they are by their geographic size.
Their findings include:
Temperatures at the cold and warm "tails" of the spatial distribution -- the 5th and 95th percentiles -- increased more than the overall average Earth temperature.
Over the 130-year record, cold anomalies increased more than warm anomalies, resulting in an overall narrowing of the range of Earth's temperatures.
In the past 30 years, however, that pattern reversed, with warm anomalies increasing at a faster rate than cold anomalies.
"Earth's temperature was becoming more homogenous with time," Robeson said, "but now it's not."
The study records separate results for the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Temperatures are considerably more volatile in the Northern Hemisphere, an expected result because there's considerably less land mass in the South to add complexity to weather systems.
The study also examined anomalies during the "pause" in global warming that scientists have observed since 1998. While a 16-year-period is too short a time to draw conclusions about trends, the researchers found that warming continued at most locations on the planet and during much of the year, but that warming was offset by strong cooling during winter months in the Northern Hemisphere.
"There really hasn't been a pause in global warming," Robeson said. "There's been a pause in Northern Hemisphere winter warming."
Co-author Jones of the University of East Anglia said the study provides scientists with better knowledge about what's taking place with the Earth's climate. "Improved understanding of the spatial patterns of change over the three periods studied are vital for understanding the causes of recent events," he said.
It may seem counterintuitive that global warming would be accompanied by colder winter weather at some locales. But Robeson said the observation aligns with theories about climate change, which hold that amplified warming in the Arctic region produces changes in the jet stream, which can result in extended periods of cold weather at some locations in the mid-northern latitudes.
And while the rate of planetary warming has slowed in the past 16 years, it hasn't stopped. The World Meteorological Organization announced this month that 2014 is on track to be one of the warmest, if not the warmest, years on record as measured by global average temperatures.
In the U.S., the East has been unusually cold and snowy in recent years, but much of the West has been unusually warm and has experienced drought. And what happens here doesn't necessarily reflect conditions on the rest of the planet. Robeson points out that the United States, including Alaska, makes up only 2 percent of the Earth's surface.
INFORMATION:
To speak with Robeson about the research, contact Steve Hinnefeld at IU Communications, 812-856-3488 orslhinnef@iu.edu. To speak with Jones, contact Lisa Horton at the University of East Anglia Communication Office, l.horton@uea.ac.uk.
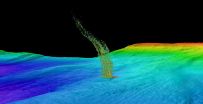
Off the West Coast of the United States, methane gas is trapped in frozen layers below the seafloor. New research from the University of Washington shows that water at intermediate depths is warming enough to cause these carbon deposits to melt, releasing methane into the sediments and surrounding water.
Researchers found that water off the coast of Washington is gradually warming at a depth of 500 meters, about a third of a mile down. That is the same depth where methane transforms from a solid to a gas. The research suggests that ocean warming could be triggering the ...
A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden shows that long-term endurance training in a stable way alters the epigenetic pattern in the human skeletal muscle. The research team behind the study, which is being published in the journal Epigenetics, also found strong links between these altered epigenetic patterns and the activity in genes controlling improved metabolism and inflammation. The results may have future implications for prevention and treatment of heart disease, diabetes and obesity.
"It is well-established that being inactive is perilous, and that regular ...
Malaria parasites invade human red blood cells; they then disrupt them and infect others. Researchers at the University of Basel and the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH) have now developed so-called nanomimics of host cell membranes that trick the parasites. This could lead to novel treatment and vaccination strategies in the fight against malaria and other infectious diseases. Their research results have been published in the scientific journal ACS Nano.
For many infectious diseases no vaccine currently exists. In addition, resistance against ...
This news release is available in German.
In the course of evolution, animals have become adapted to certain food sources, sometimes even to plants or to fruits that are actually toxic. The driving forces behind such adaptive mechanisms are often unknown. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, have now discovered why the fruit fly Drosophila sechellia is adapted to the toxic fruits of the morinda tree. Drosophila sechellia females, which lay their eggs on these fruits, carry a mutation in a gene that inhibits egg production. ...
Scientists can now explore nerves in mice in much greater detail than ever before, thanks to an approach developed by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Monterotondo, Italy. The work, published online today in Nature Methods, enables researchers to easily use artificial tags, broadening the range of what they can study and vastly increasing image resolution.
"Already we've been able to see things that we couldn't see before," says Paul Heppenstall from EMBL, who led the research. "Structures such as nerves arranged around a hair on the skin; ...
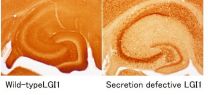
Researchers found out that the conformational defect in a specific protein causes Autosomal Dominant Lateral Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (ADLTE) which is a form of familial epilepsy. They showed that treatment with chemical corrector called "chemical chaperone" ameliorates increased seizure susceptibility in a mouse model of human epilepsy by correcting the conformational defect. This was published in Nature Medicine (December 8, 2014 electronic edition).
Mutations in the gene LGI1, encoding a secreted protein, cause familial temporal lobe epilepsy. The research group of ...
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Changing flesh to stone sounds like the work of a witch in a fairy tale.
But a new technique to transmute living cells into more permanent materials that defy rot and can endure high-powered probes is widening research opportunities for biologists who are developing cancer treatments, tracking stem cell evolution or even trying to understand how spiders vary the quality of the silk they spin.
The simple, silica-based method also offers materials scientists the ability to "fix" small biological entities like red blood cells into more commercially ...
As sand dunes march across the Sahara, vast dunes cross the surface of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. New research from a refurbished NASA wind tunnel reveals the physics of how particles move in Titan's methane-laden winds and could help to explain why Titan's dunes form in the way they do. The work is published online Dec. 8 in the journal Nature.
"Conditions on Earth seem natural to us, but models from Earth won't work elsewhere," said Bruce White, professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the University of California, Davis, and a co-author on the study. ...
ATLANTA - December 9, 2014- A new American Cancer Society study finds that despite significant drops in smoking rates, cigarettes continue to cause about three in ten cancer deaths in the United States. The study, appearing in the Annals of Epidemiology, concludes that efforts to reduce smoking prevalence as rapidly as possible should be a top priority for the U.S. public health efforts to prevent cancer deaths.
More than 30 years ago, a groundbreaking analysis by famed British researchers, Richard Doll and Richard Peto, calculated that 30 percent of all cancer deaths ...
Whether we're paying attention to something we see can be discerned by monitoring the firings of specific groups of brain cells. Now, new work from Johns Hopkins shows that the same holds true for the sense of touch. The study brings researchers closer to understanding how animals' thoughts and feelings affect their perception of external stimuli.
The results were published Nov. 25 in the journal PLoS Biology.
"There is so much information available in the world that we cannot process it all," says Ernst Niebur, Ph.D., a professor of neuroscience in the Johns Hopkins ...