(Press-News.org) Most flowering plants depend on pollinators such as bees to transfer pollen from the male anthers of one flower to the female stigma of another flower, enabling fertilization and the production of fruits and seeds. Bee pollination, however, involves an inherent conflict of interest, because bees are only interested in pollen as a food source.
"The bee and the plant have different goals, so plants have evolved ways to optimize the behavior of bees to maximize the transfer of pollen between flowers," explained Kathleen Kay, associate professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz.
In a study published December 23 in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, Kay's team described a pollination strategy involving flowers with two distinct sets of anthers that differ in color, size, and position. Darwin was mystified by such flowers, lamenting in a letter that he had "wasted enormous effort over them, and cannot yet get a glimpse of the meaning of the parts."
For years, the only explanation put forth for this phenomenon, called heteranthery, was that one set of anthers is specialized for attracting and feeding bees, while a less conspicuous set of anthers surreptitiously dusts them with pollen for transfer to another flower. This "division of labor" hypothesis has been tested in various species, and although it does seem to apply in a few cases, many studies have failed to confirm it.
The new study proposes a different explanation and shows how it works in species of wildflowers in the genus Clarkia. Through a variety of greenhouse and field experiments, Kay's team showed that heteranthery in Clarkia is a way for flowers to gradually present their pollen to bees over multiple visits.
"What's happening is the anthers open at different times, so the plant is doling out pollen to the bees gradually," Kay said.
This "pollen dosing" strategy is a way of getting the bees to move on to another flower without stopping to groom the pollen off their bodies and pack it away for delivery to their nest. Bees are highly specialized for pollen feeding, with hairs on their bodies that attract pollen electrostatically, stiff hairs on their legs for grooming, and structures for storing pollen on their legs or bodies.
"If a flower doses a bee with a ton of pollen, the bee is in pollen heaven and it will start grooming and then go off to feed its offspring without visiting another flower," Kay said. "So plants have different mechanisms for doling out pollen gradually. In this case, the flower is hiding some anthers and gradually revealing them to pollinators, and that limits how much pollen a bee can remove in each visit."
There are about 41 species of Clarkia in California, and about half of them have two types of anthers. These tend to be pollinated by specialized species of native solitary bees. Kay's team focused on bee pollination in two species of Clarkia, C. unguiculata (elegant clarkia) and C. cylindrica (speckled clarkia).
In these and other heterantherous clarkias, an inner whorl of anthers stands erect in the center of the flower, is visually conspicuous, and matures early, releasing its pollen first. An inconspicuous outer whorl lies back against the petals until after the inner anthers have opened. The outer anthers then move toward the center of the flower and begin to release their pollen gradually. A few days later, the stigma becomes erect and sticky, ready to receive pollen from another flower.
"In the field, you can see flowers in different stages, and using time-lapse photography we could see the whole sequence of events in individual flowers," Kay said.
The division of labor hypothesis requires both sets of anthers to be producing pollen at the same time. Kay said she decided to investigate heteranthery after observing clarkia flowers at a field site and realizing that explanation didn't fit. "I could see some flowers where one set was active, and some where the other set was active, but no flowers where both were active at the same time," she said.
In C. cylindrica, the two sets of anthers produce pollen with different colors, which enabled the researchers to track where it was going. Their experiments showed that pollen from both sets of anthers was collected for food and was also being transferred between flowers, contradicting the division of labor hypothesis.
"The color difference was convenient, because otherwise it's very hard to track pollen," Kay said. "We showed that bees are collecting and transporting pollen from both kinds of anthers, so they are not specialized for different functions."
Kay said she didn't realize how much time Darwin had spent puzzling over heteranthery until she started studying it herself. "He figured out so many things, it's hard to find a case where he didn't figure it out," she said. Darwin might have been on the right track, though. Shortly before his death, he requested seeds of C. unguiculata to use in experiments.
In addition to Kay, the coauthors of the paper include postdoctoral scholar Tania Jogesh and two UCSC undergraduates, Diana Tataru and Sami Akiba. Both students completed senior theses on their work and were supported by UCSC's Norris Center for Natural History.
INFORMATION:
COLUMBUS, Ohio - For those trying to live a healthy lifestyle, the choice between sugar and artificial sweeteners such as saccharin can be confusing. A new study led by researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and The Ohio State University College of Medicine found the sugar substitute saccharin doesn't lead to the development of diabetes in healthy adults as previous studies have suggested.
The study findings are published in the journal Microbiome.
"It's not that the findings of previous studies are wrong, they just didn't adequately control for things like ...
LA JOLLA, CALIF. - Jan 12, 2020 - Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute have identified the sensor in human lungs that detects SARS-CoV-2 and signals that it's time to mount an antiviral response. The study, published today in Cell Reports, provides insights into the molecular basis of severe disease and may enable new strategies for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19.
"Our research has shown that MDA-5 is the immune cop that's tasked to keep an eye out for SARS-CoV-2 and call for back-up," says Sumit Chanda, Ph.D., director of the Immunity and Pathogenesis Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys and senior author of ...
Family courts are misunderstanding and misusing research around how children form close relationships with their caregivers, say an international group of experts.
Seventy experts from across the globe argue that widespread misunderstandings around attachment research have hampered its accurate implementation, with potentially negative consequences for decisions in family courts.
In response, they have published an international consensus statement in Attachment & Human Development that aims "to counter misinformation and help steer family court applications of attachment theory in a supportive, evidence-based direction on matters related to child protection and custody decisions".
In the statement, the group sets out three principles from attachment research ...
Philadelphia, January 12, 2021 - A special issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology (JACR), published by Elsevier, challenges conventional wisdom across the imaging community. This collection of articles, the "Provocative Issue," presents extreme opinions on pressing issues confronting radiologists with the deliberate aim of sparking positive dialog and debate that will lead to innovative solutions to improve patient care and imaging-related outcomes.
The issue is guest-edited by:
Caroline Chung, MD, MSc, Director of Advanced ...
ATLANTA - JANUARY 12, 2021 - Overall cancer death rates in the United States dropped continuously from 1991 through 2018 for a total decrease of 31%, including a 2.4% decline from 2017 to 2018. The news comes from the American Cancer Society's annual Cancer Statistics, 2021 article, appearing in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, and its consumer version, Cancer Facts & Figures 2021. This year marks the American Cancer Society's 70th anniversary of reporting this data to inform the nation's fight against cancer.
The report estimates that in the U.S. in 2021, almost 1.9 million (1,898,160) new cancer cases will be diagnosed and 608,570 Americans will die from cancer. ...
Remarkably well-preserved fossils are helping scientists unravel a mystery about the origins of early animals that puzzled Charles Darwin.
Analysis of the 547 million-year-old remains has enabled researchers to trace the ancestry of some of the world's earliest animals further back than ever before.
Their study has uncovered the first known link between animals that evolved during the so-called Cambrian Explosion some 540 million-years-ago and one of their early ancestors.
Until recently, little was known about the origins of animals that evolved during the Cambrian event because of a lack of well-preserved fossil evidence.
The mysterious origins of animals that evolved at this time - when the diversity ...
Core technology includes promising bivalent single-domain antibodies simultaneously targeting two surface structures of the viral spike protein.
Lead candidates DIOS-202 and DIOS-203 are engineered for high potency and their potential to avoid the emergence of escape mutants.
DIOS-202 and DIOS-203 entered into accelerated development to initiate clinical studies later this year.
BONN, Germany, January 12, 2021 - DiosCURE SE announced a publication in Science describing its core technology of multivalent single-chain antibodies with a unique molecular mode-of-action to inactivate ...
While most people are able to eat a normal diet, many of those managing distinct nutritional requirements related to a disease or health condition rely on medical foods. Medical foods help patients meet their nutritional needs, often improving nutritional and health outcomes and quality of life. A recent publication in Current Developments in Nutrition, titled "Medical Foods: Science, Regulation, and Practical Aspects. Summary of a Workshop," shares the historical and regulatory context of medical foods and perspectives on their role in the future.
Medical foods help patients manage their nutritional needs, yet it can be very difficult for patients to have access to them. In August 2019, the Healthcare Nutrition Council (HNC), in partnership with the American Society ...
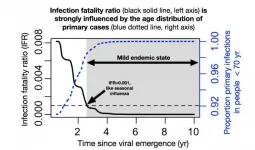
What is the endgame for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that is causing worldwide devastation? If it becomes endemic -- circulating in the general population -- and most people are exposed in childhood, SARS-CoV-2 may join the ranks of mild cold-causing coronaviruses that currently circulate in humans, according to a model developed by Emory and Penn State scientists.
The model, published January 12 in Science, draws upon studies of the four common cold coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-1. For those viruses, the term "herd immunity" is incomplete and possibly misleading, says ...
Antibodies are an important weapon in the immune system's defense against infections. They bind to the surface structures of bacteria or viruses and prevent their replication. One strategy in the fight against disease is therefore to produce effective antibodies in large quantities and inject them into the patients. The outgoing US President Donald Trump probably owes his rapid recovery to this method. However, the antibodies used to treat him have a complex structure, do not penetrate very deeply into the tissue and may cause unwanted complications. Moreover, producing antibodies is difficult and time-consuming. They are therefore probably not suitable for widespread use.
Mass production in yeast or bacteria
"We focus on another group of molecules, the nanobodies," ...