"This type of wearable would be very helpful for people with underlying medical conditions to monitor their own health on a regular basis," said Lu Yin, a nanoengineering Ph.D. student at UC San Diego and co-first author of the study published Feb. 15 in Nature Biomedical Engineering. "It would also serve as a great tool for remote patient monitoring, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic when people are minimizing in-person visits to the clinic."
Such a device could benefit individuals managing high blood pressure and diabetes--individuals who are also at high risk of becoming seriously ill with COVID-19. It could also be used to detect the onset of sepsis, which is characterized by a sudden drop in blood pressure accompanied by a rapid rise in lactate level.
One soft skin patch that can do it all would also offer a convenient alternative for patients in intensive care units, including infants in the NICU, who need continuous monitoring of blood pressure and other vital signs. These procedures currently involve inserting catheters deep inside patients' arteries and tethering patients to multiple hospital monitors.
"The novelty here is that we take completely different sensors and merge them together on a single small platform as small as a stamp," said Joseph Wang, a professor of nanoengineering at UC San Diego and co-corresponding author of the study. "We can collect so much information with this one wearable and do so in a non-invasive way, without causing discomfort or interruptions to daily activity."
The new patch is a product of two pioneering efforts in the UC San Diego Center for Wearable Sensors, for which Wang serves as director. Wang's lab has been developing wearables capable of monitoring multiple signals simultaneously--chemical, physical and electrophysiological--in the body. And in the lab of UC San Diego nanoengineering professor Sheng Xu, researchers have been developing soft, stretchy electronic skin patches that can monitor blood pressure deep inside the body. By joining forces, the researchers created the first flexible, stretchable wearable device that combines chemical sensing (glucose, lactate, alcohol and caffeine) with blood pressure monitoring.
"Each sensor provides a separate picture of a physical or chemical change. Integrating them all in one wearable patch allows us to stitch those different pictures together to get a more comprehensive overview of what's going on in our bodies," said Xu, who is also a co-corresponding author of the study.
Patch of all trades
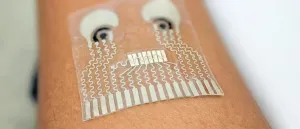
The patch is a thin sheet of stretchy polymers that can conform to the skin. It is equipped with a blood pressure sensor and two chemical sensors--one that measures levels of lactate (a biomarker of physical exertion), caffeine and alcohol in sweat, and another that measures glucose levels in interstitial fluid.
The patch is capable of measuring three parameters at once, one from each sensor: blood pressure, glucose, and either lactate, alcohol or caffeine. "Theoretically, we can detect all of them at the same time, but that would require a different sensor design," said Yin, who is also a Ph.D. student in Wang's lab.
The blood pressure sensor sits near the center of the patch. It consists of a set of small ultrasound transducers that are welded to the patch by a conductive ink. A voltage applied to the transducers causes them to send ultrasound waves into the body. When the ultrasound waves bounce off an artery, the sensor detects the echoes and translates the signals into a blood pressure reading.
The chemical sensors are two electrodes that are screen printed on the patch from conductive ink. The electrode that senses lactate, caffeine and alcohol is printed on the right side of the patch; it works by releasing a drug called pilocarpine into the skin to induce sweat and detecting the chemical substances in the sweat. The other electrode, which senses glucose, is printed on the left side; it works by passing a mild electrical current through the skin to release interstitial fluid and measuring the glucose in that fluid.
The researchers were interested in measuring these particular biomarkers because they impact blood pressure. "We chose parameters that would give us a more accurate, more reliable blood pressure measurement," said co-first author Juliane Sempionatto, a nanoengineering Ph.D. student in Wang's lab.
"Let's say you are monitoring your blood pressure, and you see spikes during the day and think that something is wrong. But a biomarker reading could tell you if those spikes were due to an intake of alcohol or caffeine. This combination of sensors can give you that type of information," she said.
In tests, subjects wore the patch on the neck while performing various combinations of the following tasks: exercising on a stationary bicycle; eating a high-sugar meal; drinking an alcoholic beverage; and drinking a caffeinated beverage. Measurements from the patch closely matched those collected by commercial monitoring devices such as a blood pressure cuff, blood lactate meter, glucometer and breathalyzer. Measurements of the wearers' caffeine levels were verified with measurements of sweat samples in the lab spiked with caffeine.
Engineering challenges
One of the biggest challenges in making the patch was eliminating interference between the sensors' signals. To do this, the researchers had to figure out the optimal spacing between the blood pressure sensor and the chemical sensors. They found that one centimeter of spacing did the trick while keeping the device as small as possible.
The researchers also had to figure out how to physically shield the chemical sensors from the blood pressure sensor. The latter normally comes equipped with a liquid ultrasound gel in order to produce clear readings. But the chemical sensors are also equipped with their own hydrogels, and the problem is that if any liquid gel from the blood pressure sensor flows out and makes contact with the other gels, it will cause interference between the sensors. So instead, the researchers used a solid ultrasound gel, which they found works as well as the liquid version but without the leakage.
"Finding the right materials, optimizing the overall layout, integrating the different electronics together in a seamless fashion--these challenges took a lot of time to overcome," said co-first author Muyang Lin, a nanoengineering Ph.D. student in Xu's lab. "We are fortunate to have this great collaboration between our lab and Professor Wang's lab. It has been so fun working together with them on this project."
Next steps
The team is already at work on a new version of the patch, one with even more sensors. "There are opportunities to monitor other biomarkers associated with various diseases. We are looking to add more clinical value to this device," Sempionatto said.
Ongoing work also includes shrinking the electronics for the blood pressure sensor. Right now, the sensor needs to be connected to a power source and a benchtop machine to display its readings. The ultimate goal is to put these all on the patch and make everything wireless.
"We want to make a complete system that is fully wearable," Lin said.
INFORMATION:
Paper: "An epidermal patch for the simultaneous monitoring of haemodynamic and metabolic biomarkers."
This research was supported by the UC San Diego Center of Wearable Sensors and the National Institutes of Health (grant no. 1R21EB027303-01A1).