INFORMATION:
Notes to Editors
The N8 AgriFood programme is a unique research collaboration, combining expertise and multiple disciplines from the 8 research intensive universities in the North of England - Durham University, Lancaster University, the University of Leeds, the University of Liverpool, the University of Manchester, Newcastle University, the University of Sheffield and the University of York.
The programme takes a food systems approach to tackling the challenges facing food security. Through effective collaboration across the sector with industry, government, SMEs, NGOs and charities, N8 AgriFood aims to generate new knowledge to tackle these complex challenges. Find out more about the N8 AgriFood programme: http://www.n8agrifood.ac.uk
N8 AgriFood has recently launched the Food Systems Policy Hub (https://policyhub.n8agrifood.ac.uk/) and is helping to address the various challenges the food system faces through academic research that has real-world impact. Find out more about how N8 AgriFood is helping to tackle childhood food poverty: https://policyhub.n8agrifood.ac.uk/launch-week/childhood-food-poverty/
Families have high awareness of healthy eating but struggle to access good food
Families have high awareness of healthy eating but low income means many struggle to access good food
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) Low-income families have a high awareness of healthy diets but can't afford good quality and nutritious food, new research shows.
The University of York study, in partnership with N8Agrifood, showed that participants tried to eat as much fruit and vegetables as they could within financial constraints, avoiding processed food wherever possible. But there was widespread acknowledgement that processed food was often more accessible than healthy options because of its lower cost.
The researchers said that while the diets of low-income households have been subject to much scrutiny and debate, there is currently limited evidence in the UK on the diet quality and food practices of households reporting food insecurity and food bank use.
Dr Maddy Power, from the Department of Health Sciences said: "This research explores lived experiences of food insecurity, the notion of individual 'choice' and the underlying drivers of diet quality among low income families.
"The findings suggest that educational interventions are likely to be less effective in tackling food insecurity and poor nutrition among people living on a low income, as the people who took part in our study had good knowledge about healthy diets, but quite simply couldn't afford to buy what was needed to maintain a recommended healthy diet."
Participants reported that access to healthy and fresh food was further constrained by geographic access. The availability of fresh and healthy food in local shops was perceived to be poor, but the cost of travelling to large supermarkets, where the quality and diversity of food may be better, was considered prohibitively expensive.
Awareness of being priced out of nutritious and fresh food because of low income reinforced the stigma of living with poverty and was a very visible and everyday example of socio-economic inequality particularly for parents and caregivers, who were keen to ensure their children had access to a healthy diet.
One respondent said, "It's not nice to feel you can't buy food that is healthy or better because it's more expensive."
Other participants acknowledged that processed food was often more accessible than 'healthy' options because of its lower cost with one person saying: "Healthy food is expensive and unhealthy food is cheap."
Researchers say policies focusing on addressing structural drivers, including poverty and geographical access to food, are needed.
The research also suggested a relationship between higher processed food consumption and having used a food bank.
Researchers say that the pandemic and the associated economic fallout has precipitated a sharp increase in food insecurity in the UK. In July 2020, roughly 16 per cent of adults - equivalent to 7.8 million people - reduced meal sizes or skipped meals due to insufficient income for food. This figure, which remained stable between April and July 2020, is roughly double rates of food insecurity before Covid-19
The study took place between 2018 and 2020 and involved participatory research conducted with families of primary school age children.
Dr Katie Jayne Pybus and Professor Kate Pickett from the Department of Health Sciences and Professor Bob Doherty from The York Management School also contributed to the research.
The paper called, "The reality is that on Universal Credit I cannot provide the recommended amount of fresh fruit and vegetables per day for my children": Moving the conversation from a behavioural to a systemic understanding of food practices and purchases is published in Emerald Open Research as part of the N8Agrifood Collection.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
For students of color, online racism leads to real-world mental health challenges
2021-02-23
Whether it's a "Zoombomb" filled with racial slurs, a racist meme that pops up in a Facebook timeline, or a hate-filled comment on an Instagram post, social media has the power to bring out the worst of the worst.
For college students of color who encounter online racism, the effect of racialized aggressions and assaults reaches far beyond any single social media feed and can lead to real and significant mental health impacts - even more significant than in-person experiences of racial discrimination, according to a recently published study from researchers at UConn and Boston College.
"I think we all suspected that we would find a relationship between the racism online in social media and student mental health," says lead author Adam McCready, an assistant professor-in-residence ...
ET phones home!
2021-02-23
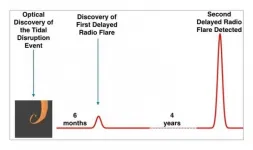
A team of researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI) led by Dr. Assaf Horesh have discovered the first evidence of radio flares emitted only long after a star is destroyed by a black hole. Published in the periodical Nature Astronomy, the discovery relied upon ultra-powerful radio telescopes to study these catastrophic cosmic events in distant galaxies called Tidal Disruption Events (TDE). While researchers had known that these events cause the release of radio flares, this latest discovery saw those flares being emitted months or even years after the stellar disruption. The team was led by Dr. Horesh from the Racah Institute of Physics at the Hebrew together with the NASA Swift space telescope director Professor Brad Cenko and Dr. Iair ...
For selenium in rivers, timing matters
2021-02-23
Selenium contamination of freshwater ecosystems is an ongoing environmental health problem around the world. A naturally occurring trace element, selenium levels are high in some geologic formations like sedimentary shales that form much of the bedrock in the Western United States. Soils derived from this bedrock, and weathering of shale outcrops, can contribute high levels of selenium to surrounding watersheds.
New research out today in Environmental Science & Technology from UConn Assistant Professor of Natural Resources and the Environment Jessica Brandt with Travis Schmidt and colleagues at the United States Geological Survey (USGS) investigates some of the complexities of selenium and how it moves through the ecosystem during runoff ...
Cre-controlled CRISPR: Conditional gene inactivation just got easier
2021-02-23
To discover the function of a gene researchers turn it off and observe the consequences. Often genes have multiple functions that differ depending on a tissue and age. Some genes are essential to growth and turning them off too early can have profound consequences that can make observing other functions impossible. To avoid it, researchers have been using conditional gene inactivation which allows turning a gene off only in a specific tissue or later in development, e.g., in adulthood.
One of the systems used for conditional gene inactivation is Cre/lox. "It is the gold standard for the conditional gene inactivation in mice but over time has also become quite important in other model ...
Spintronics: New production method makes crystalline microstructures universally usable
2021-02-23
New storage and information technology requires new higher performance materials. One of these materials is yttrium iron garnet, which has special magnetic properties. Thanks to a new process, it can now be transferred to any material. Developed by physicists at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the method could advance the production of smaller, faster and more energy-efficient components for data storage and information processing. The physicists have published their results in the journal "Applied Physics Letters".
Magnetic materials play a major role in the development of ...
The way a fish swims reveals a lot about its personality, say scientists
2021-02-23
The way a fish swims reveals a lot about its personality, say scientists
Personality has been described in all sorts of animal species, from ants to apes. Some individuals are shy and sedentary, while others are bold and active. Now a new study published in Ecology and Evolution has revealed that the way a fish swims tells us a lot about its personality.
This new research suggests experts can reliably measure animal personality simply from the way individual animals move, a type of micropersonality trait, and that the method could be used to help scientists understand about personality differences in wild animals.
A team of biologists and mathematicians from Swansea University and the University of Essex filmed the movements of 15 three-spined stickleback ...
B cells continue to work against SARS-CoV-2 months after infection, but do not recognize mutant
2021-02-23
A new analysis of B cells and more than 1,000 different monoclonal antibodies from 8 patients with COVID-19 shows that, contrary to previous hypotheses, protective B cell responses to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein remain stable and continue to evolve over a 5-month period, many months after the initial period of active viral replication. However, a large proportion of the neutralizing antibodies generated from these long-lasting B cells did not efficiently recognize various emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants from Brazil and South Africa. These results - from an academia-industry collaboration - will help inform the design of future COVID-19 vaccines that work to constrain viral evolution and stimulate ...
Scientists identify potential contributor to hyper immune responses in patients with severe COVID-19
2021-02-23
Researchers have pinpointed a helper T cell population in the lungs of patients with severe COVID-19 that may be central to the development of hyperinflammation, lung injury, and subsequent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during disease. Their data support the ongoing investigation of anti-cytokine therapies that target this cell subset, called tissue-resident memory-like Th17 cells (Trm17). To date, the bulk of research on immune responses to COVID-19 has mainly focused on T cells in the blood, while the role of tissue-specific immune cells in the inflamed lung has remained unclear. Accumulating evidence suggests that one of the causes of ...
Mouse study shows bacteriophage therapy could fight drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
2021-02-23
WHAT:
Using viruses instead of antibiotics to tame troublesome drug-resistant bacteria is a promising strategy, known as bacteriophage or "phage therapy." Scientists at the National Institutes of Health have used two different bacteriophage viruses individually and then together to successfully treat research mice infected with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 (ST258). The bacterium K. pneumoniae ST258 is included on a CDC list of biggest antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. High rates of morbidity and mortality are associated with untreated K. pneumoniae infections.
Phage therapy has been pursued for about a century, though conclusive research studies are rare and clinical results--from ...
'Walking' molecule superstructures could help create neurons for regenerative medicine
2021-02-23
Imagine if surgeons could transplant healthy neurons into patients living with neurodegenerative diseases or brain and spinal cord injuries. And imagine if they could "grow" these neurons in the laboratory from a patient's own cells using a synthetic, highly bioactive material that is suitable for 3D printing.
By discovering a new printable biomaterial that can mimic properties of brain tissue, Northwestern University researchers are now closer to developing a platform capable of treating these conditions using regenerative medicine.
A key ingredient to the discovery is the ability to control the self-assembly processes of molecules within the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
University of Miami business technology department ranked No. 1 in the nation for research productivity
Researchers build ultra-efficient optical sensors shrinking light to a chip
Why laws named after tragedies win public support
Missing geomagnetic reversals in the geomagnetic reversal history
EPA criminal sanctions align with a county’s wealth, not pollution
“Instead of humans, robots”: fully automated catalyst testing technology developed
Lehigh and Rice universities partner with global industry leaders to revolutionize catastrophe modeling
Engineers sharpen gene-editing tools to target cystic fibrosis
Pets can help older adults’ health & well-being, but may strain budgets too
First evidence of WHO ‘critical priority’ fungal pathogen becoming more deadly when co-infected with tuberculosis
World-first safety guide for public use of AI health chatbots
Women may face heart attack risk with a lower plaque level than men
Proximity to nuclear power plants associated with increased cancer mortality
Women’s risk of major cardiac events emerges at lower coronary plaque burden compared to men
Peatland lakes in the Congo Basin release carbon that is thousands of years old
Breadcrumbs lead to fossil free production of everyday goods
New computation method for climate extremes: Researchers at the University of Graz reveal tenfold increase of heat over Europe
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
[Press-News.org] Families have high awareness of healthy eating but struggle to access good foodFamilies have high awareness of healthy eating but low income means many struggle to access good food