(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill. - Pumpkin growers dread the tiny tan scabs that form on their fruit, each lesion a telltale sign of bacterial spot disease. The specks don't just mar the fruit's flesh, they provide entry points for rot-inducing fungus and other pathogens that can destroy pumpkins and other cucurbits from the inside out. Either way, farmers pay the price, with marketable yields reduced by as much as 90%.
Despite the disease's severity, scientists don't know much about the genetics of the pathogen that causes it; nearly all the molecular information required for accurate diagnostic testing and targeted treatments is lacking for the disease.
In a new study, University of Illinois scientists, with the help of two undergraduate students, have assembled the first complete genome for the bacteria that causes the disease, Xanthomonas cucurbitae, and identified genes that are activated during infection.
"Assembling a complete circular genome means we now have the resources to better understand what's happening in the field. We can use this information to look at how the pathogen is spreading, whether there are differences in host specificity among sub-populations or strains, or how likely it is to develop resistance to chemical controls," says Sarah Hind, assistant professor in the Department of Crop Sciences at Illinois and senior author on the Phytopathology study.
After sequencing the genome, Hind's group compared it to genomes from 12 other Xanthomonas species that cause diseases in a variety of crop plants like tomato, rice, citrus, and wheat. Surprisingly, given its penchant for creating havoc in the field, Xanthomonas cucurbitae had the smallest genome and had fewer genes known to be important for other Xanthomonas species to cause disease.
"As this pathogen lacks many of the known virulence (i.e., disease-causing) genes, we don't know exactly which genes are needed by the pathogen to infect cucurbit plants," Hind says. "It could be something we've never seen before, such as a new gene or a mechanism that evolved in this species that isn't seen in the rest of the family. That could be very exciting."
To get closer to an answer, the research team grew the bacteria in liquid media that mimicked its host environment and identified more than 400 genes whose expression was altered when the pathogen interacted with its "host." In particular, they observed increased expression of genes for enzymes related to the breakdown of plant tissues, which are key for further development of the disease.
If Hind's team can learn more about these factors and how cucurbits respond to them, there may be a way to prevent the bacteria from penetrating pumpkin fruits in the first place. "That would really save the farmers," she says. "They don't care as much when it gets on the leaves, but if it infects the fruit, they're in trouble."
Hind adds, "This project wouldn't have been possible without the contributions of some really talented undergraduate students. We love having students participate in our research. They bring a sense of enthusiasm and eagerness - as well as really creative ideas - to the lab that would be hard to generate otherwise."
Although both students graduated, see new Crop Sciences students contributing to Hind's other pumpkin projects in this video. High school and transfer students can learn more about Crop Sciences coursework online.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Genome sequencing and functional characterization of Xanthomonas cucurbitae, the causal agent of bacterial spot disease of cucurbits," is published in Phytopathology [DOI: 10.1094/PHYTO-06-20-0228-R]. Authors include Rikky Rai, Julius Pasion, Tanvi Majumdar, Cory Green, and Sarah Hind. The research was supported with USDA Hatch funds, as well as an ACES Undergraduate Research Scholarship to Tanvi Majumdar.
The Department of Crop Sciences is in the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Cambridge, MA - Astronomers have now obtained a new view of the supermassive black hole at the center of galaxy M87. Images released today by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration reveal how the black hole, some 55 million light-years away, appears in polarized light.
The image marks the first time astronomers have captured and mapped polarization, a sign of magnetic fields, so close to the edge of a black hole.
Scientists still don't understand how magnetic fields -- areas where magnetism affects how matter moves -- influence black hole activity. Do they help direct matter into the hungry mouths of black holes? Can ...
When clinical trials were conducted to determine the immunogenicity -- the ability to elicit an immune response -- for the first two vaccines marshaled against SARS-CoV-2the virus that causes COVID-19, one group was not among those included: people who have received solid organ transplants and others (such as those with autoimmune disorders) who are immunocompromised.
Now, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have tried to rectify that inequity, taking one of the first looks at how people who are immunocompromised respond to their first dose of one of the two mRNA vaccines -- Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech -- currently being administered worldwide. Their findings, as published March 15, 2021, in a research letter in the END ...
DANVILLE, Pa. - A survey of Geisinger employees conducted over two weeks in December 2020 found a steady increase in intent among healthcare workers to receive the COVID-19 vaccine.
On Dec. 4, 2020, an announcement about anticipated vaccine availability was emailed to all 23,784 Geisinger employees. Recipients were asked to indicate their intention to receive a vaccine when one was available to them and the reasons for any hesitation they might have. More than two-thirds of employees responded to the survey.
Of those who completed the survey before Dec. 10, when an independent FDA advisory committee ...
News coverage of expert scientific evidence on vaccine safety is effective at increasing public acceptance of vaccines, but the positive effect is diminished when the expert message is juxtaposed with a personal narrative about real side effects, new research has found.
The study, by researchers affiliated with the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Illinois, tested the effects of messages about vaccination in televised news reports. These included video clips of Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, talking about evidence supporting the value and safety of the MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine, and a mother who's refusing to vaccinate ...
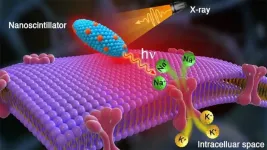
Scientists make pivotal discovery of method for wireless modulation of neurons with X-rays that could improve the lives of patients with brain disorders. The X-ray source only requires a machine like that found in a dentist's office.
Many people worldwide suffer from movement-related brain disorders. Epilepsy accounts for more than 50 million; essential tremor, 40 million; and Parkinson's disease, 10 million.
Relief for some brain disorder sufferers may one day be on the way in the form of a new treatment invented by researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and ...
Researchers Mario Guarracino the HSE Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Networks Analysis in Nizhny Novgorod and Julius ?ilinskas and Algirdas Lančinskas from Vilnius University, have proposed a new method of testing for COVID-19. This group method allows results to be obtained 13 times faster as compared to individual testing of each sample. The research paper was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The COVID-19 pandemic has already affected millions of people from over 200 countries. The rapid virus expansion demonstrated how fast such infections can spread in today's globalized world. At the beginning of the pandemic, when little was known about the virus and vaccines had not yet ...
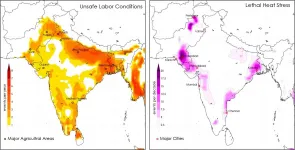
WASHINGTON--Residents of South Asia already periodically experience heat waves at the current level of warming. But a new study projecting the amount of heat stress residents of the region will experience in the future finds with 2 degrees Celsius of warming, the population's exposure to heat stress will nearly triple.
Limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius will likely reduce that impact by half, but deadly heat stress will become commonplace across South Asia, according to the new study in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU's journal publishing high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
With ...
An old technique flexes its muscles
Sarcomeres are small repeating subunits of myofibrils, the long cylinders that bundle together to make the muscle fibres. Inside the sarcomeres, filaments of the proteins myosin and actin interact to generate muscle contraction and relaxation. So far, traditional experimental approaches to investigate the structure and function of muscle tissue were performed on reconstructed protein complexes or suffered from low resolution. "Electron cryo-tomography, instead, allows us to obtain detailed and artefact-free 3D images of the frozen muscle", says Raunser.
Cryo-ET was for a long time an established yet niche methodology. But recent technical advances in electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) as well as the new development of ...
In the heart of black cherry's native range, including a part of the Allegheny Hardwoods that bills itself as the "Black Cherry Capital of the World," the tree's regeneration, growth and survival have all been declining for more than a decade. In a new analysis, a team of USDA Forest Service and University of Missouri scientists identify likely factors behind the tree's decline and, more significantly, conclude that black cherry may be the tip of the iceberg in terms of change in eastern deciduous forests.
Scientists used a combination of synthesis of existing research and new analyses to examine the leading hypotheses for black cherry's regeneration failure. They conclude that the two factors that are ...
Family-centered prevention programs that foster protective caregiving can buffer the negative effects of racial discrimination on young Black people, according to a study published by University of Georgia researchers.
Research shows that Black youth exposed to various levels of racial discrimination--including slurs, threats and false accusations--are at a high risk for poor mental health outcomes such as hopelessness, conduct problems, drug use and depression. After participating in family-oriented programs, high school-age adolescents who encountered high levels of racial discrimination and received supportive caregiving evinced fewer increases in conduct problems and depression/anxiety symptoms two years later.
"This research shows that ...