New biomarkers of malignant melanoma identified
Scientists identify new biomarkers in patients with malignant melanoma, which could help in its diagnosis and prognosis
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) Their study has shown that these malignant melanoma vesicles produced by CSCs have a different molecular composition from that of differentiated tumour cells. These molecules were also found to be detectable in exosomes present in the blood, and they presented differences in patients with malignant melanoma compared to healthy individuals. This makes them potentially suitable as biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of this disease.
The results have been published in the prestigious scientific journal Molecular Oncology.
Malignant melanoma is one of the most aggressive types of skin cancer and its prevalence has been increasing worldwide in recent years. Among the factors that contribute to the life-threatening nature and severity of this disease are the late appearance of the first symptoms, the lack of effective treatments, its high metastasis capacity, and also the difficulty of detecting this particular cancer. Unfortunately, the diagnosis of malignant melanoma therefore continues to be problematic due to the lack of indicators--known as biomarkers--to accurately signal the early stages of this disease and predict how it might evolve in a given patient, once detected.
These characteristics, which make this type of cancer such a serious disease, may be partly attributable to so-called cancer stem cells (CSCs), a sub-population of cells that exist in tumours and that present the typical characteristics of stem cells. They are responsible for tumour initiation, maintenance, and progression, as well as metastasis and recurrence--even years after a tumour has been eradicated.
Now, a team of scientists led by Professor Juan Antonio Marchal Corrales of the Department of Human Anatomy and Embryology at the University of Granada (UGR) and Director of the "Doctores Galera y Requena" Chair in Research on Cancer Stem Cells, pertaining to the Biohealth Research Institute in Granada (ibs.GRANADA) and the MNat Scientific Unit of Excellence (ModelingNature), has studied these CSCs--specifically, the microvesicles that act as "messengers" for these cells. Known as exosomes, these cells produce and send other cells and tissues to communicate via the transfer of certain biomolecules, thereby promoting the emergence of metastases.
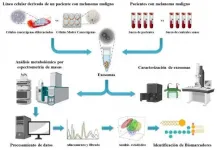
These exosomes have been shown to be involved in many tumour processes. As cells release them and circulate via the bloodstream, they offer a very interesting source of biomarkers as they can be easily isolated from a blood sample. This study focused on the molecular characterization of exosomes produced by CSCs and isolated in the blood from patients with malignant melanoma. Metabolomic techniques were used to analyse the molecular profile of biological systems in order to identify possible biomarkers for the diagnosis of this disease.
This study is the result of extensive multidisciplinary work in which translational researchers, bioinformaticians, and clinical researchers have joined forces to take another step in the field of Personalized Medicine or Precision Medicine in Oncology. The team comprises members from the UGR; Fundación MEDINA (led by Francisca Vicente and José Pérez del Palacio, Area Head and Principal Investigator of the Screening Department, respectively); and the "Virgen de las Nieves" and "San Cecilio" Teaching Hospitals in Granada (all members of ibs.GRANADA ); the University of Vigo; and the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO).
Among its findings, the study showed that the molecular composition of exosomes produced by CSCs is different from those released by differentiated tumour cells. To investigate this, using a primary patient-derived malignant melanoma cell line enriched in CSCs, both types of cells were cultivated in large quantities and the exosomes that they produced and released into the culture were isolated. Once the properties and characteristics of both the cells and the exosomes they produced had been tested, a metabolomic analysis was carried out. This enabled the molecules (metabolites) present in the biological sample to be studied. After the molecules had been detected and extracted using a mass spectrometer, which quantifies them with great precision, a series of statistical analyses were carried out to determine which molecules were found in the highest concentration in the exosomes of each cell type. Thus, the researchers tentatively identified some lipidic metabolites differentially present in exosomes of CSCs and differentiated tumour cells.
Metabolomic profile
Subsequently, and following the same scientific approach, a similar study was carried out comparing the metabolomic profile of exosomes isolated from the blood of patients with malignant melanoma in different stages and healthy individuals who acted as controls. The study concluded that certain metabolites, including some of those previously identified in CSCs, were also present in exosomes isolated from blood in different concentrations among melanoma patients and healthy individuals. By means of the corresponding statistical models, these molecules and their different concentrations in blood made it possible to distinguish individuals with malignant melanoma from those without the disease. This makes them suitable candidates for acting as potential biomarkers for its diagnosis.
However, the authors emphasise that this study is only a first step. The identification of some of these molecules, the complete characterization of those already tentatively identified, and the replication of the study with a greater number of samples to validate and verify their clinical application as biomarkers all remain pending.
Studies such as this constitute a new avenue for the discovery of cancer biomarkers aimed at improving early diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment-response prediction. And, of course, these results can be extrapolated to many other tumours, in the quest to identify biomarkers that help us better understand the pathogenesis of these diseases and achieve personalized precision medicine.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by: the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (project RTI2018-101309 -B-C2) and the Training Programme for University Teaching Staff (FPU) awarded to José Luis Palacios Ferrer (ref: FPU15/03682); the "Carlos III" Health Institute (project PIE16- 00045); the Ministry of Economy, Knowledge, Business and University of the Junta de Andalucía; the European Regional Development Fund (project SOMM17/6109/UGR, UCE-PP2017-3), the UGR's "Doctores Galera y Requena" Chair in Research on Cancer Stem Cells; and Fundación MEDINA.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-25
Dr. Rosario González-Férez, a researcher at the Department of Atomic, Molecular and Nuclear Physics and the "Carlos I" Institute of Theoretical and Computational Physics of the University of Granada, has published the article "Ultralong-Range Rydberg Bi-molecules" in the prestigious scientific journal Physical Review Letters. The results of the study show a new type of bi-molecule formed from two nitric oxide (NO) molecules, both in their ground state and in the Rydberg electronic state.
The work was made possible thanks to the scientific collaboration between the researcher and the Institute for Theoretical Atomic, Molecular ...
2021-03-25
The novel label-free assay uses unconventional L and inverse-L shaped pillars of deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) microfluidic technology to quantify and profile immune states of white blood cells (WBCs) by assessing biophysical properties of size, deformation, distribution, and cell count
The assay requires only 20 microlitres (μl) of unprocessed blood and takes just 15 minutes - much faster than existing methods which require up to 15 millilitres (ml) of blood and take at least a few hours to produce results
This new technology measures and profiles the often volatile host immune response, resulting in a more accurate assessment of patient pathophysiology
Current methods for early diagnosis of infection focus on ...
2021-03-25
For almost a century, physicists have been intrigued by the fundamental question: why are complex numbers so important in quantum mechanics, that is, numbers containing a component with the imaginary number i? Usually, it was assumed that they are only a mathematical trick to facilitate the description of phenomena, and only results expressed in real numbers have a physical meaning. However, a Polish-Chinese-Canadian team of researchers has proved that the imaginary part of quantum mechanics can be observed in action in the real world.
We need to significantly reconstruct our naive ...
2021-03-25
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have investigated how the X and Y chromosomes evolve and adapt to each other within a population. The results show that breaking up coevolved sets of sex chromosomes could lead to lower survival rates among the offspring - something that could be of importance in species conservation, for example. The study is published in the journal PNAS.
The results provide new clues on how species are formed, and suggest it could be harmful to bring together individuals from different populations that have been separated for a long time. The reason is that the offspring have lower survival rates.
"This is something worth keeping in mind in conservation biology, where you want to see a population ...
2021-03-25
By clearing forests, burning grasslands, plowing fields and harvesting crops, humans apply strong selective pressures on the plants that survive on the landscapes we use. Plants that evolved traits for long-distance seed-dispersal, including rapid annual growth, a lack of toxins and large seed generations, were more likely to survive on these dynamic anthropogenic landscapes. In the current article, researchers argue that these traits may have evolved as adaptations for megafaunal mutualisms, later allowing those plants to prosper among increasingly sedentary human populations.
The new study hypothesizes that the presence of specific anthropophilic traits explains why a select few plant families came to dominate the crop and weed ...
2021-03-25
The claim that old-growth forests play a significant role in climate mitigation, based upon the argument that even the oldest forests keep sucking CO2 out of the atmosphere, is being refuted by researchers at the University of Copenhagen. The researchers document that this argument is based upon incorrectly analysed data and that the climate mitigation effect of old and unmanaged forests has been greatly overestimated. Nevertheless, they reassert the importance of old-growth forest for biodiversity.
Old and unmanaged forest has become the subject of much debate in ...
2021-03-25
One big challenge for the production of synthetic cells is that they must be able to divide to have offspring. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a team from Heidelberg has now introduced a reproducible division mechanism for synthetic vesicles. It is based on osmosis and can be controlled by an enzymatic reaction or light.
Organisms cannot simply emerge from inanimate material ("abiogenesis"), cells always come from pre-existing cells. The prospect of synthetic cells newly built from the ground up is shifting this paradigm. However, one obstacle on this path is the question of controlled division--a requirement for having "progeny".
A team from the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg, Heidelberg ...
2021-03-25
The team of researchers at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania applied artificial intelligence (AI) methods to evaluate data of human embryo development. The AI-based system photographs the embryos every five minutes, processes the data of their development and notifies any anomalies observed. This increases the likelihood of choosing the most viable and healthy early-stage embryo for IVF procedures. The innovation was developed in collaboration with Esco Medical Technologies, a manufacturer of medical equipment.
Almost one in six couples face infertility; about 48.5 million couples, 186 million individuals worldwide are inflicted. Europe has one of the lowest birth rates in the world, with an average of just 1.55 children per woman.
The most effective form of ...
2021-03-25
By offering a microscopic "tightrope" to cells, Virginia Tech and Johns Hopkins University researchers have brought new insights to the way migrating cells interact in the body. The researchers changed their testing environment for observing cell-cell interaction to more closely mirror the body, resulting in new observations of cells interacting like cars on a highway -- pairing up, speeding up, and passing one another.
Understanding the ways migrating cells react to one another is essential to predicting how cells change and evolve and how they react in applications, such as wound healing and drug delivery. In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a team formed by Mechanical Engineering Associate ...
2021-03-25
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University jointly with colleagues from different countries have developed a new sensor with two layers of nanopores. In the conducted experiments, this sensor showed its efficiency as a sensor for one of the doping substances from chiral molecules. The research findings are published in Biosensors and Bioelectronics (IF: 10,257; Q1) academic journal.
The material is a thick wafer with pores of 20-30 nm in diameter. The scientists grew a layer of metal-organic frameworks (MOF) from Zn ions and organic molecules on these thick wafers. The MOF has about 3 nm nanopores only. It plays the role of a trap for molecules, which must be detected.
"This sensor can operate with chiral molecules. Such substances consisting of chiral molecules are a lot among medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New biomarkers of malignant melanoma identified
Scientists identify new biomarkers in patients with malignant melanoma, which could help in its diagnosis and prognosis