Discovery is key to creating heat-tolerant crops
Researchers identify gene that helps plants sense heat
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) By 2050 global warming could reduce crop yields by one-third. UC Riverside researchers have identified a gene that could put the genie back in the bottle.
Warmer temperatures signal to plants that summer is coming. Anticipating less water, they flower early then lack the energy to produce more seeds, so crop yields are lower. This is problematic as the world's population is expected to balloon to 10 billion, with much less food to eat.
"We need plants that can endure warmer temperatures, have a longer time to flower and a longer growth period," said UCR botany and plant sciences professor Meng Chen. "But, to be able to modify plants' temperature responses, you first have to understand how they work. So, that's why identifying this gene that enables heat response is so important."
The work that Chen and his colleagues did to uncover the heat-sensing gene was published this week in the journal Nature Communications. It is the second gene they've found involved in temperature sensing.
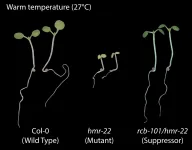
They located the first gene, called HEMERA, two years ago. Then they did an experiment to see if they could identify other genes involved in controlling the temperature-sensing process.
Ordinarily, plants react to shifts of even a few degrees in weather. For this experiment, the team began with a mutant Arabidopsis plant completely insensitive to temperature, and they modified it to once again become reactive.
Examining the genes of this twice-mutated plant revealed the new gene, RCB, whose products work closely with HEMERA to stabilize the heat-sensing function. "If you knock out either gene, your plant is no longer sensitive to temperature," Chen said.
Both HEMERA and RCB are required to regulate the abundance of a group of master gene regulators that serve multiple functions, reacting to temperature as well as light, and turning plants green. These proteins are distributed to two different parts of plant cells, the nucleus as well as organelles called chloroplasts.
Going forward, Chen says his laboratory will focus on understanding how these two parts of the cell communicate and work together to achieve growth, greening, flowering, and other functions.
"When you change light or temperature, genes in both the nucleus and chloroplasts change their expression. We think HEMERA and RCB are involved coordinating gene expression between these two cell compartments," Chen said.
Ultimately, the goal is to be able to modify temperature response to ensure the future of our food supply.
"We were excited to find this second gene," Chen said. "It's a new piece of the puzzle. Once we understand how it all works, we can modify it, and help crops cope better with climate change."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
DALLAS, April 6, 2021 -- A tsunami of chronic health conditions as a result of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, especially cardiometabolic disease, may produce an enormous wave of death and disability that demands immediate, comprehensive strategies. In addition, COVID-19 has disrupted cardiovascular science and medicine, yet it presents opportunities to transform and create novel approaches that can yield new successes. These are the opinions of two esteemed leaders in cardiovascular disease care, research and strategy, detailed in two new Frame of Reference articles published today in the American Heart Association's flagship journal Circulation.
While COVID-19 has severely impacted everyone's daily lives, its societal ...
2021-04-06
The inequality is enormous: Mothers in select African countries are more than 100 times more likely to have had a child die than mothers in high-income countries.
This is what Diego Alburez-Gutierrez (Researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) in Rostock, Germany), Emily Smith-Greenaway (Researcher at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences in Los Angeles and Guest Researcher at MPIDR), and co-authors found in their recent paper published in BMJ Global Health.
"We offer the first global estimates of the cumulative number of child deaths experienced by mothers ...
2021-04-06
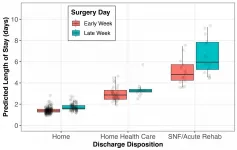
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (APRIL 6, 2021). New research by a team from the Cleveland Clinic and the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE) has determined that surgeries performed late in the workweek, and those culminating in discharge to a specialty care facility, are associated with higher costs and unnecessarily longer stays in the hospital following a common elective spine surgery.
Sebastian Salas-Vega, PhD, and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the data for all adult patients who underwent elective lumbar laminectomy over a nearly three-year period at any Ohio hospital included within ...
2021-04-06
Newer is not always better; a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) led by researchers at the University of Warwick shows that simple fetal heartbeat monitoring is still the best method for determining whether a baby is in distress during delivery and whether cesarean delivery is needed http://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.202538.
Cesarean delivery is the most common surgical procedure worldwide, performed to expedite birth and avoid neonatal complications.
Listening to the fetal heart rate using a stethoscope -- intermittent auscultation -- has been used for years to assess the fetal state and whether the baby is experiencing distress that might require a cesarean delivery. Other monitoring techniques have become ...
2021-04-06
Legalization of recreational cannabis may be associated with an increase in fatal motor vehicle collisions based on data from the United States, and authors discuss the implications for Canada in an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"Analyses of data suggest that legalization of recreational cannabis in United States jurisdictions may be associated with a small but significant increase in fatal motor vehicle collisions and fatalities, which, if extrapolated to the Canadian context, could result in as many as 308 additional driving fatalities annually," says Ms. Sarah Windle, Lady Davis Institute/McGill ...
2021-04-06
Hamilton, ON (April 6, 2021) - If you are one of the millions of people worldwide suffering from allergies, you may take an antihistamine pill to ward off hives, sneezing and watery eyes.
But you may be taking your medications incorrectly, says Derek Chu, a McMaster University allergy expert and clinical scholar.
"People need to rethink what they stock in their home cabinets as allergy medicines, what hospitals keep on formulary, and what policymakers recommend. The message needs to get out. This publication is on time for the spring allergy season and as COVID vaccines roll out, for which rashes are common and antihistamines can be helpful," said Chu.
Co-author Gordon ...
2021-04-06
The idea of implantable sensors that continuously transmit information on vital values and concentrations of substances or drugs in the body has fascinated physicians and scientists for a long time. Such sensors enable the constant monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic success. However, until now implantable sensors have not been suitable to remain in the body permanently but had to be replaced after a few days or weeks. On the one hand, there is the problem of implant rejection because the body recognizes the sensor as a foreign object. On the other hand, the sensor's color which indicates concentration changes has been unstable so far and faded over time. Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have developed a novel type of implantable sensor which can ...
2021-04-06
In 2001, the famous herpetologist Joseph B. Slowinski died from snakebite by an immature black-and-white banded krait, while leading an expedition team in northern Myanmar. The very krait that caused his death is now confirmed to belong to the same species identified as a new to science venomous snake, following an examination of samples collected between 2016 and 2019 from Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.
The new krait species, found in Southwestern China and Northern Myanmar, is described by Dr Zening Chen of END ...
2021-04-06
A new study analyzing bean production and food security across 11 countries in sub-Saharan Africa, found COVID-19 pandemic-related restrictions to significantly impact bean production. Border controls and high transport costs have led to drops in production of the key food security crop, threatening to reverse gains made in achieving Sustainable Development Goals 1 and 2, towards no poverty and zero hunger, respectively.
Even before the pandemic, 55% of the world's hungry people and 70% of the world's poorest people lived in Africa, the researchers said. In addition, food systems across Africa were already affected by the adverse impacts of climate change, disease and pests, such as the worst desert locust outbreak in 70 years impacting food security in Kenya, Somalia, ...
2021-04-06
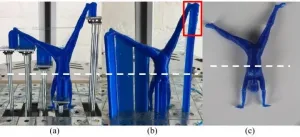
3-D printing has the potential to revolutionize product design and manufacturing in a vast range of fields--from custom components for consumer products, to 3-D printed dental products and bone and medical implants that could save lives. However, the process also creates a large amount of expensive and unsustainable waste and takes a long time, making it difficult for 3-D printing to be implemented on a wide scale.
Each time a 3-D printer produces custom objects, especially unusually-shaped products, it also needs to print supports-printed stands that balance the object as the printer creates layer by layer, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Discovery is key to creating heat-tolerant crops
Researchers identify gene that helps plants sense heat