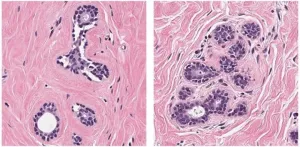
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA-- Human brain organoids are remarkable platforms for modeling features of human brain development and diseases. Building on methods to generate organoids to model different brain regions such as the cortex and the midbrain, researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania have generated the first organoids of the arcuate nucleus (ARC), an essential structure in the hypothalamus that sends signals of hunger and feeling full. This part of the hypothalamus exhibits a tremendous amount of cell diversity, and is far more complex than previously modeled parts of the brain.
In a paper published today in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at Penn report generating arcuate organoids (ARCOs) that model the ARC of the hypothalamus. END
Researchers use arcuate organoids to study development and disease of the hypothalamus
Models of brain subregion provide new opportunities to examine development of brain disorders
2021-05-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New mapping technique reveals epigenetic drivers of cancers
2021-05-10
Scientists have made major advances in understanding and developing treatments for many cancers by identifying genetic mutations that drive the disease. Now a team led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian and the New York Genome Center (NYGC) has developed a machine learning technique for detecting other modifications to DNA that have a similar effect.
The study, published May 10 in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, focuses on a type of chemical modification to DNA, called methylation, that typically silences nearby genes. The new technique can analyze the thousands of DNA methylation changes detected in tumor cells and infer which ones are likely ...
Single-cell map of early stage lung cancer and normal lung sheds light on tumor development, new therapeutic targets
2021-05-10
HOUSTON - Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have developed a first-of-its-kind spatial atlas of early-stage lung cancer and surrounding normal lung tissue at single-cell resolution, providing a valuable resource for studying tumor development and identifying new therapeutic targets. The study was published today in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The findings reveal a heterogeneous lung cancer ecosystem, with extensive interactions between cancer cells and the surrounding microenvironment that regulate early cancer development. ...
Time running out to save coral reefs
2021-05-10
New research on the growth rates of coral reefs shows there is still a window of opportunity to save the world's coral reefs--but time is running out.
The international study was initiated at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE), which is headquartered at James Cook University (JCU).
Co-author Professor Morgan Pratchett from Coral CoE at JCU said the results show that unless carbon dioxide emissions are drastically reduced the growth of coral reefs will be stunted.
"The threat posed by climate change to coral reefs is already very apparent based on recurrent episodes of mass coral bleaching," Prof Pratchett said. "But changing environmental conditions will have other far-reaching consequences."
Co-author Professor Ryan Lowe, from Coral CoE at The University ...
Turns out developing a taste for carbs wasn't a bad thing
2021-05-10
A new study looking at the evolutionary history of the human oral microbiome shows that Neanderthals and ancient humans adapted to eating starch-rich foods as far back as 100,000 years ago, which is much earlier than previously thought.
The findings suggest such foods became important in the human diet well before the introduction of farming and even before the evolution of modern humans. And while these early humans probably didn't realize it, the benefits of bringing the foods into their diet likely helped pave the way for the expansion of the human brain because of the glucose in starch, which is the brain's main fuel source.
"We think we're seeing evidence of a really ...
Flying at up to Mach 16 could become reality with UCF's developing propulsion system
2021-05-10
ORLANDO, May 10, 2021 -University of Central Florida researchers are building on their technology that could pave the way for hypersonic flight, such as travel from New York to Los Angeles in under 30 minutes.
In their latest research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers discovered a way to stabilize the detonation needed for hypersonic propulsion by creating a special hypersonic reaction chamber for jet engines.
"There is an intensifying international effort to develop robust propulsion systems for hypersonic and supersonic flight that would allow flight through our atmosphere at very high speeds and also allow efficient entry and exit from planetary atmospheres," ...
Geoscientists find that shallow wastewater injection drives deep earthquakes in Texas
2021-05-10
In a newly published paper, Virginia Tech geoscientists have found that shallow wastewater injection -- not deep wastewater injections -- can drive widespread deep earthquake activity in unconventional oil and gas production fields.
Brine is a toxic wastewater byproduct of oil and gas production. Well drillers dispose of large quantities of brine by injecting it into subsurface formations, where its injection can cause earthquakes, according to Guang Zhai, a postdoctoral research scientist in the Department of Geosciences, part of the Virginia Tech College of Science, and a ...
Grand Challenge research harnesses AI to fight breast cancer
2021-05-10
Breast cancer has recently overtaken lung cancer to become the most common cancer globally, END ...
New theory may revolutionize treatment of endometriosis
2021-05-10
Endometriosis, a disease found in up to 10 per cent of women, has been enigmatic since it was first described. A new theory developed by researchers at Simon Fraser University suggests a previously overlooked hormone -- testosterone -- has a critical role in its development. The research could have direct impacts on diagnosis and treatment of the disease, signaling hope for women with endometriosis worldwide.
The disease is caused by endometrial tissue growing outside of the uterus, usually in the pelvic area, where it contributes to pain, inflammation, and infertility. But why some women get it, and others do not, has remained unclear.
The new research is based on recent findings that women with endometriosis developed, as fetuses in their mother's womb, under conditions of relatively ...
Does driving wear you out? You might be experiencing 'accelerousal'
2021-05-10
Admit it: Daily commutes - those stops, the starts, all that stress - gets on your last nerve.
Or is that just me?
It might be, according to a new study from the University of Houston's Computational Physiology Lab. UH Professor Ioannis Pavlidis and his team of researchers took a look at why some drivers can stay cool behind the wheel while others keep getting more irked.
"We call the phenomenon 'accelerousal.' Arousal being a psychology term that describes stress. Accelarousal is what we identify as stress provoked by acceleration events, even small ones," said Pavlidis, ...
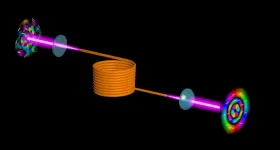
'Flipping' optical wavefront eliminates distortions in multimode fibers
2021-05-10
The use of multimode optical fibers to boost the information capacity of the Internet is severely hampered by distortions that occur during the transmission of images because of a phenomenon called modal crosstalk.
However, University of Rochester researchers at the Institute of Optics have devised a novel technique, described in a paper in Nature Communications, to "flip" the optical wavefront of an image for both polarizations simultaneously, so that it can be transmitted through a multimode fiber without distortion. Researchers at the University of South Florida and at the University of Southern California collaborated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
[Press-News.org] Researchers use arcuate organoids to study development and disease of the hypothalamusModels of brain subregion provide new opportunities to examine development of brain disorders