Origins of life researchers develop a new ecological biosignature
2021-05-20
(Press-News.org) When scientists hunt for life, they often look for biosignatures, chemicals or phenomena that indicate the existence of present or past life. Yet it isn't necessarily the case that the signs of life on Earth are signs of life in other planetary environments. How do we find life in systems that do not resemble ours?
In groundbreaking new work, a team* led by Santa Fe Institute Professor Chris Kempes has developed a new ecological biosignature that could help scientists detect life in vastly different environments. Their work appears as part of a special issue of theBulletin of Mathematical Biology collected in honor of renowned mathematical biologist James D. Murray.
The new research takes its starting point from the idea that stoichiometry, or chemical ratios, can serve as biosignatures. Since "living systems display strikingly consistent ratios in their chemical make-up," Kempes explains, "we can use stoichiometry to help us detect life." Yet, as SFI Science Board member and contributor, Simon Levin, explains, "the particular elemental ratios we see on Earth are the result of the particular conditions here, and a particular set of macromolecules like proteins and ribosomes, which have their own stoichiometry." How can these elemental ratios be generalized beyond the life that we observe on our own planet?
The group solved this problem by building on two lawlike patterns, two scaling laws, that are entangled in elemental ratios we have observed on Earth. The first of these is that in individual cells, stoichiometry varies with cell size. In bacteria, for example, as cell size increases, protein concentrations decrease, and RNA concentrations increase. The second is that the abundance of cells in a given environment follows a power-law distribution. The third, which follows from integrating the first and second into a simple ecological model, is that the elemental abundance of particles to the elemental abundance in the environmental fluid is a function of particle size.
While the first of these (that elemental ratios shift with particle size) makes for a chemical biosignature, it is the third finding that makes for the new ecological biosignature. If we think of biosignatures not simply in terms of single chemicals or particles, and instead take account of the fluids in which particles appear, we see that the chemical abundances of living systems manifest themselves in mathematical ratios between the particle and environment. These general mathematical patterns may show up in coupled systems that differ significantly from Earth.
Ultimately, the theoretical framework is designed for application in future planetary missions. "If we go to an ocean world and look at particles in context with their fluid, we can start to ask whether these particles are exhibiting a power-law that tells us that there is an intentional process, like life, making them," explains Heather Graham, Deputy Principal Investigator at NASA's Lab for Agnostic Biosignatures, of which she and Kempes are a part. To take this applied step, however, we need technology to size-sort particles, which, at the moment, we don't have for spaceflight. Yet the theory is ready, and when the technology lands on Earth, we can send it to icy oceans beyond our solar system with a promising new biosignature in hand.
INFORMATION:
Read the paper, *Christopher Kempes (Santa Fe Institute), Michael Follows (MIT), Hillary Smith (Pennsylvania State University), Heather Graham (NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center), Christopher House (Pennsylvania State University), and Simon Levin (Princeton University, Santa Fe Institute) are co-authors on the paper "Generalized Stoichiometry and Biogeochemistry for Astrobiological Applications," in the Bulletin of Mathematical Biology.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-20
The chemical bisphenol F (found in plastics) can induce changes in a gene that is vital for neurological development. This discovery was made by researchers at the universities of Uppsala and Karlstad, Sweden. The mechanism could explain why exposure to this chemical during the fetal stage may be connected with a lower IQ at seven years of age - an association previously seen by the same research group. The study is published in the scientific journal Environment International.
"We've previously shown that bisphenol F (BPF for short) may be connected with children's cognitive development. However, with this study, we can now begin to understand which biological mechanisms may explain such a link, which is unique for an epidemiological study." ...
2021-05-20
A new study provides public health planning authorities with a method of calculating the number of COVID-19 isolation beds they would need for people experiencing homelessness based on level of infection in the city. The research holds promise for controlling spread of the virus - or future infectious diseases - in a population that is highly vulnerable and less likely than many others to access health care services.
The report, developed to support public health decision-making in Austin, Texas, was recently published by PLOS ONE. The paper's first author is an undergraduate student at The University of Texas at Austin, Tanvi Ingle, who harnessed ...
2021-05-20
In April 2017, a landslide in Mocoa, Colombia, ripped through a local town, killing more than 300 people. Nicolás Pérez-Consuegra grew up about 570 miles north in Santander, Colombia, and was shocked as he watched the devastation on television. At that time, he was an undergraduate intern at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Panama. As a budding geologist raised hiking the tropical mountains of Colombia, he wondered, what causes greater erosion in some areas of the mountains than in others? And, is it tectonic forces - where Earth's tectonic plates slide against one another leading to the formation of steep mountains - or high precipitation rates, that play a more important role in causing erosion within that region?
To answer those questions would require a geological ...
2021-05-20
Scientists have discovered that the way in which neurons are connected within regions of the brain, can be a better indicator of disease progression and treatment outcomes for people with brain disorders such as epilepsy.
Many brain diseases lead to cell death and the removal of connections within the brain. In a new study, published in Human Brain Mapping, a group of scientists, led by Dr Marcus Kaiser from the School of Medicine at the University of Nottingham, looked at epilepsy patients undergoing surgery.
They found that changes in the local network within brain regions can be a better predictor ...
2021-05-20
More than 90 years ago, astronomer Edwin Hubble observed the first hint of the rate at which the universe expands, called the Hubble constant.
Almost immediately, astronomers began arguing about the actual value of this constant, and over time, realized that there was a discrepancy in this number between early universe observations and late universe observations.
Early in the universe's existence, light moved through plasma--there were no stars yet--and from oscillations similar to sound waves created by this, scientists deduced that the Hubble constant was about 67. This means the universe expands about 67 kilometers per second faster every 3.26 million light-years.
But this observation differs when scientists look at the universe's ...
2021-05-20
BOSTON - Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers are presenting dozens of research studies at the 2021 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The studies will be presented during the virtual program on June 4-8, 2021. ASCO is the world's largest clinical cancer research meeting, attracting more than 30,000 oncology professionals from around the world.
Toni K. Choueiri, MD, the director of the Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology at Dana-Farber, will present results from the randomized, double-blind, phase III KEYNOTE-564 trial evaluating pembrolizumab versus placebo after surgery in patients with renal cell carcinoma (abstract LBA5) during ASCO's Plenary Session on Sunday, June ...
2021-05-20
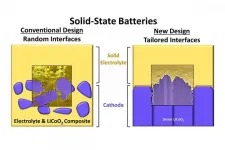
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Solid-state batteries pack a lot of energy into a small space, but their electrodes are not good at keeping in touch with their electrolytes. Liquid electrolytes reach every nook and cranny of an electrode to spark energy, but liquids take up space without storing energy and fail over time. Researchers are now putting solid electrolytes in touch with electrodes made of strategically arranged materials - at the atomic level - and the results are helping drive better solid-state battery technologies.
A new study, led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign materials science and engineering professor Paul Braun, postdoctoral research associate Beniamin Zahiri, and Xerion Advanced Battery Corp. director of research and development ...
2021-05-20
The University of Maryland (UMD) co-published a new review paper in the Annual Review of Resource Economics to examine pollinators from both an economic and ecological perspective, providing much needed insight into the complexities of valuing pollination. Pollinators are not only a critical component of a healthy ecosystem, but they are also necessary to produce certain foods and boost crop yields. While native and wild pollinators (whether they be certain bee species, other insects and animals, or just the wind) still play an important role, managed honey bee colonies are commercially trucked around the U.S. to meet the need for pollination services in agricultural products. Recent reports of ...
2021-05-20
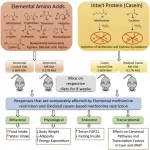
BATON ROUGE, Louisiana - A diet that improves the biomarkers of metabolic health, and that could potentially slow the aging process, has moved a step closer to reality.
"We've known for years that restricting the amino acid methionine in the diet produces immediate and lasting improvements in nearly every biomarker of metabolic health," said Thomas W. Gettys, PhD, Professor and Director, Nutrient Sensing and Adipocyte Signaling Laboratory at Pennington Biomedical Research Center. "The problem is that methionine-restricted diets have been difficult to implement because they taste so bad."
Until now. Restricting methionine normally involves diets formulated with elemental (e.g., individual) amino acids. Individual amino acids are the building blocks ...
2021-05-20
May 20, 2021 - Women with a history of weight cycling - losing and regaining 10 pounds or more, even once - have increased rates of insomnia and other sleep problems, reports a study in The Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing, official journal of the Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"History of weight cycling was prospectively associated with several measures of poor sleep, including short sleep duration, worse sleep quality, greater insomnia, greater sleep disturbances, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Origins of life researchers develop a new ecological biosignature