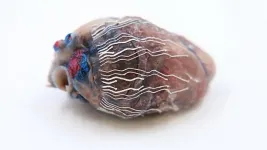
(Press-News.org) WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Surgeons may soon be able to localize critical regions in tissues and organs during a surgical operation thanks to a new, patent-pending Purdue University biosensor that can be printed in 3D using an automated printing system.
Chi Hwan Lee created the biosensor, which allows for simultaneous recording and imaging of tissues and organs during a surgical operation. Lee is the Leslie A. Geddes Assistant Professor of Biomedical Engineering in the Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering and assistant professor of mechanical engineering. Lee also has a courtesy appointment in materials engineering.
"Simultaneous recording and imaging could be useful during heart surgery in localizing critical regions and guiding surgical interventions such as a procedure for restoring normal heart rhythms," Lee said.
Traditional methods to simultaneously record and image tissues and organs have proven difficult because other sensors used for recording typically interrupt the imaging process.
"To this end, we have developed an ultra-soft, thin and stretchable biosensor that is capable of seamlessly interfacing with the curvilinear surface of organs; for example the heart, even under large mechanical deformations, for example cardiac cycles," Lee said. "This unique feature enables the simultaneous recording and imaging, which allows us to accurately indicate the origin of disease conditions: in this example, real-time observations on the propagation of myocardial infarction in 3D."
By using soft bio-inks during the rapid prototyping of a custom-fit design, biosensors fit a variety of sizes and shapes of an organ. The bio-inks are softer than tissue, stretch without experiencing sensor degradation and have reliable natural adhesion to the wet surface of organs without needing additional adhesives. Kwan-Soo Lee's research group in Los Alamos National Laboratory is responsible for the formulation and synthesis of the bio-inks.
A number of prototype biosensors using different shapes, sizes and configurations have been produced. Craig Goergen, the Leslie A. Geddes Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering in Purdue's Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, and his laboratory group have tested the prototypes in mice and pigs in vivo.
"Professor Goergen and his team were successfully able to identify the exact location of myocardial infarctions over time using the prototype biosensors," Lee said. "In addition to these tests, they also evaluated the biocompatibility and anti-biofouling properties of the biosensors, as well as the effects of the biosensors on cardiac function. They have shown no significant adverse effects."
INFORMATION:
Research about the biosensor has been published in the peer-reviewed Nature Communications.
The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization has filed a patent application on Lee's biosensor. For licensing information, please contact Dipak Narula of OTC and reference track code 2021-LEE-69211. Other steps taken to develop the sensor include exploring further applications of the bio-inks into various printable biosensors with a tailored design to fit other organs such as the stomach, which requires even higher stretchability than the heart.
Writer: Steve Martin, sgmartin@prf.org
Source: Chi Hwan Lee, lee2270@purdue.edu
ABSTRACT
Rapid Custom Prototyping of Soft Poroelastic Biosensor for Simultaneous Epicardial Recording and Imaging
Bongjoong Kim1, Arvin H. Soepriatna2, Woohyun Park1, Haesoo Moon2, Abigail Cox3, Jianchao Zhao4, Nevin S. Gupta4, Chi Hoon Park4,5, Kyunghun Kim2, Yale Jeon2,6, Hanmin Jang2,6, Dong Rip Kim6, Hyowon Lee2, Kwan-Soo Lee4,*, Craig J. Goergen2,*, Chi Hwan Lee1,2,7,*
1School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA. 2Weldon School of Biomedical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA. 3Department of Comparative Pathobiology, Purdue College of Veterinary Medicine, West Lafayette, IN, USA. 4Chemical Diagnostics and Engineering, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545, USA. 5Department of Energy Engineering, Gyeongnam National University of Science and Technology, Jinju-Si 660-758, Republic of Korea. 6School of Mechanical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul 04763, Republic of Korea. 7Department of Materials Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA. †These authors contributed equally to this work. *Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to C.H.L. (email: lee2270@purdue.edu) or C.J.G. (email: cgoergen@purdue.edu) or K.-S.L. (email: kslee@lanl.gov)
ABSTRACT
The growing need for the implementation of stretchable biosensors in the body has driven rapid prototyping schemes through the direct ink writing of multidimensional functional architectures. Recent approaches employ biocompatible inks that are dispensable through an automated nozzle injection system. However, their application in medical practices remains challenged in reliable recording due to their viscoelastic nature that yields mechanical and electrical hysteresis under periodic large strains. Herein, we report sponge-like poroelastic silicone composites adaptable for high-precision direct writing of custom-designed stretchable biosensors, which are soft and insensitive to strains. Their unique structural properties yield a robust coupling to living tissues, enabling high-fidelity recording of spatiotemporal electrophysiological activity and real-time ultrasound imaging for visual feedback. In vivo evaluations of custom-fit biosensors in a murine acute myocardial infarction model demonstrate a potential clinical utility in the simultaneous intraoperative recording and imaging on the epicardium, which may guide definitive surgical treatments.
In the realm of social media, anti-science views about COVID-19 align so closely with political ideology -- especially among conservatives -- that its predictability offers a strategy to help protect public health, a new USC study shows.
Resistance to science, including the efficacy of masks and vaccines, poses a challenge to conquering the coronavirus crisis. The goal of achieving herd immunity won't happen until society achieves consensus about science-based solutions.
The USC study's machine-learning assisted analysis of social media communications offers policymakers and public health officials new tools to anticipate shifts in attitudes ...
A rare parasitic infection imported from Europe continues to take root in Alberta, Canada. The province is now the North American hotspot for human alveolar echinococcosis (AE), which takes the form of a growth in the liver, causing serious and potentially deadly health complications.
A END ...
Only 2% of vehicles are electrified to date, but that is projected to reach 30% in 2030. A key toward improving the commercialization of electric vehicles (EVs) is to heighten their gravimetric energy density - measured in watt hours per kilogram - using safer, easily recyclable materials that are abundant. Lithium-metal in anodes are considered the "holy grail" for improving energy density in EV batteries compared to incumbent options like graphite at 240 Wh/kg in the race to reach more competitive energy density at 500 Wh/kg.
Yan Yao, Cullen Professor of electrical ...
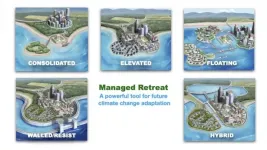
MIAMI--In a new analysis on managed retreat--the climate adaptation response of moving people and property out of harm's way--researchers explore what it would take for managed retreat to be supportive of people and their priorities. A key starting point is considering retreat alongside other responses like coastal armoring and not just as an option of last resort.
In a new paper in the journal Science, University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science researcher Katharine Mach argues that managed retreat should be viewed as a proactive option that can support communities and livelihoods in the face of climate change.
"Managed retreat ...
The surface of a material often has properties that are very different from the properties within the material. For example, a non-conducting crystal, which actually exhibits no magnetism, can show magnetisation restricted to its surface because of the way the atoms are arranged there. These distinct properties at interfaces and surfaces of materials often play a key role in the development of new functional components such as optoelectronic chips or sensors and are therefore subject to extensive research. An international research team from the University of Göttingen, the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry Göttingen and the National Research Council Canada has now succeeded in investigating the surfaces of transparent crystals using ...
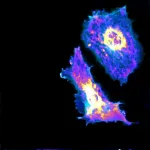
Understanding cellular metabolism - how a cell uses energy- could be key to treating a wide array of diseases, including vascular diseases and cancer.
While many techniques can measure these processes among tens of thousands of cells, researchers have been unable to measure them at the single-cell level.
Researchers at the University of Chicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering and Biological Sciences Division have developed a combined imaging and machine learning technique that can, for the first time, measure a metabolic process at both the cellular and sub-cellular levels.
Using a genetically encoded biosensor paired with artificial intelligence, ...
PHILADELPHIA - Sour taste does not have the nearly universal appeal that sweet taste does. Slightly sour foods or drinks such as yogurt and lemon juice are yummy to many, but such highly sour foods as spoiled milk are yucky, even dangerous. Like humans, many other animals, including insects, prefer slightly acidic over very acidic foods.
Evolutionary biologists surmise that the need for sour detection to be finely tuned is a two-sided coin: slightly acidic foods can enhance digestion and stimulate saliva production; relative sour-to-sweet taste can signal optimal ripeness of fruit; and extremely sour food, as with bitter taste, is a warning to what not to ingest. However, despite this usefulness, how do animals discern different concentrations ...
The brain presents different states depending on the communication between billions of neurons, and this network is the basis of all our perceptions, memories, and behaviours. It is often considered a "black box", with difficult access for clinicians and researchers, as few limited tools are available to perform accurate and spaciotemporal studies on brain neuronal behaviour. Now, researchers from the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) in collaboration with August Pi i Sunyer Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBAPS) and have added some light to the subject: they succeeded for the first time in controlling neuronal activity in the brain using a molecule responsive to light.
The study included participants ...
MADISON - In early January 2021, travelers returning to Tokyo, Japan, from Amazonas, Brazil, were screened for COVID-19 at the airport. A few days later, the National Institute of Infectious Disease of Japan announced that the travelers had returned with a new variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
That variant, known as gamma, or P.1, led to a deadly surge in COVID-19 cases in Brazil this spring, and has now spread across the world. More than 200 cases have been detected in Wisconsin. Whether current vaccines are as effective against the gamma variant remains unknown.
In a new study using variant virus recovered from one of the original travelers, ...
University of Delaware disaster researcher A.R. Siders said it's time to put all the options on the table when it comes to discussing climate change adaptation.
Managed retreat -- the purposeful movement of people, buildings and other assets from areas vulnerable to hazards -- has often been considered a last resort. But Siders said it can be a powerful tool for expanding the range of possible solutions to cope with rising sea levels, flooding and other climate change effects when used proactively or in combination with other measures.
Siders, a core faculty member in UD's Disaster Research Center, and Katharine J. Mach, associate professor at the University ...