(Press-News.org) The body's immune cells naturally fight off viral and bacterial microbes and other invaders, but they can also be reprogrammed or "trained" to respond even more aggressively and potently to such threats, report UCLA scientists who have discovered the fundamental rule underlying this process in a particular class of cells.
In END
UCLA study reveals how immune cells can be trained to fight infections
Discovery may allow doctors to 'hack' the immune system to strengthen it
2021-06-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Light-harvesting nanoparticle catalysts show promise in quest for renewable carbon-based fuels
2021-06-24
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Researchers report that small quantities of useful molecules such as hydrocarbons are produced when carbon dioxide and water react in the presence of light and a silver nanoparticle catalyst. Their validation study - made possible through the use of a high-resolution analytical technique - could pave the way for CO2-reduction technologies that allow industrial-scale production of renewable carbon-based fuels.
The study, led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign chemistry professor Prashant Jain, probes chemical activity at the surface of silver nanoparticle catalysts under visible light and uses carbon isotopes to track the origin and production of these previously undetected chemical reactions. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
Sunlight-driven ...
Muscling up with nanoparticle-based anti-inflammatory therapy
2021-06-24
By Benjamin Boettner
(Boston) - Muscular dystrophies are a group of genetic diseases that lead to the progressive loss of muscle mass and function in patients, with the incurable Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), which affects all the body's muscles primarily in boys, being particularly severe. DMD can be caused by more than 7,000 unique mutations in the largest gene of the human genome, which encodes a central protein in muscle fibers. While this astounding number of mutations all variably block muscle function, the affected muscles share another common feature - chronic inflammation.
As chronic inflammation ...
Making citizen science inclusive will require more than rebranding
2021-06-24
Scientists need to focus on tangible efforts to boost equity, diversity and inclusion in citizen science, researchers from North Carolina State University argued in a new perspective.
Published in the journal Science, the perspective is a response to a debate about rebranding "citizen science," the movement to use crowdsourced data collection, analysis or design in research. Researchers said that while the motivation for rebranding is in response to a real concern, there will be a cost to it, and efforts to make projects more inclusive should go deeper than that. Their recommendations speak to a broader discussion about how to ensure science is responsive to the needs of a diverse audience.
"At its heart, citizen science is a system of knowledge production ...
Parents of children with complex medical conditions more likely to have mental health issues
2021-06-24
Parents of children with the most complex medical conditions are more likely to report poor or fair mental health and struggle to find community help, according to a study completed by researchers at University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) and Golisano Children's Hospital. The study was published in Pediatrics, the journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
The study, "A National Mental Health Profile of Parents of Children with Medical Complexity," examined parent-reported data from the National Survey of Children's Health, and compared three groups: households of children with medical complexity (CMC), households of noncomplex children with special health care needs, and households of children ...
Ubiquitination primes cell for recovery from heat stress
2021-06-24
Not all stresses are created equal, according to a pair of new studies, which shows that distinct ubiquitination patterns underlie cell recovery following different environmental stressors. Eukaryotic cells respond to environmental stressors - such as temperature extremes, exposure to toxins or damage, for example - through adaptive programs that help to ensure their survival, including the shutdown of key cellular processes. These responses are often associated with the formation of stress granules (SGs) - dense cytoplasmic aggregations of proteins and RNA - as well as with ...
Higher doses of neutralizing antibody could protect humans against HIV
2021-06-24
Although the Antibody Mediated Prevention (AMP) study that launched in 2016 failed to show significant efficacy in a pair of clinical trials, Denis Burton argues in a Perspective that the AMP study's results represent a landmark in AIDS research; they show - for the first time - that a broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb) can protect humans against exposure to some strains of HIV. According to Burton, the AMP study's data - despite not showing a significant difference between the numbers of infected individuals in the treated groups versus those in the placebo groups - still have tremendous implications for future HIV vaccine design and passive bnAb use strategies. The AMP study evaluated the immunotherapeutic ...
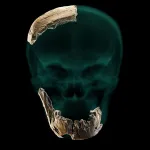
New fossil discovery from Israel points to complicated evolutionary process
2021-06-24
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Analysis of recently discovered fossils found in Israel suggest that interactions between different human species were more complex than previously believed, according to a team of researchers including Binghamton University anthropology professor Rolf Quam.
The research team, led by Israel Hershkovitz from Tel Aviv University, published their findings in Science, describing recently discovered fossils from the site of Nesher Ramla in Israel. The Nesher Ramla site dates to about 120,000-140,000 years ago, towards the very end of the Middle Pleistocene time period.
The human fossils were found by Dr. Zaidner of ...
Scientists can predict and design single atom catalysts for important chemical reactions
2021-06-24
Researchers at Tufts University, University College London (UCL), Cambridge University and University of California at Santa Barbara have demonstrated that a catalyst can indeed be an agent of change. In a study published today in Science, they used quantum chemical simulations run on supercomputers to predict a new catalyst architecture as well as its interactions with certain chemicals, and demonstrated in practice its ability to produce propylene - currently in short supply - which is critically needed in the manufacture of plastics, fabrics and other chemicals. The improvements have potential for highly efficient, "greener" chemistry with a lower carbon footprint.
The demand for propylene is ...
A new type of Homo unknown to science
2021-06-24
The discovery of a new Homo group in this region, which resembles Pre-Neanderthal populations in Europe, challenges the prevailing hypothesis that Neanderthals originated from Europe, suggesting that at least some of the Neanderthals' ancestors actually came from the Levant.
The new finding suggests that two types of Homo groups lived side by side in the Levant for more than 100,000 years (200-100,000 years ago), sharing knowledge and tool technologies: the Nesher Ramla people who lived in the region from around 400,000 years ago, and the Homo sapiens who arrived later, some 200,000 years ago.
The new discovery also gives clues about a mystery in human evolution: How did genes of Homo sapiens penetrate the Neanderthal population that had presumably lived in Europe long before ...
Battle of the Pleiades against plant immunity
2021-06-24
Mythological nymphs reincarnate as a group of corn smut proteins to launch a battle on maize immunity. One of these proteins appears to stand out among its sister Pleiades, much like its namesake character in Greek mythology. The research carried out at GMI - Gregor Mendel Institute of Molecular Plant Biology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences - is published in the journal PLOS Pathogens.
Pathogenic organisms exist under various forms and use diverse strategies to survive and multiply at the expense of their hosts. Some of these pathogens are termed "biotrophic", as they are parasites that maintain their hosts alive. These biotrophic pathogens deregulate physiological processes in their hosts by suppressing their immune defenses and favoring disease development. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] UCLA study reveals how immune cells can be trained to fight infectionsDiscovery may allow doctors to 'hack' the immune system to strengthen it