A new kind of visual illusion uncovers how our brains connect the dots
'Scintillating starburst' offers insights into visual processing
2021-06-29
(Press-News.org) A new class of illusion, developed by a visual artist and a psychology researcher, underscores the highly constructive nature of visual perception.
The illusion, which the creators label "Scintillating Starburst," evokes illusory rays that seem to shimmer or scintillate--like a starburst. Composed of several concentric star polygons, the images prompt viewers to see bright fleeting rays emanating from the center that are not actually there.
"The research illustrates how the brain 'connects the dots' to create a subjective reality in what we see, highlighting the constructive nature of perception," explains Pascal Wallisch, a clinical associate professor in New York University's Department of Psychology and Center for Data Science and senior author of the paper, which appears in the journal i-Perception.
"Studying illusions can be helpful in understanding visual processing because they allow us to distinguish the mere sensation of physical object properties from the perceptual experience," adds first author Michael Karlovich, founder and CEO of Recursia Studios, a multidisciplinary art and fashion production company.
The authors acknowledge that the visual effects of this illusion are superficially similar to a number of previously described effects of other, grid-based illusions. However, their Scintillating Starburst, unlike known visual illusions, evokes a number of newly discovered effects, among them that fleeting illusory lines diagonally connect the intersection points of the star polygons.
To better understand how we process this class of illusion, the researchers ran a series of experiments with more than 100 participants, who viewed 162 different versions of the Scintillating Starburst, which varied in shape, complexity, and brightness.
The research participants were then asked a series of questions about what they saw--for instance, "I do not see any bright lines, rays, or beams," "I maybe see bright lines, rays, or beams, but they are barely noticeable," and "I see bright lines, rays, or beams, but they are subtle and weak."
The authors found that the confluence of several factors, including contrast, line width, and number of vertices, matters.
"In particular, a large number of prominent intersection points leads to stronger and more vivid rays, as there are more cues to indicate the implied lines," observes Wallisch.
Thus, this research illustrates how the brain "connects the dots" to create one's subjective reality, even on the perceptual level, highlighting the constructive nature of perception.
INFORMATION:
DOI: 10.1177/20416695211018720
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-29
Six antibody characteristics could help scientists identify which pregnant women are at risk of placental malaria infections, finds a study published today in eLife.
Malaria infections can be devastating for pregnant mothers, particularly during their first pregnancies. If malaria parasites invade the placenta, they can starve babies of nutrition, potentially causing low birth weight, preterm deliveries, stillbirths, and pregnancy loss. But not all women are susceptible to placental malaria infections, and the new study may help clinicians to identify those at risk and researchers to develop new therapies to protect pregnant women from malaria and related complications.
A protein made by malaria parasites called VAR2CSA allows them to attach ...
2021-06-29
New insight on how our experiences during a task or interaction shape our current mood has been published today in the open-access eLife journal.
The study suggests that early experiences may have a larger effect on our mood than more recent events. These findings hold implications for the timing of events in experimental or clinical settings, and suggest new directions for mood interventions tailored to individual patients.
People routinely report on their moods during everyday activities and when they interact with clinicians providing mental health care. It is commonly believed ...
2021-06-29
Rising nighttime temperatures are curbing crop yields for rice, and new research moves us closer to understanding why. The study found that warmer nights alter the rice plant's biological schedule, with hundreds of genes being expressed earlier than usual, while hundreds of other genes are being expressed later than usual.
"Essentially, we found that warmer nights throw the rice plant's internal clock out of whack," says Colleen Doherty, an associate professor of biochemistry at North Carolina State University and corresponding author of a paper on the work.
"Most people think plants aren't dynamic, but they are. Plants are constantly regulating ...
2021-06-29
A recent proof-of-concept study finds that a low-cost training program can reduce hazardous driving in older adults. Researchers hope the finding will lead to the training becoming more widely available.
"On-road training and simulator training programs have been successful at reducing car accidents involving older drivers - with benefits lasting for years after the training," says Jing Yuan, first author of the study and a Ph.D. student at North Carolina State University. "However, many older adults are unlikely to have access to these training programs or technologies."
"We developed a training program, ...
2021-06-29
Populations of Drosophila suzukii fruit flies - so-called "spotted-wing Drosophila" that devastate soft-skinned fruit in North America, Europe and parts of South America - could be greatly suppressed with the introduction of genetically modified D. suzukii flies that produce only males after mating, according to new research from North Carolina State University.
D. suzukii are modified with a female-lethal gene that uses a common antibiotic as an off switch. Withholding the antibiotic tetracycline in the diet of larvae essentially eliminates birth of female D. suzukii flies as the modified male flies successfully mate with females, says Max Scott, an NC State entomologist who is the corresponding author of a paper describing the research.
"We use a genetic female-lethal system - a ...
2021-06-29
Researchers from the Laboratory of Oncolytic-Virus-Immuno-Therapeutics (LOVIT) at the LIH Department of Oncology (DONC) are working on the development of novel anticancer strategies based on oncolytic viruses, "good" viruses that can specifically infect, replicate in and kill cancer cells. In particular, the LOVIT team elucidated the mechanism through which the H-1PV cancer-destroying virus can attach to and enter cancer cells, thereby causing their lysis and death. At the heart of this process lie laminins, and specifically laminin γ1, a family of proteins on the surface of a cancer cell to which this virus binds, and which therefore act as the 'door' through which the virus enters the cells. The findings, which were published in the prestigious ...
2021-06-29
Beetles are creatures with built-in body armor. They are tiny tanks covered with hard shells, also known as exoskeletons, protecting their soft, skeleton-less bodies inside. In addition to providing armored protection, the beetle's exoskeleton offers functions like sensory feedback and hydration control. Notably, the exoskeletons of many beetles are also brilliantly colored and patterned, which enhances visual communication with other beetles and organisms.
Ling Li, lead investigator and assistant professor in mechanical engineering, has joined colleagues from six other universities to investigate the interplay between mechanical and optical performance ...
2021-06-29
Globally, more than 400 million people have diabetes, most of them suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Before the onset of actual type 2 diabetes, people are often diagnosed with abnormalities in glucose metabolism that are milder than those associated with diabetes. The term used to indicate such cases is prediabetes. Roughly 5-10% of people with prediabetes develop type 2 diabetes within a year-long follow-up.
Insulin resistance in muscle tissue is one of the earliest metabolic abnormalities detected in individuals who are developing type 2 diabetes, and the phenomenon is already seen in prediabetes.
In a collaborative study, researchers from the University of Helsinki, the ...
2021-06-29
URBANA, Ill. - Despite soybean's high protein and oil content and its potential to boost food security on the continent, Africa produces less than 1% of the world's soybean crop. Production lags, in part, because most soybean cultivars are bred for North and South American conditions that don't match African environments.
Researchers from the Soybean Innovation Lab (SIL), a U.S. Agency for International Development-funded project led by the University of Illinois, are working to change that. In a new study, published in Agronomy, they have developed methods to help breeders improve soybean cultivars specifically for African environments, with the intention of creating fast-maturing ...
2021-06-29
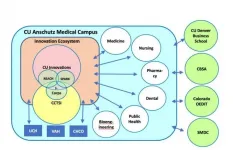
A new study highlights the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus as an example of how an academic medical center can turn groundbreaking research into commercial products that improve patient care and public health.
The paper, published recently in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Science, focuses on the unique ecosystem at CU Anschutz responsible for these innovations. And it specifically details the campus's collaborative culture and how biomedical research is commercialized.
The campus has successfully turned academic research into a variety of products. CU Anschutz, for example, developed two vaccines for shingles, Zostavax and Shingrix, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new kind of visual illusion uncovers how our brains connect the dots
'Scintillating starburst' offers insights into visual processing