(Press-News.org) July 19, 2021 - At the organization responsible for certifying the training and skills of US urologists, achieving and maintaining diversity, equity and inclusion is more than just a "numbers game," according to a special article in Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
In the new article, the American Board of Urology (ABU) points out that the practice of diversity and inclusion has been a cornerstone of its values for years. However, the Board acknowledges that while progress has been made, more work remains to be done. The authors included ABU Trustees Douglas A. Husmann, MD, Martha K. Terris, MD, and Cheryl T. Lee, MD, and Executive Director J. Brantley Thrasher, MD.
Building and sustaining diversity and inclusion at ABU
The report focuses on informing ABU diplomates about initiatives to evaluate and strengthen diversity and representation on three Committees central to the ABU's mission: The Board of Trustees and the Written and Oral Examinations Committees. For several years it has been the ABU's standard of practice to perform a yearly GAP analysis, comparing and contrasting the membership of their committees to the characteristics of their constituents: practicing urologists within the United States, as defined by the American Urology Association's 2019 annual National Census.
The selection of new Committee members is subsequently based on both the individual's merit and an attempt to match or exceed the diversity ratios defined within the Census regarding gender, race, ethnicity, geography of practice, and subspecialty area. This year's evaluation revealed the ABU committee structure consisted of 85% men and 15% women, compared to 90% and 10% in the 2019 National Census, respectively.
Regarding race and ethnicity, proportions of Committee members compared to the National Census of practicing urologists were non-Hispanic White, 74% versus 81%; Asian, 22% versus 12%; Black/African American, 3% versus 2%; and Hispanic, 1% versus 4%. Regarding region of practice, the ABU assesses the proportion of US urologists practicing within a given section, and attempts to achieve a Committee structure that is equivalent or within 1 to 4 percentage points.
While counting and comparing gender and racial/ethnic representation is a necessary first step, establishing ratios has not been found to change societal behavior or attitudes substantially - and indeed may have significant negative unintended consequences. Dr. Husmann and coauthors outline a series of "continuous and structural processes" to promote a lasting culture of diversity and inclusion. Specific aims include:
Educating ABU diplomates and Committee members regarding the benefits of diversity
Educating Committee members about the concept of unconscious bias
Performing rigorous assessments of the ABU written and oral examinations to verify the absence of implicit bias
Stressing the need to mentor today's diverse constituency of young urologists to participate and eventually take over leading roles in state, regional and national committees - giving them the experience they will need to succeed as ABU Committee members
Anticipating the changing demographics of the next generation of urologists - for example, whereas only 10 percent of urologists currently in practice are women, they account for 30 percent of residents in training
Above all else, encouraging frank and open discussions regarding diversity, equity, and inclusion
Dr. Husmann and coauthors conclude: "The ability to achieve and maintaining diversity, equity, and inclusion is an imperative requiring regular attention and discussion to ensure that we continually strive to reflect the values and principles of both the public and the diplomates we serve."
Click here to read "The American Board of Urology: In Pursuit of Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion."
DOI: 10.1097/UPJ.0000000000000244
INFORMATION:
About Urology Practice
An Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA), Urology Practice focuses on clinical trends, challenges and practice applications in the four areas of Business, Health Policy, the Specialty and Patient Care. Information that can be used in everyday practice will be provided to the urology community via peer-reviewed clinical practice articles (including best practices, reviews, clinical guidelines, select clinical trials, editorials and white papers), "research letters" (brief original studies with an important clinical message), the business of the practice of urology, urology health policy issues, urology education and training, as well as content for urology care team members.
About the American Urological Association
Founded in 1902 and headquartered near Baltimore, Maryland, the American Urological Association is a leading advocate for the specialty of urology, and has more than 23,000 members throughout the world. The AUA is a premier urologic association, providing invaluable support to the urologic community as it pursues its mission of fostering the highest standards of urologic care through education, research and the formulation of health care policy. To learn more about the AUA visit: http://www.auanet.org.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2020 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,200 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
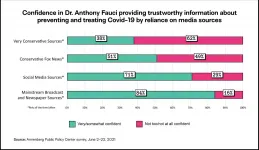
With more than two-thirds of American adults vaccinated with at least one dose of an authorized Covid-19 vaccine, the top U.S. health agencies retain the trust of the vast majority of the American public, as does Dr. Anthony Fauci, the public face of U.S. efforts to combat the virus, according to a new survey from the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania.
The survey revealed growing public confidence in both the safety and effectiveness of vaccines to prevent Covid-19.
But after months of attacks on Fauci in conservative and social media, the survey found that people who said they rely on conservative and very conservative media rather than other sources ...
Led by Dr Jonas Warneke, researchers at the Wilhelm Ostwald Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at Leipzig University have made a decisive advance in the study of one type of highly reactive particles. Based on their research, they now understand the "binding preferences" of these particles.
Their research serves as the basis for the targeted use of these highly reactive molecules, for example, to generate new molecular structures or to bind hazardous chemical "waste" and in this way dispose of it. The researchers have now published their findings in the journal Chemistry - A European Journal, and their research was featured on the cover thanks to the excellent review they received.
What molecules and people have in common
Molecules and people actually have a lot in ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Scientists who study glacier ice have found viruses nearly 15,000 years old in two ice samples taken from the Tibetan Plateau in China. Most of those viruses, which survived because they had remained frozen, are unlike any viruses that have been cataloged to date.
The findings, published today in the journal Microbiome, could help scientists understand how viruses have evolved over centuries. For this study, the scientists also created a new, ultra-clean method of analyzing microbes and viruses in ice without contaminating it.
"These glaciers were formed gradually, and along with dust and ...
In order to correctly separate vehicles into classes, for instance for mobility pricing, one must be able to clearly distinguish mid-sized cars from upper class cars or small cars from compact cars. But this is becoming increasingly difficult: On photos, an Audi A4 looks almost the same as an Audi A6, a Mini One looks similar to a Mini Countryman. To date, there is no independent procedure for doing this.
Thus far, the classes in each country have been determined by experts - to a large extend at their own discretion. Empa researcher Naghmeh Niroomand has now developed a system that can classify cars worldwide based on their dimensions. Purely mathematical and fair. Thanks to it, the current classification ...
FORT LAUDERDALE/DAVIE, Fla. - It's good to have friends.
Most humans have experienced social anxiety on some level during their lives. We all know the feeling - we show up to a party thinking it is going to be chock full of friends, only to find nearly all total strangers. While we typically attribute the long-lasting bonds of social familiarity to complex thinkers like humans, growing evidence indicates that we underestimate the importance of friendship networks in seemingly "simple" animals, like fish, and its importance for survival in the wild. To better understand how familiarity impacts social fishes, a group of research scientists studied this idea using schooling coral reef fish.
"We studied how the presence of ...
FRANKFURT, GERMANY. When SARS-CoV-2 infects a cell, it introduces its RNA into it and re-programmes it in such a way that the cell first produces viral proteins and then whole viral particles. In the search for active substances against SARS-CoV-2, researchers have so far mostly concentrated on the viral proteins and on blocking them, since this promises to prevent, or at least slow down, replication. But attacking the viral genome, a long RNA molecule, might also stop or slow down viral replication.
The scientists in the COVID-19-NMR consortium, which is coordinated by Professor Harald Schwalbe from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Goethe University, have now completed an important ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Since the Covid-19 pandemic began last year, face masks and other personal protective equipment have become essential for health care workers. Disposable N95 masks have been in especially high demand to help prevent the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19.
All of those masks carry both financial and environmental costs. The Covid-19 pandemic is estimated to generate up to 7,200 tons of medical waste every day, much of which is disposable masks. And even as the pandemic slows down in some parts of the world, health care workers are expected to continue wearing masks most of the time.
That toll could be dramatically cut by adopting reusable masks, according to a new study from MIT that has calculated the financial ...
With the looming threat of climate change, it is high time we embrace renewable energy sources on a larger scale. Photovoltaic systems, which generate electricity from the nearly limitless supply of sunlight energy, are one of the most promising ways of generating clean energy. However, integrating photovoltaic systems into existing power grids is not a straightforward process. Because the power output of photovoltaic systems depends heavily on environmental conditions, power plant and grid managers need estimations of how much power will be injected by photovoltaic systems so as to plan optimal generation and maintenance schedules, among other important operational aspects.
In line with modern trends, if something needs predicting, you can safely ...
Researchers in the BOTTLE Consortium, including from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the University of Portsmouth, have identified using enzymes as a more sustainable approach for recycling polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common plastic in single-use beverage bottles, clothing, and food packaging that are becoming increasingly relevant in addressing the environmental challenge of plastic pollution. An analysis shows enzyme-recycled PET has potential improvement over conventional, fossil-based methods of PET production across a broad spectrum of energy, carbon, and socioeconomic impacts.
The concept, if further developed and implemented at scale, could lead to ...
Neurons communicate through rapid electrical signals that regulate the release of neurotransmitters, the brain's chemical messengers. Once transmitted across a neuron, electrical signals cause the juncture with another neuron, known as a synapse, to release droplets filled with neurotransmitters that pass the information on to the next neuron. This type of neuron-to-neuron communication is known as evoked neurotransmission.
However, some neurotransmitter-packed droplets are released at the synapse even in the absence of electrical impulses. These miniature release events -- or ...