(Press-News.org) WHAT:
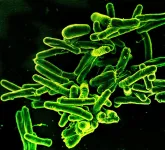
A clinical trial testing a freeze-dried, temperature-stable experimental tuberculosis (TB) vaccine in healthy adults found that it was safe and stimulated both antibodies and responses from the cellular arm of the immune system. The Phase 1 trial was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. A non-temperature stable form of the candidate previously had been tested in several clinical trials. However, this was the first clinical trial of any subunit TB vaccine candidate in a temperature-stable (thermostable) form. Results are published in Nature Communications.
The experimental vaccine, ID93+GLA-SE, was developed by Christopher B. Fox, Ph.D., and scientists at the Access to Advanced Health Institute (formerly the Infectious Disease Research Institute) in Seattle. It is a recombinant subunit vaccine made from four proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria combined with GLA-SE, an immune-stimulating adjuvant. The freeze-dried formulation does not require refrigeration and is mixed with sterile water just prior to injection. Thermostable vaccines are desirable in settings where maintaining cold or frozen vaccines for long periods can be costly and difficult.
The current trial investigated whether administering temperature-stable vaccine containing both ID93 and GLA-SE in a single vial would be as effective at inducing an immune response as a regimen in which non-thermostable ID93 and liquid GLA-SE are held in two vials and combined prior to injection. A single-vial presentation of a thermostable vaccine would have clear advantages in ease of storage, transport and administration, the investigators note.
Daniel F. Hoft, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Saint Louis University Center for Vaccine Development, led the single-site trial at the university’s School of Medicine. Twenty-three participants received the thermostable single-vial regimen, while 22 participants received the two-vial, non-thermostable regimen. Both vaccine presentations were safe and well-tolerated. Recipients of the single-vialled thermostable vaccine had robust T-cell responses and produced higher levels of antibodies in the blood than those receiving the non-thermostable two-vial presentation.
The investigators note some limitations in this small trial. For example, no established correlates of protection define what immune responses are required for vaccine-induced protection from TB disease. Therefore, it is not possible to say whether the enhanced immune responses seen in the thermostable vaccine formulation would translate to improved protective vaccine efficacy. Nevertheless, they conclude, results of this trial demonstrate “a proof-of-concept that adjuvant-containing vaccines can be formulated in a freeze-dried single-vial presentation without detrimentally impacting clinical immunogenicity or safety characteristics.”
ARTICLE:
ZK Sagawa et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a thermostable formulation of the ID93 + GLA-SE tuberculosis vaccine candidate in healthy adults. Nature Communications DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36789-2 (2023).
WHO:
Lakshmi Ramachandra, Ph.D., program officer, Tuberculosis and Other Mycobacterial Diseases Section, Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, NIAID, is available to discuss this trial.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Anne A. Oplinger, (301) 402-1663, niaidnews@niaid.nih.gov.
This research was funded under NIAID contract HHSN272201400041C. Additional information about the trial is available on ClinicalTrials.gov using the identifier NCT03722472.
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
NIH...Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
The Access to Advanced Health Institute (AAHI) published results of a Phase 1 clinical trial demonstrating the safety and immune responses in a new vaccine against tuberculosis (TB), the world’s second deadliest infectious disease (NCT03722472). AAHI’s TB vaccine combines several proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the bacterium that causes TB, into a fusion protein (“ID93”) with a proprietary immune-stimulating adjuvant (“GLA-SE”) in a freeze-dried formulation that can be stored at elevated temperatures ...
A global team of researchers has created an algorithmic tool that can identify existing drugs in order to combat future pandemics. The work, reported in the Cell Press journal Heliyon, offers the possibility of responding more quickly to public-health crises.
“There is no silver bullet to defeat the Covid pandemic as it takes us over a public-health roller-coaster of deaths and devastation,” explains Naomi Maria, an immunologist, a visiting scientist at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, and the paper’s lead author. “However, using this AI tool, coupled with in vitro data and other resources, we’ve ...
Study’s findings may lead to more personalized follow-up care for patients.
New research indicates that for patients with breast cancer, the cancer’s stage and receptor status can help clinicians predict whether and when cancer might recur after initial treatment. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, Heather Neuman, MD, MS, of the University of Wisconsin, and her colleagues analyzed data on 8,007 patients with stage I–III breast cancer who participated in nine clinical trials from 1997–2013 ...
In the earliest days of human flight, before the invention of the first radio beacons and ground-based electronic systems, and modern GPS, pilots commonly navigated by following roads and railways – striking linear landscape elements at ground level that guide towards a destination of interest.
Enter the honeybee. A century of research has shown that honeybees are navigators par excellence. They can navigate by their sense of smell, the sun, the sky’s pattern of polarized light, vertical landmarks that stand out from the panorama, and possibly the Earth’s magnetic field. They are also clever learners, able to recognize associations between disparate ...
PITTSBURGH, March 6, 2023 — The monthly opioid overdose death (ODD) rate fell by 30% in Pennsylvania counties that implemented a novel community-focused strategy developed by University of Pittsburgh researchers, according to a new study published today in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
By analyzing counties that did or didn’t implement the Pennsylvania Opioid Overdose Reduction Technical Assistance Center (ORTAC) strategy over time, the researchers estimate that this cost-effective, community-led approach prevented 1,818 opioid-related deaths over two years.
“I ...
Conifers are generally better than broadleaved trees at purifying air from pollutants. But deciduous tree may be better at capturing particle-bound pollution. A new study led by the University of Gothenburg shows that the best trees for air purification depend on the type of pollutant involved.
Trees and other greenery in cities provide many benefits that are important for the well-being of residents. Leaves and needles on trees filter air pollutants and reduce exposure to hazardous substances in the air. But which trees purify the air most effectively? Researchers from the University ...
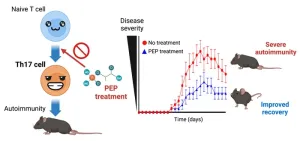
Scientists in Japan have revealed a chemical compound that could be used for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. These diseases occur when the body’s immune response goes wiry. The immune system, which normally attacks pathogens and infections, instead attacks healthy cells and tissues. For the millions of people who suffer from autoimmune diseases worldwide, the result can be debilitating—rheumatoid arthritis causes excessive joint pain, while multiple sclerosis can disable one’s brain and spinal cord function.
“The key to the development of autoimmune ...
Promoting physical activity and other behavioural support can help people wanting to reduce their smoking to quit in the short-term.
However, after nine months, physical activity delivers no noticeable benefits – compared with offering no additional support – in the rates of people stopping smoking, according to the findings of a major national study.
The Trial of physical Activity and Reduction of Smoking (TARS) study, led by the University of Plymouth with funding from the National Institute for Health and Care Research, took place across four cities – Plymouth, Nottingham, Oxford and ...
A total of 1,261,990 people will die from cancer in 2023 in the EU (EU-27). A further 172,314 people will die from the disease in the UK, according to new research published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday).
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), a professor at the University of Milan (Italy), estimate there will be a 6.5% fall in cancer death rates in men and a 3.7% fall in women between 2018 and 2023.
They predict that death rates from the ten most common cancers will continue to fall in most European countries in 2023, although the numbers of people dying will go up ...
Globally, activated sludge treats the majority of urban wastewaters; yet it is one of the most complex biological processes used. It is a sophisticated microbial process fraught with operational problems leading to occasional failures in achieving required effluent quality standards. With the increasing problem of partially treated and raw sewage entering rivers and estuaries, the pressure on the process to cope with ever increasing volumes of wastewater has never been so great.
With increasing volumes of dilute wastewater entering treatment plants the high variability in hydraulic and organic ...