(Press-News.org)
A lot of factors go into an individual’s comfort, and it’s more than just how one feels about the temperature
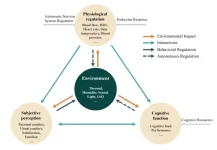
The thermal environment refers to the physical surroundings as it pertains to the heat exchange of an individual and its environment. Naturally, the thermal environment also relates to comfort, or more specifically, thermal comfort. This type of comfort is an important metric to measure an individual’s feelings as it relates to their environment and can be directly associated with health, efficiency, comfort, and energy consumption. However, how these subjective values are measured is not necessarily the most effective or accurate. Here, researchers reassess how thermal comfort and thermal sensation play into an individual’s health and well-being, both physiologically and on a cognitive level.
Researchers published their findings in Building Simulation on 19 January 2024.
The predominant metric of classifying thermal comfort is called “Thermal Sensation” in which a seven-level scale and the specific question in a questionnaire are utilized. The scale’s seven levels are as follows: cold, cool, slightly cool, neutral, slightly warm, warm, and hot. The individual is also asked what their general thermal sensation is. The issue with this question, and the scale, is that it fails to ask or acknowledge the comfort, satisfaction, and acceptability of that thermal sensation.
“In laboratory studies, the focus is often on the impact of specific factors while neglecting the comprehensive effects of the overall environment on the human body and limiting some regulatory behaviors,” said Zhiwei Lian, author and researcher of the study. Even the most recognized model when it comes to thermal comfort, the predicted mean vote (PMV) model, showed only 34% accuracy when compared to real environments as opposed to laboratory settings.
Therefore, researchers thought it appropriate to ask themselves some follow-up questions to further elucidate thermal sensation and thermal comfort to the individual’s overall well-being. For example, questions that need to be answered include whether the thermally neutral state genuinely aligns with the highest probability of comfort, satisfaction, and acceptability, and if individuals experience these same emotions simply by being in the same state of thermal sensation.
To answer these questions, the thermal comfort evaluation system needs a bit of an overhaul. Firstly, addressing the appropriate metrics based on the design goal for a given environment rather than solely on thermal neutrality or sensation might provide a more accurate method of evaluating the thermal environment. Secondly, a unified questionnaire based on psychological research can be an invaluable tool. This means a survey that can stand up against translation into a variety of languages without losing the subtle, but important, differences in meaning. Finally, besides thermal sensation model, more accurate prediction models for other thermal perception would need to be developed, which should take into consideration the comprehensive interaction of various factors of the overall environment and an individual’s needs.
We know that there are many nuances in the way humans interface with their environment and how the environment can affect an individual’s ability to function, from both a physiological and cognitive standpoint. Once a better model is put into place, individuals might be able to see more personalized comfort in their environment.
“The ultimate goal may vary in different environments, such as seeking comfort in residential
settings, pursuing efficiency in work or study environments, and aiming for sleep quality in sleep environments,” said Lian. The fluidity in goals is key in advancing the study of thermal environment, comfort and sensation.
As the study points out, the thermal environment is closely intertwined with comfort, health, efficiency, and building energy consumption. With economic development, technological progress, we now have the capability to pursue a more comfortable, satisfactory, and healthy environment. However, blindly using thermal sensation or thermal neutrality to evaluate the environment or HVAC systems hinders the realization of this pursuit. The future of assessing thermal comfort and sensation should consider these factors for more accurate and impactful data.
Zhiwei Lian of the Shanghai Jiao Tong University contributed to this research.
About Building Simulation
An International Journal publishes original, high quality, peer-reviewed research papers and review articles dealing with modeling and simulation of buildings including their systems. The goal is to promote the field of building science and technology to such a level that modeling will eventually be used in every aspect of building construction as a routine instead of an exception. Of particular interest are papers that reflect recent developments and applications of modeling tools and their impact on advances of building science and technology.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
END
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A neighborhood alcohol control project in Sacramento that reduced cases of child abuse and neglect soon after implementation still had a positive impact seven years later, a new study found.
Results showed that, in one of the neighborhoods where the program was put into place, total entries into foster care were reduced by 11.8% and alcohol-related foster care entries were reduced by 11.2% a full seven years after implementation.
These new results were not as strong as those found right after the project was implemented, and there are other caveats to the success of the program. But the results are still very encouraging, said Bridget Freisthler, ...
An observational study found links between prenatal substance exposure and mental health in children 10–12, but also found that controlling for environment and genetics eliminated many associations. Qiang Luo and colleagues analyzed longitudinal data from almost 10,000 participants in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development cohort, looking for associations of maternal self-report of prenatal exposure to caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana with mental health outcomes from age 10 to 12. Although the authors found many associations between prenatal exposure to the ...
A new study in mice shows that replacement of a dysfunctional gene could prolong survival in some people with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), a rare inherited disorder in which the muscular walls of the heart progressively weaken and put patients at risk of dangerous irregular heartbeats.
The investigational treatment targets the loss of function of a gene implicated in many cases of ARVC, plakophilin-2 (PKP2). The PKP2 gene provides instructions for making a protein that holds heart tissues together. When the gene — one of several thought to contribute to the disease —is defective ...
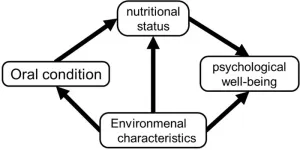
In humans, oral health influences general health and well-being in many ways. Other than reducing the need for oral rehabilitation later in life, maintaining good oral health reduces the risk of several systemic diseases. Therefore, investing time and effort into improving oral health can be highly beneficial for older adults. However, whether the health benefits of improved oral health extend to psychological domains remains unclear.
Positive psychological well-being is known to positively affect the survival rates of both healthy and unhealthy populations. Thus, to increase life expectancy, it is important to identify the factors associated with ...
What does an asparagus have in common with a vanilla orchid? Not much, if you are just looking at the two plants’ appearances. However, when you look inside - their leaves are more similar than you would think – as revealed by the composition of their cell walls.
By studying plant cell walls – which are to plants what skeletons are to humans – we can reveal the composition of how leaves and stems of plants are actually constructed. This is exactly what a team of University of Copenhagen researchers has done, in a large comprehensive study. In doing so, they have created something truly novel: a large "reference catalogue" ...
Using a virus-like delivery particle made from DNA, researchers from MIT and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT, and Harvard have created a vaccine that can induce a strong antibody response against SARS-CoV-2.
The vaccine, which has been tested in mice, consists of a DNA scaffold that carries many copies of a viral antigen. This type of vaccine, known as a particulate vaccine, mimics the structure of a virus. Most previous work on particulate vaccines has relied on protein scaffolds, but the proteins used in those vaccines tend to generate an unnecessary immune response that can distract the immune system from the target.
In the mouse study, the researchers found that the ...
A new research study examined the results from data generated by citizen scientists using a simple web-based motor test. The big data approach provides researchers with a unique way to explore how people correct for motor control errors. The resulting insights may one day pave the way for personalized physical therapy or tailor an athlete’s training routine. The results are available in the January 30th issue of the journal Nature Human Behaviour.
“This exploratory approach does not replace lab based studies, but complements ...
New research into the marine phosphorus cycle is deepening our understanding of the impact of human activities on ecosystems in coastal seas.
The research, co-led by the University of East Anglia, in partnership with the Sino-UK Joint Research Centre at the Ocean University of China, looked at the impact of aerosols and river run-off on microalgae in the coastal waters of China.
It identified an ‘Anthropogenic Nitrogen Pump’ which changes the phosphorus cycle and therefore likely coastal biodiversity and associated ecosystem services.
In a balanced ecosystem, microalgae, also known as phytoplankton, provide food for a wide ...
Life has a challenging tempo. Sometimes, it moves faster or slower than we’d like. Nevertheless, we adapt. We pick up the rhythm of conversations. We keep pace with the crowd walking a city sidewalk.
“There are many instances where we have to do the same action but at different tempos. So the question is, how does the brain do it," says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Assistant Professor Arkarup Banerjee.
Now, Banerjee and collaborators have uncovered a new clue that suggests the brain bends our processing of time to suit our ...
People of religious faith may have experienced lower levels of unhappiness and stress than secular people during the UK’s Covid-19 lockdowns in 2020 and 2021, according to new University of Cambridge research.
The findings follow a recently published Cambridge-led study suggesting that worsening mental health after experiencing Covid infection – either personally or in those close to you – was also somewhat ameliorated by religious belief. This study looked at the US population during early 2021.
University of Cambridge economists argue ...