(Press-News.org) About The Study: Survey respondents reported substantial acceptability of hospital-at-home care, which did not vary across sociodemographics, health insurance coverage, health status, prior hospitalizations, or telehealth use. Approximately half of respondents agreed that hospital-at-home care was effective, safe, and convenient. Most indicated capacity to perform many caregiver tasks.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Melissa A. Frasco, Ph.D., email mfrasco@usc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.10035)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.10035?guestAccessKey=b575190f-6bf6-4ff8-9f49-66549ee1f6f4&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=070824
END
Acceptability of hospital-at-home care and capacity for caregiver burden
JAMA
2024-07-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Semaglutide vs tirzepatide for weight loss in adults with overweight or obesity
2024-07-08
About The Study: In this population of adults with overweight or obesity, use of tirzepatide was associated with significantly greater weight loss than semaglutide. Future study is needed to understand differences in other important outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicholas L. Stucky, M.D., email nicholass@truveta.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.2525)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
AJPH study shows that permit to purchase laws are a promising avenue to reduce suicides in young adults
2024-07-08
In 2020, suicide ranked as the third leading cause of death for adults aged 18 to 20 years in the United States. Firearms were implicated in approximately half of these cases, and by 2017, they had surpassed motor vehicles as the leading cause of death in this age group. While ongoing debates on gun violence and mental health have increased public support for restricted firearm access, not much is known about the impact of gun control policies on young adults.
To fill this knowledge gap, a recent study published in the August issue of the American Journal of Public Health on July 03, ...
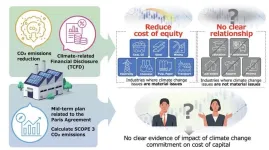
Companies that mitigate climate change reduce their cost of capital
2024-07-08
Fukuoka, Japan —The climate crisis is hitting home with more frequent extreme weather events. Companies, particularly those in high-emission industries, are major contributors to global carbon emissions, therefore making them key players in the fight against climate change. Recognizing this responsibility, many businesses are now taking proactive measures to reduce their carbon footprint, by reducing carbon emissions and transparently sharing their environmental strategies and data.
The Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures ...
Case Western Reserve University receives $1.5M grant from Foundation Fighting Blindness to test possible new treatment for inherited retinal disease
2024-07-08
CLEVELAND—There’s only one U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved therapy for an inherited retinal disease, and dozens of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) genes for which no therapy is available.
With a new three-year, $1.5 million grant from the Foundation Fighting Blindness, Shigemi Matsuyama, an associate professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, will test a possible breakthrough drug that can be taken by mouth—one that may address many RP disease manifestations, regardless of the underlying genetic mutation.
“We believe it can serve as the basis of an oral medicine to prevent blindness in RP ...
How to stop cancer cachexia? Start at the top
2024-07-08
Cancer is insidious. Throughout tumor progression, the disease hijacks otherwise healthy biological processes—like the body’s immune response—to grow and spread. When tumors elevate levels of an immune system molecule called Interleukin-6 (IL-6), it can cause severe brain dysfunction. In about 50%-80% of cancer patients, this leads to a lethal wasting disease called cachexia. “It’s a very severe syndrome,” says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Bo Li.
“Most people with cancer die of cachexia instead of cancer. And once the patient enters this stage, there’s ...
Pulsed field ablation procedures found safe and effective for atrial fibrillation patients
2024-07-08
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is safe for treating patients with common types of atrial fibrillation (AF), according to the largest study of its kind on this new technology, led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
The “MANIFEST-17K” international study is the first to show important safety outcomes in a large patient population, including no significant risk of esophageal damage, with PFA. PFA is the latest ablation modality approved by the Food and Drug Administration that can be used to restore a regular heartbeat. The findings, published July 8 in Nature Medicine, could lead to more frequent use of PFA instead of conventional therapies to manage AF patients.
“MANIEFST-17K ...
Why some abusive bosses get a pass from their employees
2024-07-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Why do employees sometimes accept working for an abusive boss?
A new study suggests that when a leader is seen as a high performer, employees are more likely to label abuse as just “tough love.”
Results showed that workers were less likely to show hostility to abusive bosses when the leader’s performance was high, and employees were even likely to think their career could be boosted by a successful – if abusive – boss.
The findings suggest that employees may be reluctant to call a successful boss abusive – ...
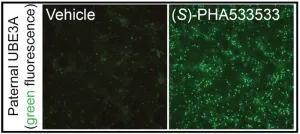
UNC researchers identify potential treatment for Angelman syndrome
2024-07-08
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Angelman syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in the maternally-inherited UBE3A gene and characterized by poor muscle control, limited speech, epilepsy, and intellectual disabilities. Though there isn't a cure for the condition, new research at the UNC School of Medicine is setting the stage for one.
Ben Philpot, PhD, the Kenan Distinguished Professor of Cell Biology and Physiology at the UNC School of Medicine and associate director of the UNC Neuroscience Center, and his lab have identified a small molecule that could be safe, non-invasively delivered, and capable of ...
Study: Weaker ocean circulation could enhance CO2 buildup in the atmosphere
2024-07-08
As climate change advances, the ocean’s overturning circulation is predicted to weaken substantially. With such a slowdown, scientists estimate the ocean will pull down less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, a slower circulation should also dredge up less carbon from the deep ocean that would otherwise be released back into the atmosphere. On balance, the ocean should maintain its role in reducing carbon emissions from the atmosphere, if at a slower pace.
However, a new study by an MIT researcher finds that scientists may have to rethink the relationship between the ocean’s circulation and its ...
Brain size riddle solved as humans exceed evolution trend
2024-07-08
The largest animals do not have proportionally bigger brains - with humans bucking this trend - a new study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution has revealed.
Researchers at the University of Reading and Durham University collected an enormous dataset of brain and body sizes from around 1,500 species to clarify centuries of controversy surrounding brain size evolution.
Bigger brains relative to body size are linked to intelligence, sociality, and behavioural complexity – with humans having evolved exceptionally large brains. The new research, published today (Monday, 8 July), reveals the largest animals do not have proportionally bigger brains, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
[Press-News.org] Acceptability of hospital-at-home care and capacity for caregiver burdenJAMA