(Press-News.org) ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Testing weapons and components in a lab-controlled environment has always been at the center of Sandia National Laboratories’ mission. Since the U.S. stopped underground explosives tests on weapons in the early 1990s, Sandia has developed other methods to conduct experiments that mimic the range of environments a weapons unit might experience. A newly developed method is getting better results, with fewer tests, in less time.
“Our job in the laboratory is to simulate the environment and lifetime of stress that the weapon units experience out in the field,” said Kevin Cross, a mechanical engineer who oversees Sandia’s vibration lab. “Using multiple input, multiple output testing is a much more realistic representation of what those units experience in flight and out in the field.”
One multiple input, multiple output testing machine is called the six degrees of freedom shaker. The shaker table simultaneously moves the x-, y- and z-axes, while also rotating each axis.
Over the past few years, Sandia has been expanding the methodology for multiple input, multiple output experiments for nuclear deterrence systems.
Qualification testing
Sandia recently used the six degrees of freedom shaker for qualification of the W80-4 — a first for a weapons system that will go into the U.S. stockpile. A variety of information is used for qualification — or ensuring the system meets requirements — including experimental data.
“This capability has been beneficial because it more accurately represents the environment a deterrence system would withstand in the field,” said Christy Turner, who oversees system and environmental testing for the W80-4. “It’s also beneficial from a schedule standpoint. Testing using the six degrees of freedom shaker takes about a third of the time as a full mechanical shock and vibration test.”
Sandia has one of only a few six degrees of freedom machines in the country.
“In single-axis testing, we test each axis independent of each other, so it’s three times the amount of testing than in a multiple input, multiple output test,” Cross said. “We by far lead the way here at Sandia on multiple input, multiple output testing.”
Building techniques and capacity
To carry out qualification tests for the W80-4, Cross and his team developed specific methodology for the system and built a bespoke multiple input, multiple output test stand for it.
“The testing equipment and methodology are building capacity to meet the mission, and it’s giving us higher fidelity data,” Cross said.
Turner has been pleased with the teamwork.
“The experts at the vibration facility have brought us a solution that helps reduce risk from a schedule standpoint,” she said. “This is an important example of collaboration across divisions at Sandia.”
Since recent environmental tests were completed on the W80-4, other nuclear deterrence programs have taken notice and are exploring similar multiple input, multiple output experiments for their systems.
“The big selling point in terms of the nuclear deterrence community is that we can significantly reduce the amount of test time required,” Cross said. “Not only are we getting a much better, much more realistic dataset, but we’re also doing it considerably faster.”
###
Sandia National Laboratories is a multimission laboratory operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International Inc., for the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration. Sandia Labs has major research and development responsibilities in nuclear deterrence, global security, defense, energy technologies and economic competitiveness, with main facilities in Albuquerque, New Mexico, and Livermore, California.
Sandia news media contact: Kenny Vigil, kcvigi@sandia.gov, 505-537-1528
END
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to share the news that Midwestern University has successfully launched a new faculty profiles portal powered by Symplectic Elements.
Midwestern has been utilizing Symplectic Elements as its Research Information Management System since 2019, and has made the decision to expand its use by adding public profiles. The faculty profiles repurpose the comprehensive data already within Elements to populate enhanced profiles, including biographical information as ...
MND is a devastating disease affecting the motor neurones in the brain and spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. Despite decades of research, several scientific challenges continue to impede the development of effective therapies for the thousands of people living with MND in the UK.
The MND Research Data Catalyst is a new initiative led by HDR UK and DPUK, with the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) and in partnership with the MND research community, to accelerate the discovery of new diagnostics, treatments and support better care for MND patients. This will be achieved by harnessing the UK’s trustworthy, large-scale health ...
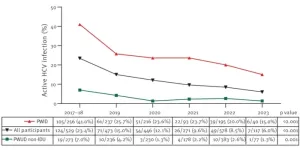
A study conducted through a mobile screening unit in Madrid, Spain from 2017 to 2023 and published in Eurosurveillance found that active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection decreased from 23% to 6% in that period among people who use drugs (PWUD) that visited the unit. The study found that the use of intravenous drugs was the most significant risk factor for infection among PWUD. It confirmed that HCV screening and treatment programmes targeting this at-risk population are effective and can help achieve the World Health Organization goal of HCV elimination as public health threat by 2030.
Study participants and methods
Participants were recruited in ‘hotspots’ ...
In 2016, President-elect Donald Trump vowed to deport thousands of immigrants. His anti-immigration message vilified foreign-born people living in the U.S. as criminals and rapists. Besides making good on many harsh, immigration-related promises, the years after his election stoked the anxieties of millions of people.
Now, with Trump once again in contention for the White House, a new study from the University of California, Berkeley, reveals the surprising — and potentially lifelong — association between those early Trump years and the health of society's newest citizens.
In ...
A gentle rumble ran under Ngan Huang’s feet as a rocket carrying her research—live, human muscle cells grown on scaffolds fixed on tiny chips—lifted off, climbed, and disappeared into the sky to the International Space Station National Laboratory. These chips would help Huang better understand muscle impairment, often seen in astronauts and older adults, and test drugs to counter the condition.
Now, the results are back. Reporting in a study published July 25 in Stem Cell Reports, Huang’s team showed that space-travelling muscle had metabolic changes that indicate ...
Findings from a small, proof-of-concept clinical trial have suggested that fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) can boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy in a range of gastrointestinal cancers. In the study, published July 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, six of 13 patients who had previously shown resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors benefited from receiving FMTs from donors who had previously responded to treatment. The investigators also identified specific strains of bacteria associated with better or worse responses to FMT and immune checkpoint drugs.
“This research highlights the complex interplay between beneficial ...
Newly announced research by Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) examining greenhouse gas emissions from the drying lake bed of Great Salt Lake, Utah, calculates that 4.1 million tons of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases were released in 2020. This research suggests that drying lake beds are an overlooked but potentially significant source of greenhouse gases, which may further increase due to climate change. These results were announced in the paper, “A desiccating saline lake bed is a significant source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions,” published in the journal One Earth.
“Human-caused ...
About The Study: Hospitals in communities with the greatest level of socioeconomic disadvantage had the lowest likelihood of becoming stroke certified while hospitals in the most advantaged communities had the highest likelihood in this cohort study. These findings suggest that there is a need to support hospitals in disadvantaged communities to obtain stroke certification as a way to reduce stroke disparities.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Renee Y. Hsia, M.D., M.Sc., email renee.hsia@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
About The Study: This cohort study indicates that the risk of dying of breast cancer increases substantially after experiencing a contralateral breast cancer. Women with breast cancer treated with bilateral mastectomy had a greatly diminished risk of contralateral breast cancer; however, they experienced similar mortality rates as patients treated with lumpectomy or unilateral mastectomy.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Steven A. Narod, M.D., email steven.narod@wchospital.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2212)
Editor’s ...
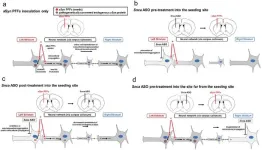
TMDU researchers demonstrate proof of concept of antisense nucleic acid therapy to prevent the spread of α-synuclein pathologies in synucleinopathies.
Tokyo, Japan – Parkinson’s disease (PD), as well as many other neurodegenerative disorders, has shown a link between the abnormal aggregation of a protein called α-synuclein (aSyn) and neuronal death. These aggregates, known as Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites depending on their subcellular localization, can spread by continuously causing normal endogenous aSyn to misfold. The complex nature of this aggregation process poses significant challenges ...