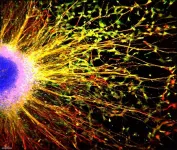
(Press-News.org) A new method to measure the continuous spectrum of light, developed in the lab of University of Houston professor of electrical and computer engineering Jiming Bao, is set to improve thermal imaging and infrared thermography, techniques used to measure and visualize temperature distributions without direct contact with the subject being photographed.
Because they are highly sensitive, thermal cameras and infrared thermometers measure temperature accurately from a distance, making them versatile and valuable tools in many fields from the military to medical diagnostics. They detect infrared radiation, invisible to the human eye, and convert it into visible images. Different colors on the image represent varying temperatures, allowing users to see heat patterns and differences.
APPLICATIONS:
- Medical Diagnostics: Identifying inflammation and poor blood flow
- Building Inspections: Detecting heat loss, insulation issues and water leaks
- Military, Security and Surveillance: Spotting people or animals in low visibility conditions
- Mechanical Inspections: Finding overheating machinery or electrical faults
Both techniques rely on the principle of blackbody radiation – a theoretical perfect emitter - where objects emit infrared radiation based on their temperature. By capturing this radiation, the tools provide valuable insights into the thermal properties and behaviors of various objects and environments.
But Houston, we have a problem
Thermal cameras and infrared thermometers cannot provide accurate readings because they rely on emissivity, a measure of how effectively a real object emits thermal radiation, and that varies with temperature—to determine temperature. Multi-spectral techniques address this by measuring infrared intensity at multiple wavelengths, but their accuracy depends on their emissivity models.
And at the University of Houston, a solution
“We designed a technique using a near-infrared spectrometer to measure the continuous spectrum and fit it using the ideal blackbody radiation formula,” reports Bao, in the journal Device. “This technique includes a simple calibration step to eliminate temperature- and wavelength-dependent emissivity.”
Bao demonstrates his technique by measuring the temperature of a heating stage with errors less than 2°C and measuring the surface temperature gradient of a catalyst powder under laser heating. Using the near-infrared spectrometer, thermal radiation from a hot target is collected with an optical fiber and recorded by a computer. The collected spectrum is normalized using a system calibration response and fitted to determine the temperature.
“This technique overcomes challenges faced by conventional thermal cameras and infrared thermometers due to the unknown emissivity of targets and reveals much higher surface temperatures of photothermal catalysts than those measured by a buried thermocouple under strong light illumination,” said Bao.
HIGHLIGHTS
- Overcoming limitations of single-wavelength and multi-spectral thermometry
- Simple calibration to eliminate wavelength- and temperature-dependent emissivity
- Accurate temperature determination over a wide temperature range
- Revealed a huge temperature gradient in a catalyst powder under laser heating
“This technique overcomes challenges faced by conventional thermal cameras and infrared thermometers due to the unknown emissivity of targets and reveals much higher surface temperatures of photothermal catalysts than those measured by a buried thermocouple under strong light illumination,” said Bao.
END
UH engineer develops technique that enhances thermal imaging and infrared thermography for police, medical, military use
Overcomes challenges faced by conventional thermal imaging, eliminates wavelength and temperature dependence
2024-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer drug could ease cognitive function for some with autism
2024-07-25
An experimental cancer drug could make thinking easier for individuals with Rett syndrome, a rare disorder linked to autism, according to new research from the University of California San Diego — a discovery that could lead to therapies for patients with other neurological conditions.
The findings, published July 25 in Stem Cell Reports, highlight the role of microglia — a type of white blood cell found in the central nervous system — in the formation of the human brain.
While such cells have been better studied in neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic ...
Oregon State University research uncovers better way to produce green hydrogen
2024-07-25
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers at Oregon State University have developed a material that shows a remarkable ability to convert sunlight and water into clean energy.
A collaboration led by Kyriakos Stylianou of the OSU College of Science created a photocatalyst that enables the high-speed, high-efficiency production of hydrogen, used in fuel cells for cars as well as in the manufacture of many chemicals including ammonia, in the refining of metals and in making plastics.
The findings represent a potential new tool to use against greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, said Stylianou, whose research focuses ...
Transforming environmental testing one shake at a time
2024-07-25
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Testing weapons and components in a lab-controlled environment has always been at the center of Sandia National Laboratories’ mission. Since the U.S. stopped underground explosives tests on weapons in the early 1990s, Sandia has developed other methods to conduct experiments that mimic the range of environments a weapons unit might experience. A newly developed method is getting better results, with fewer tests, in less time.
“Our job in the laboratory is to simulate the environment and lifetime of stress ...
Midwestern launches public research profiles through Symplectic Elements
2024-07-25
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to share the news that Midwestern University has successfully launched a new faculty profiles portal powered by Symplectic Elements.
Midwestern has been utilizing Symplectic Elements as its Research Information Management System since 2019, and has made the decision to expand its use by adding public profiles. The faculty profiles repurpose the comprehensive data already within Elements to populate enhanced profiles, including biographical information as ...
Accelerating motor neurone disease research by harnessing the power of health data
2024-07-25
MND is a devastating disease affecting the motor neurones in the brain and spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. Despite decades of research, several scientific challenges continue to impede the development of effective therapies for the thousands of people living with MND in the UK.
The MND Research Data Catalyst is a new initiative led by HDR UK and DPUK, with the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) and in partnership with the MND research community, to accelerate the discovery of new diagnostics, treatments and support better care for MND patients. This will be achieved by harnessing the UK’s trustworthy, large-scale health ...
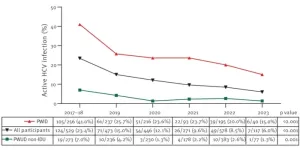
World Hepatitis Day 2024: Madrid study shows decrease in active hepatitis C infection among risk groups, indicating effectiveness of public health measures
2024-07-25
A study conducted through a mobile screening unit in Madrid, Spain from 2017 to 2023 and published in Eurosurveillance found that active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection decreased from 23% to 6% in that period among people who use drugs (PWUD) that visited the unit. The study found that the use of intravenous drugs was the most significant risk factor for infection among PWUD. It confirmed that HCV screening and treatment programmes targeting this at-risk population are effective and can help achieve the World Health Organization goal of HCV elimination as public health threat by 2030.
Study participants and methods
Participants were recruited in ‘hotspots’ ...
After Trump’s election, women of color had more underweight, premature babies, study finds
2024-07-25
In 2016, President-elect Donald Trump vowed to deport thousands of immigrants. His anti-immigration message vilified foreign-born people living in the U.S. as criminals and rapists. Besides making good on many harsh, immigration-related promises, the years after his election stoked the anxieties of millions of people.
Now, with Trump once again in contention for the White House, a new study from the University of California, Berkeley, reveals the surprising — and potentially lifelong — association between those early Trump years and the health of society's newest citizens.
In ...
Space-trekking muscle tests drugs for microgravity-induced muscle impairment
2024-07-25
A gentle rumble ran under Ngan Huang’s feet as a rocket carrying her research—live, human muscle cells grown on scaffolds fixed on tiny chips—lifted off, climbed, and disappeared into the sky to the International Space Station National Laboratory. These chips would help Huang better understand muscle impairment, often seen in astronauts and older adults, and test drugs to counter the condition.
Now, the results are back. Reporting in a study published July 25 in Stem Cell Reports, Huang’s team showed that space-travelling muscle had metabolic changes that indicate ...
In clinical trial, fecal matter transplant helped half of patients with gastrointestinal cancers overcome resistance to immunotherapy treatment
2024-07-25
Findings from a small, proof-of-concept clinical trial have suggested that fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) can boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy in a range of gastrointestinal cancers. In the study, published July 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, six of 13 patients who had previously shown resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors benefited from receiving FMTs from donors who had previously responded to treatment. The investigators also identified specific strains of bacteria associated with better or worse responses to FMT and immune checkpoint drugs.
“This research highlights the complex interplay between beneficial ...
Royal Ontario Museum scientist identifies Great Salt Lake as a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions
2024-07-25
Newly announced research by Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) examining greenhouse gas emissions from the drying lake bed of Great Salt Lake, Utah, calculates that 4.1 million tons of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases were released in 2020. This research suggests that drying lake beds are an overlooked but potentially significant source of greenhouse gases, which may further increase due to climate change. These results were announced in the paper, “A desiccating saline lake bed is a significant source of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions,” published in the journal One Earth.
“Human-caused ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] UH engineer develops technique that enhances thermal imaging and infrared thermography for police, medical, military useOvercomes challenges faced by conventional thermal imaging, eliminates wavelength and temperature dependence