(Press-News.org) DETROIT — Mark Lumley, Ph.D., distinguished professor of psychology in Wayne State University’s College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, was recently awarded the 2024 Nathan W. Perry, Jr. Award for Career Service to Health Psychology from the Society for Health Psychology.
The Society for Health Psychology is a national nonprofit that seeks to improve the lives of individuals and society by promoting health, preventing illness and improving health care through research, practice, education, training and advocacy.
“I’m delighted and greatly honored for this recognition,” said Lumley. “I, along with my excellent students and collaborators, have been contributing to the field of health psychology for nearly four decades and I am so pleased that my colleagues in this national society recognize the influence that our work has had on the field, particularly chronic pain disorders.”
Lumley is a native of Detroit and attended Wayne State University as an undergraduate, majoring in both psychology and biology. In 1990, he completed his Ph.D. in clinical and health psychology at the University of Florida in Gainesville. After a one-year post-doctoral fellowship in behavioral medicine at the University of Michigan, he joined the faculty in the Department of Psychology at Wayne State University. He became a distinguished professor in 2017, worked as the director of training for Wayne State’s clinical psychology Ph.D. program for 17 years and has mentored nearly 50 students to their Ph.D. In 2018, the Society for Health Psychology recognized Lumley with the Excellence in Health Psychology Mentoring Award.
Lumley was lauded by the society and many of his colleagues for his development of a psychological therapy addressing trauma and suppressed emotions that often underlie some types of chronic pain and other “psychophysiological” or “stress-related” somatic conditions. Along with his colleague, Howard Schubiner, M.D., from Michigan State University, Lumley developed a new therapy called Emotional Awareness and Expression Therapy (EAET). Unlike traditional psychological treatments for chronic pain, EAET focuses on a person's emotional experiences — with particular attention to how these experiences developed over the course of the patient’s life, how emotions that are suppressed or avoided contribute to pain, and how therapy can reverse this emotional avoidance and reduce or even eliminate pain.
“My early research showed how a lack of expressing one’s feelings can contribute to chronic pain and that writing or talking about stressors and your feelings can improve chronic pain,” said Lumley. “This work then allowed us to develop and test a new psychological therapy for chronic pain. The society has recognized my goal of moving the field forward toward new methods of treatment with the potential to help so many more people.”
Lumley and his colleague, John Burns, Ph.D., of Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, are principal investigators on a four-year, $3,064,088 grant, “Comparative mechanisms (mediators, moderators) of psychosocial chronic pain treatments,” from the National Institute of Nursing Research of the National Institutes of Health. They are conducting a clinical trial comparing EAET to two leading psychological pain management approaches in the field. This trial will determine how these therapies compare on outcomes, as well as how the therapies work and who is helped the most by each one. For more information about the study, email paintreatmentstudy@gmail.com.
“Dr. Lumley is most deserving of this recognition for his important research focused on chronic pain disorders,” said Ezemenari M. Obasi, Ph.D., vice president for research & innovation at Wayne State University. “His contributions to this field are making a difference in the lives of countless people.”
The grant number for the award from the National Institute of Nursing Research of the National Institutes of Health is NR020610.
# # #
About Wayne State University
Wayne State University is one of the nation’s pre-eminent public research universities in an urban setting. Through its multidisciplinary approach to research and education, and its ongoing collaboration with government, industry and other institutions, the university seeks to enhance economic growth and improve the quality of life in the city of Detroit, state of Michigan and throughout the world. For more information about research at Wayne State University, visit research.wayne.edu.
Wayne State University’s research efforts are dedicated to a prosperity agenda that betters the lives of our students, supports our faculty in pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation further, and strengthens the bonds that interconnect Wayne State and our community. To learn more about Wayne State University’s prosperity agenda, visit president.wayne.edu/prosperity-agenda.
END
URBANA, Ill. -- Elephant conservation is a major priority in southern Africa, but habitat loss and urbanization mean the far-ranging pachyderms are increasingly restricted to protected areas like game reserves. The risk? Contained populations could become genetically isolated over time, making elephants more vulnerable to disease and environmental change.
A recent study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Pretoria in South Africa demonstrates how African conservation managers could create and optimize elephant movement corridors across a seven-country ...
Social media’s rise to popularity between 2010 and 2020 has been strongly correlated with the nationwide freefall in youth mental health that characterized the 2010s. Lawmakers have put increasing pressure on the U.S. government to take social media regulation more seriously, with cases about platforms like Facebook, Instagram and X rising to the Supreme Court level.
But despite the ubiquity of social media, scientists at Northwestern Medicine and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that in Illinois, youth emergency room visits and hospitalizations for depression and anxiety decreased ...
or many plants, more branches means more fruit. But what causes a plant to grow branches? New research from the University of California, Davis shows how plants break down the hormone strigolactone, which suppresses branching, to become more “bushy.” Understanding how strigolactone is regulated could have big implications for many crop plants.
The study was published August 1 in Nature Communications.
“Being able to manipulate strigolactone could also have implications beyond plant architecture, including on a plant’s resilience to drought and pathogens,” said senior author Nitzan Shabek, an associate professor in the UC Davis Department of ...
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Some proteins, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), can stop the immune system from attacking cancer cells and, therefore, support the growth of cancer. Therapies targeting these proteins can be highly effective, but tumors can become resistant.
We applied a method to detect proteins on a single–cell level to uncover human carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) patterns in melanoma. We found that increased ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named six new Damon Runyon Clinical Investigators. The recipients of this prestigious award are outstanding, early-career physician-scientists conducting patient-oriented cancer research at major research centers under the mentorship of the nation's leading scientists and clinicians.
The Clinical Investigator Award program was designed to increase the number of physicians capable of translating scientific discoveries into new treatments for cancer patients. Each Awardee will receive $600,000 over three years, ...
August 6, 2024 — Thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (TOPLL) is a rare condition associated with ectopic bone formation in the thoracic spine. A long-term follow-up study from Japan shows significant and lasting improvement in outcomes with posterior decompression and fixation surgery for patients with T-OPLL, reports The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Surgical treatment of T-OPLL is effective in improving neurological function, quality ...
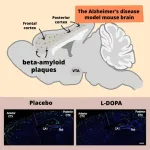
A new way to combat Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by Takaomi Saido and his team at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan. Using mice with the disease, the researchers found that treatment with dopamine could alleviate physical symptoms in the brain as well as improve memory. Published in the scientific journal Science Signaling on August 6, the study examines dopamine’s role in promoting the production of neprilysin, an enzyme that can break down the harmful plaques in the brain that are the ...
Millions of Americans consume supplements that contain potentially hepatoxic botanical ingredients, according to a study from University of Michigan researchers.
Over a 30-day period, 4.7% of the adults surveyed in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2017 to 2020 took herbal and dietary supplements containing at least one of the botanicals of interest: turmeric; green tea; ashwagandha; black cohosh; garcinia cambogia; and red yeast rice containing products.
The resulting paper, “Estimated Exposure ...
Sometimes you just can’t win, and that goes double for people navigating the increasingly polarized political landscape in the United States.
Having nuanced opinions of politics in the U.S. turns out to be a very lonely, and unpopular, road, according to a recent study from a research team that includes assistant professor Aviva Phillipp-Muller from Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the study found that people who express ambivalence about political topics – ranging from COVID-19 mask mandates, immigration and the death ...
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 6, 2024) – Grab a drink with friends at happy hour and you’re likely to feel chatty, friendly and upbeat. But grab a drink alone and you may experience feelings of depression. Researchers think they now know why this happens.
“Social settings influence how individuals react to alcohol, yet there is no mechanistic study on how and why this occurs,” said Kyung-An Han, Ph.D., a biologist at The University of Texas at El Paso who uses fruit flies to study alcoholism.
Now, Han and a team of UTEP faculty and students have taken a key step in understanding the neurobiological process behind social drinking and how it boosts ...