Activated bamboo charcoal’s slow-release properties for enhanced anti-acne formulations containing bamboo vinegar
2024-08-23
(Press-News.org)
Bamboo vinegar is a concentrated liquid obtained from bamboo under high temperature and anaerobic conditions. It contains more than 200 organic components, including organic acids, phenols, ketones, alcohols, and esters, among which acetic acid is the main component. Although bamboo vinegar has been approved by the China Food and Drug Administration as a cosmetic raw material, commercially available bamboo vinegar often contains impurities whose efficacy is not clear, and phenolic compounds and aromatic hydrocarbons in it may be harmful to humans.
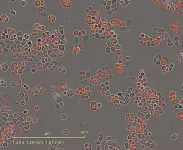
Nevertheless, bamboo vinegar has anti-acne potential, especially against the inhibitory effect of Propionibacterium acnes, the key microorganism in the pathogenesis of acne. While antibiotics are commonly used to treat acne, the concerns for drug resistance have limited their use.
In a study published in the Volume 1, Issue 2 in Journal of Dermatologic Science and Cosmetic Technology, a team of researchers from Central South University of Forestry and Technology in China explored the mechanism of the controlled-release system of bamboo vinegar and its application potential of in cosmetics.
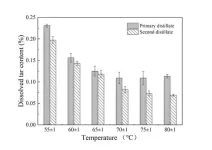
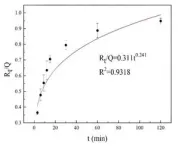
“Bamboo vinegar was refined through reduced-pressure distillation, which increased the content of organic acids, reduced tar content and enhanced the active ingredients while minimizing harmful components,” explains corresponding author Sheng Zhang. “We used activated bamboo charcoal to adsorb the bamboo vinegar, allowing for a gradual release over a period exceeding two hours, effectively demonstrating a slow-release effect.”
The findings auggest that refined bamboo vinegar could be a promising raw material for anti-acne cosmetic formulations. The release rate of the bamboo charcoal/bamboo vinegar complex in water reached 70.57% within 15 minutes and then slowed to a plateau. This slow-release behavior aligns with the Ritger-Peppas model, which is advantageous for reducing skin irritation and extending the bacteriostatic duration.
“The findings present a novel concept for anti-acne cosmetics and lay the groundwork for further research into the use of bamboo vinegar slow-release systems with bamboo charcoal as a carrier,” adds Zhang. “Future studies should explore additional cosmetic benefits of bamboo vinegar, such as dandruff removal, anti-wrinkle effects and more.”
###
Contact the author: Sheng Zhang, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha 410004, China, gingshen123@126.com
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-23
How effective medications are depends on various factors, including the time of day when they are administered. Why? Because our bodies don’t always function exactly the same. Instead, they follow the cycle set by their internal clock, otherwise known as circadian rhythm. But since each person’s circadian rhythm is different and depends on a number of different factors, it is difficult to tailor medication schedules to an individual patient’s body clock. Researchers at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have now developed a method for determining the optimum time of cancer treatment based on certain breast cancer ...
2024-08-23
Obesity-related cancer rates in China were rising at an alarming 3.6% every year between 2007 and 2021 while non-obesity-related cancers remained stable, according to the first comprehensive study published August 22 in the Cell Press journal Med. The increase is particularly pronounced among young people, highlighting the urgent need for better public health policies to address China’s growing overweight and obesity rates.
“If we don’t drastically change the obesity epidemic, the rates of cancer associated with obesity will inevitably continue to rise,” says Jin-Kui Yang, the paper’s corresponding author and an endocrinologist ...
2024-08-23
About The Study: Researchers found corresponding increases in hypertension prevalence as neighborhood disadvantage and the percentage of Black patients residing in a neighborhood increased in this cross-sectional study. A higher burden of midlife hypertension was identified in Black adults compared with other racial and ethnic groups that persisted across levels of socioeconomic disadvantage. This study also found that living in socioeconomically disadvantaged neighborhoods was associated with higher hypertension ...
2024-08-23
The elimination of damaged cell components is essential for the maintenance of the body’s tissues and organs. An international research team led by the University of Bonn has made significant findings on mechanisms for the clearing of cellular wastes, showing that strength training activates such mechanisms. The findings could form the basis for new therapies for heart failure and nerve diseases, and even afford benefits for manned space missions. A corresponding article has been published in the latest issue of the journal Current Biology. EMBARGOED: Do not publish until 5 pm CEST ...
2024-08-23
Exploring new energy storage and conversion technologies is crucial for sustainable human development. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and metal-air batteries are particularly promising due to their high energy efficiency and environmental friendliness. A key component in these technologies is the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst. Traditionally, ORR catalysts rely on expensive platinum group metals (PGM), which are cost-prohibitive for widespread use. This has spurred interest in developing non-precious metal alternatives, such as transition metal/nitrogen-doped carbon-based materials (M–N–C). Among these, Fe–N–C ...
2024-08-23
This study is led by Prof. Shunxin Wang (State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine and Offspring Health, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Women, Children and Reproductive Health, Shandong University) and Prof. Liangran Zhang (Advanced Medical Research Institute, Shandong University). In their study of meiosis in budding yeast, the research team found that yeast senses temperature changes by increasing the level of DNA negative supercoils to increase crossovers and modulate chromosome organization ...
2024-08-23
Individual cells divide through a process called mitosis, during which the cell’s copied DNA is separated between two resulting daughter cells. Despite recent advances in cell biology, the mechanism by which DNA condenses during mitosis is still poorly understood. Researchers recently tracked small stretches of DNA wound around histone proteins, called nucleosomes, to better characterize nucleosome behavior during cell division.
DNA is organized as chromatin, which are dynamic structures comprised of DNA, RNA, and proteins that regulate the accessibility of genes for expression and the overall configuration of genetic material in the cell. Histone proteins, for example, are positively ...
2024-08-23
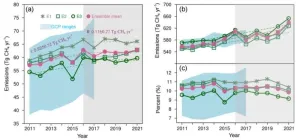
Methane is a potent greenhouse gas. Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric methane concentrations have nearly doubled, with its radiative forcing accounting for one-third of all greenhouse gases. As one of the world's largest methane emitters, China made a clear commitment as early as 2007 to "strive to control the growth rate of methane emissions." The country's 12th, 13th, and 14th Five-Year Plans all proposed measures to control methane emissions. In 2023, China released the "Methane Emission Control Action ...
2024-08-23
The income and education levels of a child’s environment determine their relationship to nature, not whether they live in a city or the countryside. This is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at Lund University, Sweden. The results run counter to the assumption that growing up in the countryside automatically increases our connection to nature, and yet the study also shows that nature close to home increases children’s well-being.
There is a general concern that, with urbanisation, people have lost contact with nature. According to research, less contact ...
2024-08-23
An international study led by Institute of Natural Resources and Agrobiology of Seville (IRNAS-CSIC), of the Spanish National Research Council (CISC), has shown that as the number of global change factors increases, terrestrial ecosystems become more sensitive to the impacts of global change. The results, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience, show that the resistance of our ecosystems to global change decreases significantly as the number of environmental stressors increases, especially when this stress is sustained over time.
This is the conclusion reached by the Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Activated bamboo charcoal’s slow-release properties for enhanced anti-acne formulations containing bamboo vinegar