(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS – Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have cumulatively been awarded nearly $4 million in grant funding through the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs' Merit Review Award and Career Development programs to support research on diabetes, skin inflammation, cancer and aging.
The Merit Review Award Program supports investigator-initiated research conducted by eligible VA investigators at either VA medical centers or approved sites. This program serves as the VA's primary method for funding basic, preclinical, and behavioral biomedical research as well as clinical research on illnesses and disorders that are significant to veterans' health.
The goal of the Merit Review Award program is to provide grant funding to applications that propose research that is scientifically exemplary and relevant to veterans' health.
Merit Review Awardees for the Spring 2024 cycle:
"Novel roles for RIP kinases in islet inflammation and beta-cell cytotoxicity in type 2 diabetes."
Andrew T. Templin, PhD, assistant professor of medicine
Amount: $1,124,281
"Immunomodulatory functions of insulin growth factor-like proteins in skin inflammation."
Matthew J. Turner, MD, PhD, assistant professor of clinical dermatology and clinical microbiology and immunology
Amount: $710,000
"Evaluating the impact of intermittent fasting in combination with checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer."
Shadia I. Jalal, MD, Lawrence H. Einhorn Professor of Oncology and professor of medicine
Amount: $994,479
The Career Development Program attracts, develops, and retains talented researchers working in crucial areas to enhance the health and medical care of our nation's veterans. Awardees have gone on to lead long, successful careers as VA scientists, research administrators and center directors.
2024 Career Development Awardee:
"Using DNA repair and damage as a tool in personalizing aging and aging related diseases"
Nawar Al Nasrallah, MD, assistant professor of medicine
Amount: $1,138,732
About the IU School of Medicine
The IU School of Medicine is the largest medical school in the U.S. and is annually ranked among the top medical schools in the nation by U.S. News & World Report. The school offers high-quality medical education, access to leading medical research and rich campus life in nine Indiana cities, including rural and urban locations consistently recognized for livability. According to the Blue Ridge Institute for Medical Research, the IU School of Medicine ranks No. 13 in 2023 National Institutes of Health funding among all public medical schools in the country.
Writer: Luke Norton, lcnorton@iu.edu
For more news, visit the IU School of Medicine Newsroom: medicine.iu.edu/news
Follow us on X: @IUMedSchool
END
VA funds IU School of Medicine research projects relevant to veterans’ health
2024-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify effective materials for protecting astronauts from harmful cosmic radiation on Mars
2024-08-23
Abu Dhabi, August 23, 2024: Researchers have identified specific materials, including certain plastics, rubber, and synthetic fibers, as well as Martian soil (regolith), which would effectively protect astronauts by blocking harmful space radiation on Mars. These findings could inform the design of protective habitats and spacesuits, making long-duration Mars missions more feasible. Because Mars lacks Earth’s thick atmosphere and magnetic field, astronauts exploring the planet would be exposed to dangerous levels of radiation.
Dimitra Atri, Investigator, ...
People seen as wise share these characteristics, according to a new study
2024-08-23
What makes someone seem wise? People view wisdom through the lens of applying knowledge and thinking logically as well as considering others’ feelings and perceptions, finds a new study led by University of Waterloo researchers who looked at perceptions of wisdom across 12 countries and five continents.
Researchers examined the underlying principles guiding who we perceive as wise in political leadership, science, and daily life. Across different cultures, participants’ judgements converged on two dimensions: reflective orientation and ...
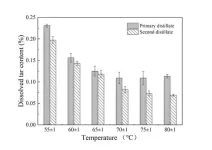
Activated bamboo charcoal’s slow-release properties for enhanced anti-acne formulations containing bamboo vinegar
2024-08-23
Bamboo vinegar is a concentrated liquid obtained from bamboo under high temperature and anaerobic conditions. It contains more than 200 organic components, including organic acids, phenols, ketones, alcohols, and esters, among which acetic acid is the main component. Although bamboo vinegar has been approved by the China Food and Drug Administration as a cosmetic raw material, commercially available bamboo vinegar often contains impurities whose efficacy is not clear, and phenolic compounds and aromatic hydrocarbons ...
When is the best time of day for cancer treatment?
2024-08-23
How effective medications are depends on various factors, including the time of day when they are administered. Why? Because our bodies don’t always function exactly the same. Instead, they follow the cycle set by their internal clock, otherwise known as circadian rhythm. But since each person’s circadian rhythm is different and depends on a number of different factors, it is difficult to tailor medication schedules to an individual patient’s body clock. Researchers at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin have now developed a method for determining the optimum time of cancer treatment based on certain breast cancer ...
Rates of obesity-related cancer are rising sharply in young Chinese people
2024-08-23
Obesity-related cancer rates in China were rising at an alarming 3.6% every year between 2007 and 2021 while non-obesity-related cancers remained stable, according to the first comprehensive study published August 22 in the Cell Press journal Med. The increase is particularly pronounced among young people, highlighting the urgent need for better public health policies to address China’s growing overweight and obesity rates.
“If we don’t drastically change the obesity epidemic, the rates of cancer associated with obesity will inevitably continue to rise,” says Jin-Kui Yang, the paper’s corresponding author and an endocrinologist ...
Neighborhood-level disparities in hypertension prevalence and treatment among middle-aged adults
2024-08-23
About The Study: Researchers found corresponding increases in hypertension prevalence as neighborhood disadvantage and the percentage of Black patients residing in a neighborhood increased in this cross-sectional study. A higher burden of midlife hypertension was identified in Black adults compared with other racial and ethnic groups that persisted across levels of socioeconomic disadvantage. This study also found that living in socioeconomically disadvantaged neighborhoods was associated with higher hypertension ...
Strength training activates cellular waste disposal
2024-08-23
The elimination of damaged cell components is essential for the maintenance of the body’s tissues and organs. An international research team led by the University of Bonn has made significant findings on mechanisms for the clearing of cellular wastes, showing that strength training activates such mechanisms. The findings could form the basis for new therapies for heart failure and nerve diseases, and even afford benefits for manned space missions. A corresponding article has been published in the latest issue of the journal Current Biology. EMBARGOED: Do not publish until 5 pm CEST ...
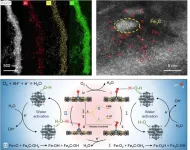
Water activation induced strong interfacial hydrogen bonding interactions for efficient oxygen reduction reaction
2024-08-23
Exploring new energy storage and conversion technologies is crucial for sustainable human development. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and metal-air batteries are particularly promising due to their high energy efficiency and environmental friendliness. A key component in these technologies is the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyst. Traditionally, ORR catalysts rely on expensive platinum group metals (PGM), which are cost-prohibitive for widespread use. This has spurred interest in developing non-precious metal alternatives, such as transition metal/nitrogen-doped carbon-based materials (M–N–C). Among these, Fe–N–C ...
Temperature regulates negative supercoils to modulate meiotic crossovers and chromosome organization
2024-08-23
This study is led by Prof. Shunxin Wang (State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine and Offspring Health, Center for Reproductive Medicine, Institute of Women, Children and Reproductive Health, Shandong University) and Prof. Liangran Zhang (Advanced Medical Research Institute, Shandong University). In their study of meiosis in budding yeast, the research team found that yeast senses temperature changes by increasing the level of DNA negative supercoils to increase crossovers and modulate chromosome organization ...
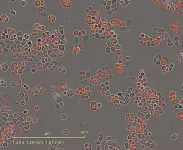
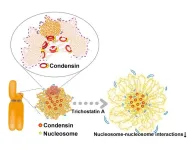
Single nucleosomes tracked in live cells during cell division using super-resolution microscopy
2024-08-23
Individual cells divide through a process called mitosis, during which the cell’s copied DNA is separated between two resulting daughter cells. Despite recent advances in cell biology, the mechanism by which DNA condenses during mitosis is still poorly understood. Researchers recently tracked small stretches of DNA wound around histone proteins, called nucleosomes, to better characterize nucleosome behavior during cell division.
DNA is organized as chromatin, which are dynamic structures comprised of DNA, RNA, and proteins that regulate the accessibility of genes for expression and the overall configuration of genetic material in the cell. Histone proteins, for example, are positively ...