(Press-News.org) Shortly after Kelly Cervantes’ daughter Adelaide was born, she started having terrible seizures. Doctors were unable to give her a solution, or even a cause.
“We never had an overarching diagnosis for her, which was extraordinarily frustrating and isolating,” she says. “If we did, we could join groups or talk to people who had various symptoms in common. We also had no idea what her prognosis looked like, or if we could have other children.”
Over time her condition worsened and sadly she died five days before her fourth birthday.
“She never really progressed past about a three-to-six-month physical development, and we’re not entirely sure where she was intellectually. She was incredible but her life was really challenging and really hard.”
Cervantes had enrolled her daughter in a research program for people with undiagnosed illnesses. After her daughter’s death she got a call asking if she’d like to participate in a study being conducted at The Neuro. Now the results of that study have been published.
The scientists analyzed samples from Adeliade and 21 other people with the condition. By growing stem cells in a dish using the participants’ genetic code, the scientists found that mutations in a gene called DENND5A create disfunction, and this disfunction stops brain cells from dividing properly during development. The result is a developing brain with less stem cells, shortening the crucial time period that the brain forms as an embryo.
The finding provides answers to family of people with this rare condition. It also allowed family members to be tested for the mutations so they can make informed choices about family planning. For example, for aspiring parents who carry the mutation, genetic counselors can recommend genetic testing for their partners and give the odds of passing on the condition.
With advancements in gene editing technology, one day the mutation might be corrected with the knowledge this study provides. While such a step is years away at best, Cervantes says it would provide comfort knowing her daughter contributed to a cure.
“Maybe someday down the road, the next Adelaide will have a treatment, and there will be an answer for that family. And how incredible is that to think, that my baby girl had a hand in that?”
END
Discovery gives answers to parents of children with rare disease
Scientists identify gene mutations that cause debilitating neurodevelopmental problems in infancy
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry names director of Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research
2024-08-27
SAN ANTONIO, Aug. 27, 2024 – Kenneth M. Hargreaves, DDS, PhD, professor of endodontics at the School of Dentistry of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), has been named inaugural director of the school’s Center for Pain Therapeutics and Addiction Research.
Hargreaves, who chaired the Department of Endodontics at the school for 26 years, is a world-renowned expert in pain research and has served as principal or co-principal investigator on numerous National Institutes of Health, Department of Defense and foundation-funded projects totaling more than $139 million.
Just recently, his research proposal, ...
Researchers develop affordable, rapid blood test for brain cancer
2024-08-27
Researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a novel, automated device capable of diagnosing glioblastoma, a fast-growing and incurable brain cancer, in less than an hour. The average glioblastoma patient survives 12-18 months after diagnosis.
The crux of the diagnostic is a biochip that uses electrokinetic technology to detect biomarkers, or active Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors (EGFRs), which are overexpressed in certain cancers such as glioblastoma and found in extracellular vesicles.
“Extracellular vesicles or exosomes are unique ...
NREL advances method for recyclable wind turbine blades
2024-08-27
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) see a realistic path forward to the manufacture of bio-derivable wind blades that can be chemically recycled and the components reused, ending the practice of old blades winding up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
The findings are published in the new issue of the journal Science. The new resin, which is made of materials produced using bio-derivable resources, performs on par with the current industry standard of blades made from a thermoset resin and outperforms certain thermoplastic resins intended to be recyclable.
The researchers built a prototype 9-meter blade to ...
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
2024-08-27
Atomic resolution of the broad-spectrum antiviral drug cascade to facilitate the design of antiviral drugs
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002743
Article Title: The activation cascade of the broad-spectrum antiviral bemnifosbuvir characterized at atomic resolution
Author Countries: France, United States, Germany
Funding: see manuscript END ...
This new technique for studying cell receptors could have sweeping implications for drug development
2024-08-27
One in every three FDA-approved drugs targets a single superfamily of receptors dotting the surfaces of human cells. From beta blockers to antihistamines, these essential, life-saving medications trigger winding biochemical pathways, via these receptors, to ultimately prevent a heart attack, or stop an allergic reaction in its tracks.
But scientists have learned that their story is much more complicated than initially believed—a number of these drugs are in fact targeting a complex composed of one receptor and one associated protein. Now, a ...
Bringing environmental justice to disadvantaged communities
2024-08-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Not all communities in the United States face the same risks for environmental problems such as air pollution, noise and wastewater. But how can federal agencies fairly identify which areas deserve the most help?
A new consensus study report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine (NASEM) offer recommendations for developing tools that can help answer that question.
“Our job was to create methods to identify disadvantaged communities that most need federal resources to address environmental justice issues,” said Harvey Miller, ...
Wiener studying learning & metacognition for the perception of time
2024-08-27
Wiener Studying Learning & Metacognition For The Perception Of Time
Martin Wiener, Associate Professor, Psychology, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding to study learning and metacognition for the perception of time.
Via this research, Wiener will conduct a series of studies that will inform metacognition and interval timing. He holds that this work will lead to a new domain of study to further understand how humans learn and adapt to temporal intervals.
By understanding how the brain measures and learns intervals of time, we can better understand ...
Dumas receives funding for study of how distinct NMDA receptor signaling domains regulate hippocampal network dynamics
2024-08-27
Dumas Receives Funding For Study Of How Distinct NMDA Receptor Signaling Domains Regulate Hippocampal Network Dynamics
Theodore Dumas, Associate Professor, Psychology, College of Humanities and Social Sciences (CHSS), received funding for the project: “Distinct NMDA receptor signaling domains regulate hippocampal network dynamics.
Dumas and his collaborators hypothesize that in wildtype mice, NMDA receptors regulate hippocampal network oscillatory activity (slow gamma frequency) in the absence of ion conductance (nonionotropic) and that enhancing GluN2B subunit-type nonionotropic signaling will increase slow gamma power and enhance spatial memory retrieval.
The researchers ...
Second genetic sensor for DNA methylation discovered
2024-08-27
DNA methylation is a process in which a methyl group is attached to the cytosine base of the DNA molecule, and a major way that DNA is epigenetically marked. Epigenetic modifications can act as on-off switches to regulate gene expression and help generate diverse cell types without changing the underlying DNA sequence. It is how the body ensures that brain-related genes don’t get turned on in heart cells, for example.
For this reason, maintenance of the DNA methylation pattern is important to ensure the correct and consistent function of each cell type. But this is no easy feat: the DNA methylation pattern can change over time, and this is linked to a variety of diseases. One ...
New sensor technology enhances detection of tiny particles
2024-08-27
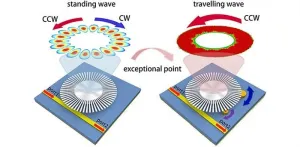
In recent years, advances in photonics and materials science have led to remarkable developments in sensor technology, pushing the boundaries of what can be detected and measured. Among these innovations, non-Hermitian physics has emerged as a crucial area of research, offering new ways to manipulate light and enhance sensor sensitivity. A recent study published in Advanced Photonics Nexus reports a breakthrough in this field, presenting a new type of sensor that leverages exceptional points (EPs) to achieve unprecedented levels of sensitivity.
This study introduces a highly sensitive and reconfigurable sensor based on a single ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Discovery gives answers to parents of children with rare diseaseScientists identify gene mutations that cause debilitating neurodevelopmental problems in infancy