New python package, ERTool, developed for efficient multi-source evidence fusion
2024-11-11
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from Peking University have developed ERTool, an open-source Python package designed to simplify the implementation of the Evidential Reasoning (ER) approach for multi-source evidence fusion. This tool addresses the challenges of integrating data from multiple sources in uncertain decision-making environments. The results are published in Health Data Science.
Multi-source evidence fusion plays a critical role in fields such as healthcare management, business analytics, and environmental risk assessment. However, the traditional application of the ER approach has been complicated, requiring expertise in coding. To overcome these challenges, Associate Research Professor Guilan Kong and her team at the National Institute of Health Data Science at Peking University designed ERTool, which automates the ER approach, making it accessible to a wider audience, including non-experts.
“Our goal was to make the ER approach more user-friendly, particularly for non-specialists,” explained Guilan Kong. “ERTool bridges the gap between complex algorithms and real-world applications, enabling researchers and professionals to integrate multi-source data for evidence-based decision-making more easily.”
The ERTool package simplifies the process of fusing evidence from different sources and addresses uncertainty in decision-making. It features a clean interface and high computational efficiency, making it a versatile tool for a range of applications. ERTool can be accessed via the Python Package Index or used through its online version, which supports real-time evidence fusion and result visualization.
In comparison with other systems like the Intelligent Decision System (IDS), ERTool is more accessible and easier to use, thanks to its open-source nature. It is freely available to the public, which enhances its potential for widespread use in various fields.
Moving forward, the research team plans to integrate a database management system (DBMS) into ERTool, which will allow it to handle larger volumes of evidence data. “Our ultimate goal is to make ERTool the leading solution for multi-source evidence fusion, continually evolving alongside the latest developments in evidential reasoning,” added Guilan Kong.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-11-11
A new AI-based software has been developed that can be integrated with an ultrasound device to ‘guide’ childbirth by providing precise, real-time information on the baby’s head position. It can clearly indicate to operators—using a traffic light system—whether to proceed with a natural descent in the birth canal, whether to use a vacuum extractor, or even if an emergency cesarean is needed.
This tool, which could be available in delivery rooms starting in 2028, was developed and validated as part of a ...
2024-11-11
Doha, November 11, 2024 – The Arab Global Scholars (AGS) community gathered at Hamad Bin Khalifa University (HBKU) in Qatar Foundation’s Education City last week to herald the latest evolution of an initiative nurturing a contemporary renaissance of Arab science and research.
An initiative led by Qatar Foundation, AGS aims to reconnect scholars and intellectuals with roots in the Arab world back to their region to contribute to its positive development and long-term future.
Its beginnings going back almost two decades, AGS has solidified itself as an innovation-focused community linking 895 Arab scholars, as well as research ...
2024-11-11
Climate governance is dominated by men, yet the health impacts of the climate crisis often affect women, girls, and gender-diverse people disproportionately, argue researchers ahead of the upcoming 29th United Nations Climate Summit (COP29) in Azerbaijan.
In an article published today in Lancet Planetary Health, a team of researchers – including several from the University of Cambridge – argue that much more needs to be done to mitigate the impacts of climate change on women, girls and gender-diverse individuals.
Focusing specifically on the intersection between climate change, gender, and human health, ...
2024-11-11
The dual goals of climate action and ending violence against children can be achieved according to a new paper by Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and colleagues at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. For the first time, governments are committing funds and making concrete pledges to reach the UN Sustainable Development Goal target of ending violence against children. On November 7th and 8th, the Government of Colombia, with support of the Government of Sweden, UNICEF, the UN Special Representative of the Secretary-General on Violence Against Children, and the World Health Organization will attend the first Global Ministerial Conference on ending ...
2024-11-11
(Toronto, November 11, 2024) A new study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research by JMIR Publications reveals promising results from a digital health intervention that is based on a decade of research at Harvard Medical School and designed to alleviate depressive symptoms. The study, titled "Facilitating Thought Progression to Reduce Depressive Symptoms: Randomized Controlled Trial," found that participants experienced substantial reduction of depressive symptoms by using a gamified mobile app focused on disrupting ruminative thinking.
Led by Prof. Moshe Bar and colleagues, the research ...
2024-11-11
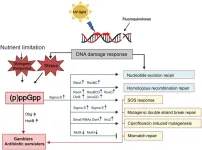
Bacteria frequently encounter adverse environmental conditions, such as nutrient scarcity and antibiotic exposure, which can induce DNA damage. Efficient DNA repair mechanisms are essential for bacterial survival, particularly under such stress conditions. A critical player in these processes is the signaling molecule (p)ppGpp, a phosphorylated guanosine synthesized by bacteria during periods of stress. Initially discovered in Escherichia coli under amino acid starvation, (p)ppGpp is now recognized for its broader roles in modulating cellular functions essential for DNA repair and stress response. By regulating diverse cellular processes, (p)ppGpp not ...
2024-11-11
New research in Social Psychological and Personality Science identifies a widespread stereotype linking wealth to perceived trustworthiness across diverse cultures. The research, led by Mélusine Boon-Falleur from the Center for Research on Social Inequalities at Sciences Po in Paris, shows that individuals with fewer material resources are consistently viewed as less trustworthy.
The study, conducted across eight countries including Brazil, Colombia, Democratic Republic of Congo, India, France, Nigeria, Philippines, and the United Kingdom, employed a novel method to uncover stereotypes while avoiding social desirability bias.
"People ...
2024-11-11
Highlights:
Delaware watersheds show high microbial impairment.
Researchers collected samples from Delaware waters over 2 years and identified microbial DNA signatures present in the water.
The findings suggest that both treated and untreated human waste are the culprit, likely due to infrastructural issues.
Washington, D.C.—Delaware has numerous inland waterways with high microbial impairment from unknown sources. Now, a new study suggests that human waste, both treated and untreated, is responsible for the waterway impairment in these Delaware watersheds. The study was published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, ...
2024-11-11
Heat stroke is primarily classified into exertional and non-exertional forms. Exertional heat stroke results from strenuous physical activity in high heat, while non-exertional heat stroke typically affects those exposed to extreme heat without engaging in significant physical exertion. Symptoms include elevated body temperature, impaired consciousness, headaches, muscle spasms, and, in severe cases, cardiovascular overload, cerebral hypoxia, and organ failure. Western medicine’s primary treatments include cooling methods, rehydration, and pharmacological interventions like dexamethasone ...
2024-11-11
Waltham — November 11, 2024 — Two measures of patient well-being, designed for use in busy clinical settings, are described in a Perspective piece in a supplement to Medical Care, the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The Medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New python package, ERTool, developed for efficient multi-source evidence fusion