(Press-News.org) A new study details generational health trends among adolescents and young adults in the U.K. The study, published December 11, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Olivia Righton from King’s College London, U.K., and colleagues, has broad implications for reducing health disparities and designing targeted public health interventions.
Optimizing health in women and men before conception can improve pregnancy outcomes, reduce the risk of non-communicable diseases in both parents, and improve childhood health. Prior research has shown that many women enter pregnancy with risk factors that put them at higher risk for complications—poor diet, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and obesity—that disproportionately affect those from disadvantaged backgrounds. The U.K. has established initiatives to optimize and reduce inequalities in preconception health, and while there have been studies on women’s health during prenatal visits, there hasn’t been a national picture of preconception health of men and women of reproductive age.
This study looked at health behaviors and indicators across adolescence and adulthood in three cohorts in the U.K. born approximately ten years apart: up to 17,198 people born in 1970, up to 15,770 people born in 1989-1990, and up to 19,517 people born in 2000-2002. Data on various health indicators and behaviors were collected at age 16/17 and 25/26.
The study found that some suboptimal health behaviors, such as low fruit consumption, persisted in both men and women across generations. Other unhealthy behaviors, such as alcohol and tobacco use and soda consumption decreased in younger generations, though the prevalence of obesity increased.
Trends for several key health indicators important for pregnancy health, such as folic acid supplementation, cervical screening, and mental health conditions, could not be identified, as these were not consistently reported across the three cohorts.
The trends revealed can help to tailor public health interventions to reduce inequalities and improve the overall health and well-being of the preconception population.
The authors add: “Our findings from multiple generations of adolescents and young adults in the UK show improvements in alcohol, tobacco, and soft drink consumption, but persistent low fruit intake and surging obesity rates. These behaviors have important transgenerational health implications, highlighting the urgent need for public health interventions that target the root causes of health behaviors.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299061
Citation: Righton O, Flynn A, Alwan NA, Schoenaker D (2024) Preconception health in adolescence and adulthood across generations in the UK: Findings from three British birth cohort studies. PLoS ONE 19(12): e0299061. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0299061
Author Countries: U.K., Ireland
Funding: DS is supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) through an NIHR Advanced Fellowship (NIHR302955) and the NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre (NIHR203319)". The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
New study provides a picture of preconception health across three generations in the UK
Some unhealthy behaviors such as smoking and soda consumption have decreased over time while rates of overweight and obesity have increased
2024-12-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US veterans report average happiness levels of 5.41 out of 7, with greater happiness most associated with reporting greater purpose in life, lower depressive symptoms, and higher optimism, emotional s
2024-12-11
U.S. veterans report average happiness levels of 5.41 out of 7, with greater happiness most associated with reporting greater purpose in life, lower depressive symptoms, and higher optimism, emotional stability, and resilience
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0313609
Article Title: Happiness in US military veterans: Results from a nationally representative study
Author Countries: U.S.
Funding: Preparation of this report was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs 1IK1CX002532-01 (PJN). Funders did not play any role in the ...
Tattoo or not tattoo: Testing the limits of beauty in body art
2024-12-11
German survey respondents rated images of tattooed models as less beautiful than images of the same models with no tattoos, however younger people, tattoo artists and those with body art tolerated more ink, according to a study published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on December 11, 2024 by Selina M. Weiler and colleagues from Helmut Schmidt University/University of the Federal Armed Forces Hamburg, Germany.
Tattoos are a millennia-old practice estimated to adorn up to one in four people in the world today. The 1950s saw a resurgence of this once-marginalized medium in Western culture, with widespread acceptance ...
New study reveals unique insights into the life and death of Stone Age individuals from modern-day Ukraine
2024-12-11
A research group led by Johannes Müller at the Institute of Prehistoric and Protohistoric Archaeology, at Kiel University, Germany, have shed light on the lives of people who lived over 5,600 years ago near Kosenivka, Ukraine. Published on December 11, 2024, in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, the researchers present the first detailed bioarchaeological analyses of human diets from this area and provide estimations on the causes of death of the individuals found at this site.
The people associated with the Neolithic Cucuteni-Trypilla culture lived across Eastern Europe from approximately 5500 to 2750 BCE. With up to 15,000 inhabitants, some of their mega-sites are ...
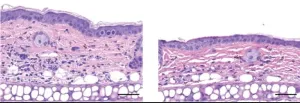
Feeling itchy? Study suggests novel way to treat inflammatory skin conditions
2024-12-11
A new approach to treat rosacea and other inflammatory skin conditions could be on the horizon, according to a University of Pittsburgh study published today in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers found that a compound called SYM2081 inhibited inflammation-driving mast cells in mouse models and human skin samples, paving the way for new topical treatments to prevent itching, hives and other symptoms of skin conditions driven by mast cells.
“I’m really excited about the clinical possibilities of this research,” said senior author Daniel Kaplan, M.D., Ph.D., professor ...
Caltech creates minuscule robots for targeted drug delivery
2024-12-11
In the future, delivering therapeutic drugs exactly where they are needed within the body could be the task of miniature robots. Not little metal humanoid or even bio-mimicking robots; think instead of tiny bubble-like spheres.
Such robots would have a long and challenging list of requirements. For example, they would need to survive in bodily fluids, such as stomach acids, and be controllable, so they could be directed precisely to targeted sites. They also must release their medical cargo only when they reach their target, and then be absorbable by the body without causing harm.
Now, ...
Noninvasive imaging method can penetrate deeper into living tissue
2024-12-11
Metabolic imaging is a noninvasive method that enables clinicians and scientists to study living cells using laser light, which can help them assess disease progression and treatment responses.
But light scatters when it shines into biological tissue, limiting how deep it can penetrate and hampering the resolution of captured images.
Now, MIT researchers have developed a new technique that more than doubles the usual depth limit of metabolic imaging. Their method also boosts imaging speeds, yielding richer and more detailed images.
This new technique does not require tissue to be ...
Researchers discover zip code that allows proteins to hitch a ride around the body
2024-12-11
Researchers at The Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa have discovered an 18-digit code that allows proteins to attach themselves to exosomes - tiny pinched-off pieces of cells that travel around the body and deliver biochemical signals. The discovery, published in Science Advances, has major implications for the burgeoning field of exosome therapy, which seeks to harness exosomes to deliver drugs for various diseases.
“Proteins are the body’s own home-made drugs, but they don’t necessarily travel well around the body,” said Dr. Michael Rudnicki, senior ...
The distinct nerve wiring of human memory
2024-12-11
The black box of the human brain is starting to open. Although animal models are instrumental in shaping our understanding of the mammalian brain, scarce human data is uncovering important specificities. In a paper published in Cell, a team led by the Jonas group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) and neurosurgeons from the Medical University of Vienna shed light on the human hippocampal CA3 region, central for memory storage.
Many of us have relished those stolen moments with a grandparent by the fireplace, our hearts racing to the intrigues of their stories from good old times, recounted with vivid imagery ...
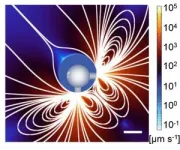
Researchers discover new third class of magnetism that could transform digital devices
2024-12-11
A new class of magnetism called altermagnetism has been imaged for the first time in a new study. The findings could lead to the development of new magnetic memory devices with the potential to increase operation speeds of up to a thousand times.
Altermagnetism is a distinct form of magnetic order where the tiny constituent magnetic building blocks align antiparallel to their neighbours but the structure hosting each one is rotated compared to its neighbours.
Scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Physics and Astonomy have shown that this new third class ...
Personalized blood count could lead to early intervention for common diseases
2024-12-11
A complete blood count (CBC) screening is a routine exam requested by most physicians for healthy adults. This clinical test is a valuable tool for assessing a patient’s overall health from one blood sample. Currently, the results of CBC tests are analyzed using a one-size-fits-all reference interval, but a new study led by researchers from Mass General Brigham suggests that this approach can lead to overlooked deviations in health. In a retrospective analysis, researchers show that these reference intervals, or setpoints, are unique to each patient. The study revealed that one healthy ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children born with upper limb difference show the incredible adaptability of the young brain
How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
Fast-paced lives demand faster vision: ecology shapes how “quickly” animals see time
Global warming and heat stress risk close in on the Tour de France
New technology reveals hidden DNA scaffolding built before life ‘switches on’
New study reveals early healthy eating shapes lifelong brain health
Trashing cancer’s ‘undruggable’ proteins
Industrial research labs were invented in Europe but made the U.S. a tech superpower
Enzymes work as Maxwell's demon by using memory stored as motion
Methane’s missing emissions: The underestimated impact of small sources
Beating cancer by eating cancer
How sleep disruption impairs social memory: Oxytocin circuits reveal mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities
Natural compound from pomegranate leaves disrupts disease-causing amyloid
A depression treatment that once took eight weeks may work just as well in one
New study calls for personalized, tiered approach to postpartum care
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
[Press-News.org] New study provides a picture of preconception health across three generations in the UKSome unhealthy behaviors such as smoking and soda consumption have decreased over time while rates of overweight and obesity have increased