Organic molecules of unprecedented size discovered on Mars
2025-03-24
(Press-News.org)
The longest organic molecules identified to date on Mars have recently been detected by scientists from the CNRS1, together with their colleagues from France, the United States of America, Mexico and Spain. These long carbon chains, containing up to 12 consecutive carbon atoms, could exhibit features similar to the fatty acids produced on Earth by biological activity2. The lack of geological activity and the cold, arid climate on Mars have helped preserve this invaluable organic matter in a clay-rich sample for the past 3.7 billion years. It therefore dates from the period during which life first emerged on Earth. These findings are due to be published on March 24th 2025 in the journal PNAS.
The discovery was made using SAM3, co-funded by the French space agency CNES4. This is one of the instruments onboard NASA's Curiosity rover, which has been studying the Gale crater on Mars since 2012. This success paves the way for future interplanetary science missions in search of signs of complex, life-like chemistry. This will be one of the goals of ESA's upcoming ExoMars mission launched in 2028, and of the joint NASA-ESA Mars Sample Return mission in the 2030s. With an eye to exploration further out in the Solar System, the same international teams will build an instrument similar to SAM for Dragonfly, the drone that is due to explore the surface of Titan, Saturn's largest satellite, from 2034 onwards.
Notes
1 – From the « Atmosphères et observations spatiales » laboratory (CNRS/Sorbonne Université/Université de Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines/Université Paris Saclay).
2 – They’re present within animals fats, as well as vegetable fats and oils.
3 – Built by a French-American team of scientists, Sample Analysis at Mars is a small laboratory within Curiosity. its gas chromatograph and mass spectrometer allow it to identify molecules in collected samples.
4 - Centre national d’études spatiales – National Centre for Space Studies.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-24
Next time you cross a crowded plaza, crosswalk, or airport concourse, take note of the pedestrian flow. Are people walking in orderly lanes, single-file, to their respective destinations? Or is it a haphazard tangle of personal trajectories, as people dodge and weave through the crowd?
MIT instructor Karol Bacik and his colleagues studied the flow of human crowds and developed a first-of-its-kind way to predict when pedestrian paths will transition from orderly to entangled. Their findings may help inform the design of public spaces that promote safe and efficient thoroughfares.
In a paper appearing in the Proceedings of the National Academy ...
2025-03-24
New Haven, Conn. — Most job candidates know to dress nicely for Zoom interviews and to arrange a professional-looking background for the camera. But a new Yale study suggests they also ought to test the quality of their microphones.
A tinny voice caused by a cheap mic, researchers say, could sink their chances.
Through a series of experiments, the study demonstrates that tinny speech — a thin, metallic sound — during video conferences can have surprisingly deep social consequences, leading listeners to lower their judgments of a speaker’s intelligence, credibility, and romantic desirability. ...
2025-03-24
A team of biologists at Queen Mary University of London has discovered that a neurohormone controlling appetite in humans has an ancient evolutionary origin, dating back over half a billion years. The findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, reveal that this satiety-inducing molecule, known as bombesin, is not only present in humans and other vertebrates but also in starfish and their marine relatives.
Bombesin, a small peptide, plays a key role in regulating hunger by signalling when we’ve had enough to eat. But its story doesn’t start with humans or even mammals. New research shows that ...
2025-03-24
By Leah Shaffer
The cells in human bodies are subject to both chemical and mechanical forces. But up until recently, scientists have not understood much about how to manipulate the mechanical side of that equation. That’s about to change.
“This is a major breakthrough in our ability to be able to control the cells that drive fibrosis,” according to Guy Genin, the Harold and Kathleen Faught Professor of Mechanical Engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, speaking of research recently published in Nature Materials.
Fibrosis is an affliction wherein ...
2025-03-24
Imagine trying to listen to a friend speak over the commotion of a loud party. It is difficult to detect and process sounds in noisy environments, especially for those with hearing loss. Previous research has typically focused on how competing sounds influence cortical brain activity, with the end goal of informing treatment strategies for people who are hard of hearing. But in a new eNeuro study, Melissa Polonenko and Ross Maddox, from the University of Rochester, explored a lesser-studied influence of competing sounds on subcortical brain ...
2025-03-24
The high comorbidity of type 2 diabetes (T2D) with psychiatric or neurodegenerative disorders points to a need for understanding what links these diseases. A potential link is the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). The ACC supports behaviors related to cognition and emotions and is involved in some T2D-associated diseases, like mood disorders and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). James Hyman and colleagues, from the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, used a rat model of T2D that affects only males to explore whether diabetes affects ACC activity and behavior. Their work is featured in JNeurosci’s ...
2025-03-24
Embargoed for release: Monday, March 24, 12:00 PM ET
Key points:
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in plant-based foods, with low to moderate intake of healthy animal-based foods and lower intake of ultra-processed foods, was linked to a higher likelihood of healthy aging—defined as reaching age 70 free of major chronic diseases, with cognitive, physical, and mental health maintained—according to a 30-year study of food habits among more than 105,000 middle-aged adults.
All the eight dietary patterns studied were associated with healthy aging, suggesting that there is no one-size-fits-all healthy diet.
The study is among the ...
2025-03-24
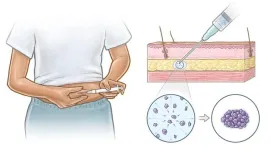
Mass General Brigham and MIT investigators have developed a long-acting contraceptive implant that can be delivered through tiny needles to minimize patient discomfort and increase the likelihood of medication use.
Their findings in preclinical models provide the technological basis to develop self-administrable contraceptive shots that could mimic the long-term drug release of surgically implanted devices.
The new approach, which would reduce how often patients need to inject themselves and prove valuable for patients with less access to hospitals and other medical care ...
2025-03-24
Motion sickness is a very common condition that affects about 1 in 3 people, but the brain circuits involved are largely unknown. In the current study published in Nature Metabolism, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children’s Hospital describe a new brain circuit involved in motion sickness that also contributes to regulating body temperature and metabolic balance. The findings may provide unconventional strategies ...
2025-03-24
MEDIA INQUIRES
WRITTEN BY
Laura Muntean
Adam Russell
laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu
601-248-1891
FOR ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Organic molecules of unprecedented size discovered on Mars