December 25, 2012 (Press-News.org) Unpaid child support payments leaving an $11 billion hole in the Texas economy
Texas parents are struggling with the effects of prolonged unemployment and other economic pressures by missing child support payments in record numbers, leaving a gaping, multi-billion-dollar hole in the state's economy. The huge deficit doesn't just apply to missed payments, though; more parents than ever before are also seeking downward modifications of existing orders, most often to account for a loss in income for the paying parent. On the flip side, parents who aren't receiving much-needed support checks are hitting the state's family courts more frequently than ever before to have child support orders enforced.
The huge arrearage is attributed to several different economic and societal factors, including:
A sluggish economy leading to unemployment or involuntary underemployment
-Higher cost of living
-Still-high foreclosure rates
-Loss of employment leading to loss of health insurance and other benefits
A recent survey by the Texas Attorney General's office showed that a whopping 46 percent of parents in Dallas County are behind on their child support payments. Furthermore, the Houston Chronicle recently reported that nearly half of the roughly one million residents currently ordered to provide financial support for their children are not doing so in a timely manner, having fallen behind at least one month in the past year. Statewide, that amounts to nearly $11 billion in unpaid support arrearages, fines and court costs associated with enforcement.
Getting help with child support obligations
Regardless of whether a parent owes support or is due to receive support payments, he or she can rely on the services offered by the Child Support Division of the Office of the Texas Attorney General. The AG's office is responsible for both establishing initial child support obligations and enforcing existing orders. Support is ordered on a case-by-case basis using a formula set out by the Texas state legislature.
The child support guidelines are set forth in Title 5, Section 154 of the Texas family code. They dictate the general way by which income and other factors are used to make initial support orders and modify existing ones. In most cases, the guidelines say that the non-custodial parent has to pay 20 percent of his or her income as child support each month, but deviations from that formula can be made depending on the individual circumstances of both parents and any special needs of the children.
Collecting unpaid amounts
The Texas family court and the AG's office have several tools available to collect unpaid court-ordered child support payments, including:
-Withholding tax returns
-Garnishing lottery or gambling winnings
-Suspending professional licenses
-Garnishing regular wages
Whether you are in need of having a support order enforced or you are a paying parent that needs a temporary downward deviation, consider seeking the advice of an experienced family law attorney in your area; doing so can make the family court system easier to navigate and could increase your chances of success.
Article provided by Law Offices of Disrud and Garcia
Visit us at www.disrudgarcialaw.com/
Unpaid Child Support Payments Leaving An $11 Billion Hole In The Texas Economy
Past due and unpaid child support payments amount to nearly $11 billion in Texas.
2012-12-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ECRI Releases "The Top 10 Health Technology Hazards for 2013"
2012-12-25
Advances in technology can enhance the health care industry, providing various improvements and benefits. However, such developments can also create new opportunities for injury.
The Economic Cycle Research Institute, a nonprofit organization that researches the best approaches to improving patient care, recently released a report entitled "The Top 10 Health Technology Hazards for 2013." The institute intends to use the report to raise awareness of the potential dangers associated with the use of particular medical systems and devices.
The list is updated ...
Oregon Prescription Drug Crimes -- When Prescription Use Violates the Law
2012-12-25
It's not unheard of for prescription drug use to get out of hand. When you are suffering from a serious medical condition, the right pills can manage a great deal of pain, suffering and discomfort; when the medical condition begins to improve, it is not always easy to stop taking the pills you have come to depend on.
But when does prescription drug use cross the line? Under Oregon and federal law, you can be found guilty of a drug crime by misusing or overusing prescription medication; and drivers of motor vehicles need to be aware that even if you are within your prescription, ...
Chinese medicine yields secrets to scientists at The Scripps Research Institute
2012-12-24
LA JOLLA, CA – December 23, 2012 – The mysterious inner workings of Chang Shan—a Chinese herbal medicine used for thousands of years to treat fevers associated with malaria—have been uncovered thanks to a high-resolution structure solved at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI).
Described in the journal Nature this week, the structure shows in atomic detail how a two-headed compound derived from the active ingredient in Chang Shan works. Scientists have known that this compound, called halofuginone (a derivative of the febrifugine), can suppress parts of the immune system—but ...
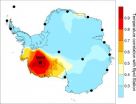
Study shows rapid warming on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet
2012-12-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio—In a discovery that raises further concerns about the future contribution of Antarctica to sea level rise, a new study finds that the western part of the ice sheet is experiencing nearly twice as much warming as previously thought.
The temperature record from Byrd Station, a scientific outpost in the center of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS), demonstrates a marked increase of 4.3 degrees Fahrenheit (2.4 degrees Celsius) in average annual temperature since 1958—that is, three times faster than the average temperature rise around the globe.
This temperature ...
Fat influences decisions taken by brain cells for production and survival
2012-12-24
Scientists at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified two molecules that play an important role in the survival and production of nerve cells in the brain, including nerve cells that produce dopamine. The discovery, which is published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology, may be significant in the long term for the treatment of several diseases, such as Parkinson's disease.
The same scientists have previously shown that receptors known as "liver X receptors" or LXR, are necessary for the production of different types of nerve cells, or neurons, in the developing ...
Understanding cell organization to tackle cancer
2012-12-24
Scientists at The University of Manchester have identified how cells know which way up they need to be. The discovery could help in the fight against cancer because in the early stages of the disease the cells become disorganised.
Professor Charles Streuli and Dr Nasreen Akhtar of the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell-Matrix Research have conducted new research that leads to a better understanding of cell polarity. Properly organised tissues are vital to maintaining functional organs and a healthy body. Part of being organised includes cells being in the correct position ...
Research sheds new light on mechanisms of T-ALL, a form of leukemia that primarily affects children
2012-12-24
Acute lymphatic leukemia (ALL) is the most common cancer in children under the age of 14 years. With optimum treatment, approximately 75 % of children are currently cured, but the treatment consists of severe chemotherapy with many side effects. In collaboration with international research teams, scientists at VIB, KU Leuven and UZ Leuven have identified new genetic mutations that lead to T-ALL, a variant of ALL. They have unmasked the ribosome – the molecular machine in the cell that is involved in the production of proteins – as a weak spot in leukemia cells. Their research ...
Neuroscientists find excessive protein synthesis linked to autistic-like behaviors
2012-12-24
Autistic-like behaviors can be partially remedied by normalizing excessive levels of protein synthesis in the brain, a team of researchers has found in a study of laboratory mice. The findings, which appear in the latest issue of Nature, provide a pathway to the creation of pharmaceuticals aimed at treating autism spectrum disorders (ASD) that are associated with diminished social interaction skills, impaired communication ability, and repetitive behaviors.
"The creation of a drug to address ASD will be difficult, but these findings offer a potential route to get there," ...
3 new genetic links to colorectal cancer
2012-12-24
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center investigators have identified three new genetic "hotspots" linked to colorectal cancer.
These variants, reported Dec. 23 in an Advanced Online Publication in Nature Genetics, provide new insight into the biology of colorectal cancer – and could represent new therapeutic targets for the disease.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide – and rates are particularly high in the United States and other developed countries. Genetics plays an important role in both sporadic and familial (inherited) forms of ...
OpGen announces sequence assembly and finishing of first reference genome of domestic goat
2012-12-24
Gaithersburg, Md.—December 23, 2012— OpGen, Inc. today announced its ARGUS® Whole Genome Mapping System technology was used in combination with next-generation sequencing (NGS) to produce the first, high-quality reference genome of the domestic goat. The study, which was led by BGI-Shenzhen and Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences was published online today in Nature Biotechnology. The paper, titled Sequencing and automated whole-genome optical mapping of the genome of a domestic goat (Capra hircus), demonstrates the value, efficiency and cost effectiveness ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Unpaid Child Support Payments Leaving An $11 Billion Hole In The Texas EconomyPast due and unpaid child support payments amount to nearly $11 billion in Texas.