Living with a killer: How an unlikely mantis shrimp-clam association violates a biological principle
2024-08-06
Media
When clams gamble on living with a killer, sometimes their luck may run out, according to a University of Michigan study.
A longstanding question in ecology asks how can so many different species co-occur, or live together, at the same time and at the same place. One influential theory called the competitive exclusion principle suggests that only one species can occupy a particular niche in a biological community at any one time.
But out in the wild, researchers find many instances of different species that appear to occupy the same ...
Researchers urge united nations to reject growth-driven framework in favor of lower population and consumption
2024-08-06
In a new peer-reviewed article in The Journal of Population and Sustainability, demographic experts are urging the United Nations to reject the current “‘growth’ paradigm which treats Earth and its nonhuman inhabitants as mere resources” and to take the lead in “contracting the large-scale variables of the human enterprise” in order to “forge a path out of multiple environmental and social crises,” and “reverse our advanced state of ecological overshoot.”
Earth Overshoot Day, the date when humanity’s demand on nature’s resources surpasses Earth’s capacity ...
Future enterovirus outbreaks could be exacerbated by climate change
2024-08-06
Outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD), which causes fever and rash in young children, typically occur in the summer months. Similarly, historic cases of polio were observed in the summer months in the United States. Both diseases are caused by different species of enteroviruses, a large genus of RNA viruses. However, the drivers of the seasonal patterns of these diseases have remained somewhat unclear.
A common set of drivers can explain the timing of outbreaks of both HFMD and polio according a recent study by researchers at Brown University, Princeton University ...
Genetic ‘episignatures’ guide researchers in identifying causes of unsolved epileptic neurological disorders
2024-08-06
(Memphis, Tenn. – August 6, 2024) To effectively treat a disease or disorder, doctors must first know the root cause. Such is the case for developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (DEEs), whose root causes can be hugely complex and heterogeneous. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital demonstrated the value of DNA methylation patterns for identifying the root cause of DEEs, showing specific gene methylation and genome-wide methylation “episignatures” ...
Study explores effects of racial discrimination on Black parents and children
2024-08-06
URBANA, Ill. – Black Americans experience racial discrimination on a regular basis, and it is a cause of chronic and pervasive stress. It is known to contribute to elevated risk for poor mental health outcomes, but most research has focused on individuals. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign looks at the interpersonal effects of discrimination on parents and their adolescent children.
“A person’s experiences with racial discrimination are not just their own but may spill over into the ...
Wayne State University professor receives career achievement award from the Society for Health Psychology
2024-08-06
DETROIT — Mark Lumley, Ph.D., distinguished professor of psychology in Wayne State University’s College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, was recently awarded the 2024 Nathan W. Perry, Jr. Award for Career Service to Health Psychology from the Society for Health Psychology.
The Society for Health Psychology is a national nonprofit that seeks to improve the lives of individuals and society by promoting health, preventing illness and improving health care through research, practice, education, training and advocacy.
“I’m delighted and greatly honored for this recognition,” ...
Elephants on the move: Mapping connections across African landscapes
2024-08-06
URBANA, Ill. -- Elephant conservation is a major priority in southern Africa, but habitat loss and urbanization mean the far-ranging pachyderms are increasingly restricted to protected areas like game reserves. The risk? Contained populations could become genetically isolated over time, making elephants more vulnerable to disease and environmental change.
A recent study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Pretoria in South Africa demonstrates how African conservation managers could create and optimize elephant movement corridors across a seven-country ...
Youth mental health-related emergency room trips declined significantly after Illinois ended COVID-19 lockdown
2024-08-06
Social media’s rise to popularity between 2010 and 2020 has been strongly correlated with the nationwide freefall in youth mental health that characterized the 2010s. Lawmakers have put increasing pressure on the U.S. government to take social media regulation more seriously, with cases about platforms like Facebook, Instagram and X rising to the Supreme Court level.
But despite the ubiquity of social media, scientists at Northwestern Medicine and Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that in Illinois, youth emergency room visits and hospitalizations for depression and anxiety decreased ...
How plants become bushy, or not
2024-08-06
or many plants, more branches means more fruit. But what causes a plant to grow branches? New research from the University of California, Davis shows how plants break down the hormone strigolactone, which suppresses branching, to become more “bushy.” Understanding how strigolactone is regulated could have big implications for many crop plants.
The study was published August 1 in Nature Communications.
“Being able to manipulate strigolactone could also have implications beyond plant architecture, including on a plant’s resilience to drought and pathogens,” said senior author Nitzan Shabek, an associate professor in the UC Davis Department of ...
Research spotlight: Identifying potential new protein targets for melanoma therapeutics
2024-08-06
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Some proteins, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), can stop the immune system from attacking cancer cells and, therefore, support the growth of cancer. Therapies targeting these proteins can be highly effective, but tumors can become resistant.
We applied a method to detect proteins on a single–cell level to uncover human carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) patterns in melanoma. We found that increased ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
2024-08-06
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named six new Damon Runyon Clinical Investigators. The recipients of this prestigious award are outstanding, early-career physician-scientists conducting patient-oriented cancer research at major research centers under the mentorship of the nation's leading scientists and clinicians.
The Clinical Investigator Award program was designed to increase the number of physicians capable of translating scientific discoveries into new treatments for cancer patients. Each Awardee will receive $600,000 over three years, ...
Good outcomes 10 years after surgery for ectopic bone in thoracic spine
2024-08-06
August 6, 2024 — Thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (TOPLL) is a rare condition associated with ectopic bone formation in the thoracic spine. A long-term follow-up study from Japan shows significant and lasting improvement in outcomes with posterior decompression and fixation surgery for patients with T-OPLL, reports The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Surgical treatment of T-OPLL is effective in improving neurological function, quality ...
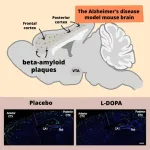
Dopamine treatment alleviates symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-06
A new way to combat Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by Takaomi Saido and his team at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan. Using mice with the disease, the researchers found that treatment with dopamine could alleviate physical symptoms in the brain as well as improve memory. Published in the scientific journal Science Signaling on August 6, the study examines dopamine’s role in promoting the production of neprilysin, an enzyme that can break down the harmful plaques in the brain that are the ...
Do your supplements contain potentially hepatoxic botanicals?
2024-08-06
Millions of Americans consume supplements that contain potentially hepatoxic botanical ingredients, according to a study from University of Michigan researchers.
Over a 30-day period, 4.7% of the adults surveyed in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2017 to 2020 took herbal and dietary supplements containing at least one of the botanicals of interest: turmeric; green tea; ashwagandha; black cohosh; garcinia cambogia; and red yeast rice containing products.
The resulting paper, “Estimated Exposure ...
No room for nuance in polarized political climate: SFU study
2024-08-06
Sometimes you just can’t win, and that goes double for people navigating the increasingly polarized political landscape in the United States.
Having nuanced opinions of politics in the U.S. turns out to be a very lonely, and unpopular, road, according to a recent study from a research team that includes assistant professor Aviva Phillipp-Muller from Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the study found that people who express ambivalence about political topics – ranging from COVID-19 mask mandates, immigration and the death ...
What happens to your brain when you drink with friends?
2024-08-06
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 6, 2024) – Grab a drink with friends at happy hour and you’re likely to feel chatty, friendly and upbeat. But grab a drink alone and you may experience feelings of depression. Researchers think they now know why this happens.
“Social settings influence how individuals react to alcohol, yet there is no mechanistic study on how and why this occurs,” said Kyung-An Han, Ph.D., a biologist at The University of Texas at El Paso who uses fruit flies to study alcoholism.
Now, Han and a team of UTEP faculty and students have taken a key step in understanding the neurobiological process behind social drinking and how it boosts ...
University of Houston researchers create new treatment and vaccine for flu and various coronaviruses
2024-08-06
A team of researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered two new ways of preventing and treating respiratory viruses. In back-to-back papers in Nature Communications, the team - from the lab of Navin Varadarajan, M.D. Anderson Professor of William A. Brookshire Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering - reports the development and validation of NanoSTING, a nasal spray, as a broad-spectrum immune activator for controlling infection against multiple respiratory viruses; and the development of NanoSTING-SN, a pan-coronavirus nasal vaccine, that can protect against infection and disease by all members of the coronavirus family.
NanoSTING ...
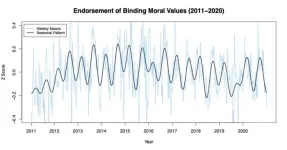
People's moral values change with the seasons
2024-08-06
A new UBC study has revealed regular seasonal shifts in people’s moral values.
The finding has potential implications for politics, law and health—including the timing of elections and court cases, as well as public response to a health crisis.
The research published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) analyzed survey responses from more than 230,000 people in the U.S. over 10 years and revealed that people’s embrace of certain moral ...
Researchers reveal atomic-scale details of catalysts’ active sites
2024-08-06
The chemical and energy industries depend upon catalysts to drive the reactions used to create their products. Many important reactions use heterogeneous catalysts — meaning that the catalysts are in a different phase of matter than the substances they are reacting with, such as solid platinum reacting with gases in an automobile’s catalytic converter.
Scientists have investigated the surface of well-defined single crystals, illuminating the mechanisms underlying many chemical reactions. However, there is much more to be learned. For heterogeneous catalysts, their 3D atomic structure, their chemical composition and the nature of ...
The prescription for a healthier democracy
2024-08-06
When we’re sick, the first step on the road to recovery is a visit to the doctor’s office.
It turns out the same may also be true for breathing life into America’s democracy.
A Rutgers University–New Brunswick study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum finds that physicians can play a crucial role in strengthening political inclusion of marginalized groups by aiding patients in voter registration.
“Hospitals aren’t the first place we think of when it comes to voter registration,” said Katherine McCabe, an associate professor of American politics at Rutgers University-New Brunswick and lead ...
New substrate material for flexible electronics could help combat e-waste
2024-08-06
Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a rapidly growing global problem, and it’s expected to worsen with the production of new kinds of flexible electronics for robotics, wearable devices, health monitors, and other new applications, including single-use devices.
A new kind of flexible substrate material developed at MIT, the University of Utah, and Meta has the potential to enable not only the recycling of materials and components at the end of a device’s useful life, but also the scalable manufacture of more ...
Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists probe molecular cause of COVID-19 related diarrhea, revealing potential treatments
2024-08-06
Working with human stem cells that form a kind of “mini intestine-in-a-dish,” Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have found several molecular mechanisms for COVID-19-related diarrhea, suggesting potential ways to control it.
Details of the experiments in a model of human intestinal tissue, called enteroids, are described on July 30 in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Along with the unpleasant aches, fever, sore throat, cough, respiratory distress and other symptoms that may accompany COVID-19 infection, up to half of people who get the virus will experience diarrhea. Some 30% of them will go on to develop ...
New open-source platform for high-resolution spatial transcriptomics
2024-08-06
Leuven, 6 August 2024 - A team of researchers from the lab of Prof. Stein Aerts (VIB-KU Leuven) presents Nova-ST, a new spatial transcriptomics technique that promises to transform gene expression profiling in tissue samples. Nova-ST will make large-scale, high-resolution spatial tissue analysis more accessible and affordable, offering significant benefits for researchers. The research was published in Cell Reports Methods.
Transcriptomics is the study of gene expression in a cell or a population of cells, but it usually does not include spatial information about where those genes were active. This hurdle limited our understanding of complex ...
Targeted cancer therapy: initial high concentration may slow down selection for resistance
2024-08-06
BUFFALO, NY- August 6, 2024 – On July 28, 2024, Mikhail V. Blagosklonny M.D., Ph.D., from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center published a new editorial in Volume 16, Issue 14 of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), entitled, “Targeted cancer therapy: the initial high concentration may slow down the selection for resistance.”
“Unfortunately, any targeted therapy is, always, started with low levels of the drug in the organism, selecting for drug resistance. One should propose that initial drug levels must be maximized, ...
Lehigh University researchers dig deeper into stability challenges of nuclear fusion—with mayonnaise
2024-08-06
Mayonnaise continues to help researchers better understand the physics behind nuclear fusion.
“We’re still working on the same problem, which is the structural integrity of fusion capsules used in inertial confinement fusion, and Hellmann’s Real Mayonnaise is still helping us in the search for solutions,” says Arindam Banerjee, the Paul B. Reinhold Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics at Lehigh University and Chair of the MEM department in the P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science.
In simple terms, fusion reactions are what power the sun. If the process could ...
[1] ... [1005]
[1006]
[1007]
[1008]
[1009]
[1010]
[1011]
[1012]
1013
[1014]
[1015]
[1016]
[1017]
[1018]
[1019]
[1020]
[1021]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.