Texas Tech professor receives grant for printable semiconductors research
2024-08-06
Minxiang “Glenn” Zeng, an assistant professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Texas Tech University, has been awarded a $250,000 grant from the Launching Early-Career Academic Pathways in the Mathematical and Physical Sciences (LEAPS-MPS) award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to further his research about printable semiconductors and electronics under extreme environments.
The grant supports Zeng’s work in understanding and controlling the thermal degradation pathways of printed metal chalcogenides, which are semiconductor materials including selenides, tellurides and sulfides. His goal is to develop strategies to enhance the thermal stability ...
Digital Olfaction Society 2024: Revolutionizing scent digitization and global transfer
2024-08-06
The 8th Annual Meeting of the Digital Olfaction Society (DOS) will take place on December 5-6, 2024, in Tokyo, Japan, and Online. The DOS meeting is uniquely aimed at digitizing scents, transferring them, and re-creating them in different parts of the world. The two-day event includes one day dedicated to talks and another day for demonstrations. Under the slogan "Olfaction to Digital Olfaction", the congress will explore the latest advances in olfaction science and digital olfaction technologies, highlighting their transformative impact across multiple fields.
The first day of the congress will focus on olfaction science, scent-based diagnosis and treatment ...
New York City’s fireworks display prompts temporary surge of air pollution
2024-08-06
In 2023, roughly 60,000 firework shells exploded above Manhattan’s East River as part of Macy’s Fourth of July show. The resulting air pollutant levels were many times higher in the hours after the display than those seen when smoke from a Canadian wildfire had blanketed the area a month before.
This is according to the results of a new study, led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, which measured air quality just before and after the Independence Day event, one of the largest in the United States. Tiny particles of hazardous metals and organic compounds peaked at 3,000 micrograms per cubic meter at an air sampling site ...
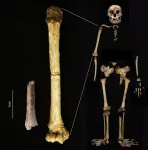
Smallest arm bone in human fossil record sheds light on the dawn of Homo floresiensis
2024-08-06
A paper out today in Nature Communications reports the discovery of extremely rare early human fossils from the Indonesian island of Flores, including an astonishingly small adult limb bone.
Dated to about 700,000 years old, the new findings shed light on the evolution of Homo floresiensis, the so-called ‘Hobbits’ of Flores whose remains were uncovered in 2003 at Liang Bua cave in the island’s west by a team co-led by Australian-New Zealand archaeologist Professor Mike Morwood (1950–2013).
Archaeological evidence suggests these diminutive, small-brained humans inhabited Liang Bua ...
Type 2 diabetes and fracture risk in older women
2024-08-06
About The Study: The results from this study suggest that the higher fracture risk among older women with type 2 diabetes may be due to impaired physical function and not skeletal characteristics.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Mattias Lorentzon, MD, PhD, email mattias.lorentzon@medic.gu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25106)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and ...
AI for early detection of pediatric eye diseases using mobile photos
2024-08-06
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, the artificial intelligence (AI) model demonstrated strong performance in accurately identifying myopia, strabismus, and ptosis using only smartphone images. These results suggest that such a model could facilitate the early detection of pediatric eye diseases in a convenient manner at home.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Lin Li, MD, PhD (jannetlee130@gmail.com), and Jie Xu, DHM (xujie@pjlab.org.cn).
To access the embargoed ...
Demographic representation of generative AI images of physicians
2024-08-06
About The Study: This study identifies demographic biases in artificial intelligence (AI)-generated images of physicians with disproportionate representation of white and male physicians and concerning underrepresentation of other races and ethnicities (Asian and Latino) and female physicians in some platforms. This bias has the potential to reinforce stereotypes and undermine diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives within health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sang Won Lee, MSc, email sangwon_lee@hms.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
When faster is not better: New study links premature development of human neurons to brain developmental disorders
2024-08-06
Leuven, 7 August 2024—The mechanisms underlying intellectual disabilities or autism remain largely unknown. Researchers in the labs of Prof. Pierre Vanderhaeghen and Prof. Vincent Bonin at the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Brain & Disease Research and NERF have discovered that mutations in a gene called SYNGAP1 disrupt the prolonged development of human neurons, which is thought to be essential for normal cognitive function. Their work has interesting implications for our understanding and treatment ...
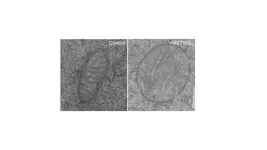
Meteorin-like protein drains energy from T cells, limiting immune system’s power to fight cancer
2024-08-06
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL AUG. 6 AT 11 A.M. ET**
A protein called Meteorin-like (METRNL) in the tumor microenvironment saps energy from T cells, thereby severely limiting their ability to fight cancer, according to new research directed by investigators at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and its Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. Finding ways to block the effects of METRNL signaling on tumor-infiltrating T cells may allow these immune cells to regain the energy necessary to eliminate tumors.
A report about the work was published Aug. 6 in the journal Immunity.
METRNL ...
Live longer, die healthier
2024-08-06
Everyone wants to live to a ripe old age, but no one wants to be decrepit. Now, University of Connecticut researchers have demonstrated a treatment that could lengthen life—and vigor—up to the very end.
Even as human lifespans have lengthened over the past century, most people in old age suffer a serious health decline in the last decade of life. Chronic illnesses such as cancer, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease may begin, followed by frailty. Many interventions can prolong life, but not necessarily good health. And nobody wants to spend the last ...
Novel machine learning-based cluster analysis method that leverages target material property
2024-08-06
In materials science, substances are often classified based on defining factors such as their elemental composition or crystalline structure. This classification is crucial for advances in materials discovery, as it allows researchers to identify promising classes of materials and explore new ones with similar functions and properties. A recent Advanced Intelligent Systems study led by Researcher Nobuya Sato and Assistant Professor Akira Takahashi from Tokyo Institute of Technology developed a new machine learning-powered clustering technique. This technique groups similar materials by taking into account both their ...
CT health screening can identify diabetes risk
2024-08-06
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Analysis of CT scans in people who undergo imaging for health screening can identify individuals at risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Researchers said the findings underscore CT’s value in opportunistic imaging—the use of information from routine imaging examinations to learn more about a patient’s overall health.
For the new study, researchers evaluated the ability of automated CT-derived markers ...
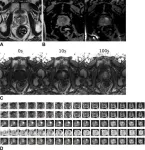
AI model effective in detecting prostate cancer
2024-08-06
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A deep learning model performs at the level of an abdominal radiologist in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer on MRI, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The researchers hope the model can be used as an adjunct to radiologists to improve prostate cancer detection.
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men worldwide. Radiologists typically use a technique that combines different MRI sequences (called multiparametric MRI) to diagnose clinically significant prostate cancer. ...
Exposure to wildfire smoke may affect patients undergoing surgery
2024-08-06
CHICAGO – Nearly 100 wildfires are currently raging throughout the country, burning more than 2 million acres. The rising frequency of these fires poses a special concern for anesthesiologists – the potential for increased rates of adverse outcomes from anesthesia and surgery among patients exposed to wildfire smoke, according to a special article in the Online First edition of Anesthesiology, the peer-reviewed journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA).
"Wildfire smoke causes inflammation and is known to worsen heart and lung disease and pregnancy outcomes," said senior author Vijay Krishnamoorthy, M.D., M.P.H., Ph. D., chief of the Critical Care ...
Visiting an art exhibition can make you think more socially and openly. But for how long?
2024-08-06
A new study by an international team of collaborators led by researchers at the University of Vienna, and in collaboration with the Dom Museum Wien, aimed to address the questions of whether art exhibitions can make us more empathic or even change our attitudes and behaviors? The researchers were able to show that, indeed, looking through the exhibition reduced xenophobia and increased acceptance of immigration. Even more, by employing a new cellphone-based experience sampling method, they could track how long ...
Heating for fusion: Why toast plasma when you can microwave it!
2024-08-06
Some believe the future of fusion in the U.S. lies in compact, spherical fusion vessels. A smaller tokamak, it is thought, could offer a more economical fusion option. The trick is squeezing everything into a small space. New research suggests eliminating one major component used to heat the plasma, freeing up much-needed space.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), the private company Tokamak Energy and Kyushu University in Japan have proposed a design for a compact, spherical fusion pilot plant ...
Nudges fail to motivate vaccination
2024-08-06
One popular strategy to motivate people to get vaccinated is the nudge—a message designed to take advantage of human tendencies to conform to social norms, seek to protect loved ones or community, and to prefer treatments with high efficacy rates. Jiseon Chang and colleagues sought to assess the efficacy of such nudges in real world contexts during the COVID-19 pandemic. The authors paid for ads to appear on Facebook between October 2021 and January 2022, reaching almost 15 million users in Brazil, Russia, South Africa, Taiwan, ...
Caregiving: Poll reveals who’s providing care and who they’re caring for
2024-08-06
More than 1 in 4 people age 50 and older helps take care of at least one family member or friend who has a health problem or disability, a new poll finds.
And among those caregivers, the new results from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging reveal a lot about who they are and who they’re caring for.
In all, 30% of all people in their 50s and early 60s provide care to at least one person with a health issue or disability, compared with 23% of people over 65. And 1 in 10 caregivers in their 50s and early 60s are juggling taking care of three or more people.
In ...
To predict tax revenue, look at corporate earnings
2024-08-06
To Predict Tax Revenue, Look at Corporate Earnings
States can make more accurate budget forecasts and avoid midyear cuts if they include growth in corporate earnings
AUSTIN, Texas -- In the complex task of building a state budget, much rides on the accuracy of its fiscal crystal ball: its forecast of how much tax revenue will come in to fund services during the year ahead. Forecasting errors have increased since 2001 due to revenue volatility, such as wider swings in personal income and consumer spending.
New research from Texas ...
New visual technique could advance early detection of neurodegenerative diseases
2024-08-06
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (08/06/2024) — Researchers at the University of Minnesota, have developed a new visual diagnostic technique that can be used to advance early detection for neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's disease and similar diseases that affect animals, including Chronic Wasting Disease in deer.
The research is published in npj Biosensing, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature.
Named Cap-QuIC (Capillary-enhanced Quaking-Induced Conversion), researchers will now be able to distinguish infected samples with the naked eye, which makes testing ...
ALS diagnosis and survival linked to metals in blood, urine
2024-08-06
People with higher levels of metals found in their blood and urine may be more likely to be diagnosed with — and die from — amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, a University of Michigan-led study suggests.
Researchers have known that ALS, a rare but fatal neurodegenerative condition, is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, including exposure to pesticides and metals.
This latest study examined the levels of metals in the blood and urine of people with and without ALS, finding that exposure to individual and mixtures of metals is associated with a greater risk for ALS and shorter survival.
The ...
Anxiety reframed can make business pitches more effective
2024-08-06
PULLMAN, Wash. – It may be possible to turn anxiety into a superpower in some scenarios, recent research with entrepreneurs indicates.
A Washington State University-led study found that if entrepreneurs preparing to make a funding pitch connected their pitch anxiety to their passion for their venture, judges ranked their performance higher. Perhaps even more importantly, the judges were also more likely to recommend them for funding.
This emotion reframing involved the entrepreneurs recognizing that they were feeling anxious partly because the project means so much to them. Entrepreneurs who tried other strategies ...
Study finds refined corn flour with added corn bran can lower cholesterol
2024-08-06
The findings of the randomized crossover clinical trial, available online now and slated to appear in an upcoming issue of the Journal of Nutrition, reveal simply swapping in foods made from refined corn flour + corn bran can lower LDL cholesterol concentrations by anywhere from 5% - 13.3% in just four weeks.
The trial compared the impact of whole-grain corn meal, refined corn meal, and a blend (refined corn meal plus corn bran) and found that 70% of the participants saw significant reductions in LDL cholesterol concentrations when consuming the blend. For the other corn flours, participants did not see a decrease in their LDL or total cholesterol ...
Carvings at ancient monument may be world’s oldest calendar
2024-08-06
Markings on a stone pillar at a 12,000 year-old archaeological site in Turkey likely represent the world’s oldest solar calendar, created as a memorial to a devastating comet strike, experts suggest.
The markings at Göbekli Tepe in southern Turkey – an ancient complex of temple-like enclosures adorned with intricately carved symbols – could record an astronomical event that triggered a key shift in human civilisation, researchers say.
The research suggests ancient people were able to record their observations of the sun, moon and constellations in ...
Sport or snack? How our brain decides
2024-08-06
In brief:
The chemical messenger orexin and the orexin neurons in the brain mediate the decision between exercise and snacking. Researchers at ETH Zurich made this discovery in mice. The results are likely to be transferable to humans.
In the experiment, mice with a blocked orexin system opted more frequently for the milkshake offered them and less for exercise.
These results could help in researching and developing new strategies to promote physical activity in people.
Should I go and exercise, or would I rather go to the café ...
[1] ... [1006]
[1007]
[1008]
[1009]
[1010]
[1011]
[1012]
[1013]
1014
[1015]
[1016]
[1017]
[1018]
[1019]
[1020]
[1021]
[1022]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.