AI saving humans from the emotional toll of monitoring hate speech
2024-05-29
A team of researchers at the University of Waterloo have developed a new machine-learning method that detects hate speech on social media platforms with 88 per cent accuracy, saving employees from hundreds of hours of emotionally damaging work.
The method, dubbed the Multi-Modal Discussion Transformer (mDT), can understand the relationship between text and images as well as put comments in greater context, unlike previous hate speech detection methods. This is particularly helpful in reducing false positives, which are often ...
Chicken feathers to deliver chemotherapy drugs and repair enzymes
2024-05-29
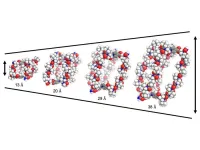
A new method of drug delivery using proline, an amino acid found in chicken feathers and skin tissue, could be used to limit the side effects of chemotherapy and repair important enzymes, new research suggests.
Published in the journal Chem today, researchers have designed a cage (a box made of single molecules) from biologically compatible peptides, short amino acids that form the basis of proteins. These cages can house drugs of different sizes and transport them in the body with high levels of precision.
The negative ...
Bio-inspired cameras and AI help drivers detect pedestrians and obstacles faster
2024-05-29
It’s every driver’s nightmare: a pedestrian stepping out in front of the car seemingly out of nowhere, leaving only a fraction of a second to brake or steer the wheel and avoid the worst. Some cars now have camera systems that can alert the driver or activate emergency braking. But these systems are not yet fast or reliable enough, and they will need to improve dramatically if they are to be used in autonomous vehicles where there is no human behind the wheel.
Quicker detection using less computational ...
Graphene gets cleaned up
2024-05-29
Graphene has been called “the wonder material of the 21st century.” Since its discovery in 2004, the material—a single layer of carbon atoms—has been touted for its host of unique properties, which include ultra-high electrical conductivity and remarkable tensile strength. It has the potential to transform electronics, energy storage, sensors, biomedical devices, and more. But graphene has had a dirty little secret: it's dirty.
Now, engineers at Columbia University and colleagues at the University of Montreal and the National Institute of Standards and Technology are poised to clean things up with an oxygen-free chemical vapor ...
Study finds older adults hospitalized for heart failure had high risk of kidney complications
2024-05-29
In a study of Medicare beneficiaries, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital found that one year after hospitalization for heart failure, 6 percent of patients had progressed to dialysis.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Study led by Brigham researchers found that among older adults hospitalized for heart failure, nearly 3 in 4 were discharged with reduced kidney function.
Lower kidney function was associated with substantially higher risk of kidney complications and other adverse clinical outcomes among older adults, with more than 1 in 20 progressing to dialysis within one year after heart failure hospitalization.
These findings emphasize the need ...
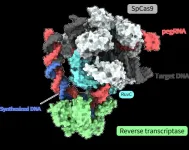
Editing without “cutting”: Molecular mechanisms of new gene-editing tool revealed
2024-05-29
Joint research led by Yutaro Shuto, Ryoya Nakagawa, and Osamu Nureki of the University of Tokyo determined the spatial structure of various processes of a novel gene-editing tool called “prime editor.” Functional analysis based on these structures also revealed how a “prime editor” could achieve reverse transcription, synthesizing DNA from RNA, without “cutting” both strands of the double helix. Clarifying these molecular mechanisms contributes greatly to designing gene-editing tools accurate enough for gene therapy treatments. The findings were published in the journal Nature.
The ...
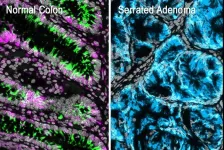
Identifying the initial steps in colorectal cancer formation
2024-05-29
Research led by Weill Cornell Medicine provides new evidence that most colorectal cancers begin with the loss of intestinal stem cells, even before cancer-causing genetic alterations appear. The results, published on May 29 in Developmental Cell, overturn the prevailing theory for colorectal tumor initiation and suggest new ways to diagnose the disease before it has a chance to become established.
“Colorectal cancer is very, very heterogeneous, which has made it difficult for many years to classify these tumors in order to inform therapy,” said senior author Dr. ...
hnRNPM, a guardian of the integrity of cellular protein production
2024-05-29
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions have discovered that a protein called hnRNPM helps protect the integrity of the process cells use to make proteins. hnRNPM works by preventing the cell from making mistakes while it is putting together the different components leading to newly produced proteins. In cancer cells, loss of hnRNPM triggers an interferon immune response, suggesting that this protein may hold clinical promise. The findings appeared in Molecular Cell.
“Synthesizing a protein is like putting together the different parts of a machine. If during the assembly process parts that do not belong are incorporated ...
Children often exposed to problematic click bait during YouTube searches
2024-05-29
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – When a child peruses YouTube, the content recommended to them is not always age appropriate, a new study suggests.
Researchers mimicked search behaviors of children using popular search terms, such as memes, Minecraft and Fortnite, and captured video thumbnails recommended at the end of each video.
Among the 2,880 thumbnails analyzed, many contained problematic click bait, such as violence or frightening images, according to the Michigan Medicine led research in JAMA Network Open.
“Children spend a significant amount of time on free video sharing platforms that ...
Modular, scalable hardware architecture for a quantum computer
2024-05-29
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Quantum computers hold the promise of being able to quickly solve extremely complex problems that might take the world’s most powerful supercomputer decades to crack.
But achieving that performance involves building a system with millions of interconnected building blocks called qubits. Making and controlling so many qubits in a hardware architecture is an enormous challenge that scientists around the world are striving to meet.
Toward this goal, researchers at MIT and MITRE have demonstrated a scalable, modular hardware platform that ...
Landmark study is step towards energy-efficient quantum computing in magnets
2024-05-29
Researchers from Lancaster University and Radboud University Nijmegen have managed to generate propagating spin waves at the nanoscale and discovered a novel pathway to modulate and amplify them.
Their discovery, published in Nature, could pave the way for the development of dissipation free quantum information technologies. As the spin waves do not involve electric currents these chips will be free from associated losses of energy.
The rapidly growing popularity of artificial intelligence comes with an increasing desire for fast and energy efficient computing devices and calls for novel ...
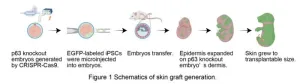
Grow the skin you’re in: in vivo generation of chimeric skin grafts
2024-05-29
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that donor keratinocytes injected into mouse embryos form sheets of epidermis that can be used as autologous skin grafts
Tokyo, Japan – Skin grafting is an essential procedure used to treat severe skin wounds. In the case of extensive wounds, however, it can be challenging to harvest enough donor skin, and generating artificial skin substitutes that include hair follicles and sweat glands and can engraft on deep wounds has not been successful. Now, researchers from Japan report a new way to “grow your own” donor skin that could help improve the success of skin graft generation.
In a study published last ...
BGU researchers and colleagues discover therapeutic potential of increasing MIF protein levels as a novel approach for treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
2024-05-29
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, May 29, 2024 – A recent collaborative research endeavor, published in the prestigious Cell Press journal Cell Reports Medicine, highlights a promising therapeutic avenue for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Led by researchers from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in conjunction with counterparts from Germany, the USA, and Canada, the study delves into the potential of augmenting macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) protein levels as a novel approach to tackling ALS.
ALS, often referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a devastating neurodegenerative condition characterized by the progressive loss of motor neurons, leading to muscle ...
War magnifies politicians’ gendered behavior, public biases, research finds
2024-05-29
Women’s participation in politics is essential to advancing women’s rights and contributes to countries’ overall stability and economic prosperity. According to a 2023 report by UN Women and the Inter-Parliamentary Union, one-fourth of parliamentary positions worldwide are held by women. Although current representation is still far from equal, it represents a significant increase over the last 20 years.
However, a new paper from Washington University in St. Louis — published ...
International experts reach consensus on the labeling of spatial neglect
2024-05-29
East Hanover, NJ, May 29, 2024 — A consensus has been achieved by an international team of rehabilitation researchers and clinicians on the standardized labeling of spatial neglect, a common disorder following neurological injury, which is characterized by a lack of awareness or response to objects or stimuli on the side opposite a brain lesion. The panel reached a 75% consensus to adopt "spatial neglect" as the standard term for the disorder.
The consensus paper, titled “An International and ...
Gaps in transition from pediatric to adult care for individuals living with sickle cell disease associated with more hospital visits
2024-05-29
(WASHINGTON, May 29, 2024) – Individuals living with sickle cell disease (SCD) who experience a delay of more than six months in transitioning from pediatric to adult care are twice as likely to be hospitalized compared to those who transition in less than two months, according to a study published in Blood Advances.
SCD is the most common inherited red blood cell disorder in the United States, affecting an estimated 100,000 people. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, SCD affects one out of every 365 Black or African American births and one out of every 16,300 ...
STEP Demo supercritical CO2 pilot plant generates electricity for the first time
2024-05-29
SAN ANTONIO — May 29, 2024 —The Supercritical Transformational Electric Power (STEP) Demo pilot plant has generated electricity for the first time using supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO2) power cycles. The $169 million, 10-megawatt sCO2 facility at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in San Antonio is demonstrating next-generation power production technology in a project led by GTI Energy in collaboration with SwRI, GE Vernova, the U.S. Department of Energy/National Energy Technology Laboratory (U.S. DOE/NETL), and several industry participants.
“The impact of demonstrating that the sCO2 technology works cannot be overstated,” said SwRI Project Manager Dr. Jeff ...
Risky path to meeting climate targets for Stockholm
2024-05-29
The Swedish capital Stockholm aims to capture more carbon dioxide than is emitted by 2030. Therefore, the city is investing in new technology at a combined heat and power plant. But it is a strategy that has been adopted without sufficient discussion of the risks, says researchers at Linköping university, Sweden.
“Stockholm has a very ambitious climate policy. But there’s also been a kind of resignation. This new technology has appeared to offer the promise of a solution. And that’s perhaps why there’s been no critical discussion at all,” says researcher Alexander Olsson at the Department of Thematic ...
Longer freight trains have a higher risk of derailment, new study shows
2024-05-29
In February 2023, 38 cars from a 151-car, 9,300-foot-long freight train derailed in East Palestine, Ohio, leading to the release of hazardous materials that required the evacuation of more than 2,000 residents. In recent years, such longer and heavier freight trains have become more common, primarily driven by fuel efficiency, cost-savings, and emissions reduction measures in the railroad industry.
New research in the journal Risk Analysis has confirmed that longer freight trains bring with them a higher risk of derailment. The study found that a 100-car train is more than twice as likely to experience a derailment than ...
The 2024 Global Food Policy Report stresses urgent need for transformative action to achieve sustainable healthy diets and improved nutrition
2024-05-29
Washington DC, May 29, 2024: In the face of growing challenges posed by unhealthy diets, all forms of malnutrition, and environmental constraints, the 2024 Global Food Policy Report (GFPR) — released today by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) — underscores the importance of transforming complex global food systems to ensure sustainable healthy diets for all.
Progress in reducing undernutrition and micronutrient deficiencies has slowed in low- and middle-income countries, while overweight and obesity has rapidly increased worldwide. Many countries ...
Electrochromic films — like sunglasses for your windows?
2024-05-29
Advances in electrochromic coatings may bring us closer to environmentally friendly ways to keep inside spaces cool. Like eyeglasses that darken to provide sun protection, the optical properties of these transparent films can be tuned with electricity to block out solar heat and light. Now, researchers in ACS Energy Letters report demonstrating a new electrochromic film design based on metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that quickly and reliably switch from transparent to glare-diminishing green to thermal-insulating red.
Hongbo Xu and colleagues used MOFs in their electrochromic film because of the crystalline substances’ abilities to form thin ...
Chocolate’s tasty flavors might pose a risk in other desserts
2024-05-29
What makes chocolate taste and smell so delicious? Chemistry, of course! A variety of molecules work together to create that unmistakable aroma, but those same molecules might carry some unwanted health effects if there are too many around. According to research published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, while many of the compounds appeared in chocolate in low enough concentrations to be safe, higher amounts were found in some baked sweet treats.
When making chocolate, cocoa beans are roasted to help their chocolatey flavors shine. During this process, new molecules ...
The New York Academy of Sciences and the Leon Levy Foundation Announce the 2024 Leon Levy Scholars in Neuroscience
2024-05-29
New York, NY, May 29, 2024 — The New York Academy of Sciences and the Leon Levy Foundation announced today the 2024 cohort of Leon Levy Scholars in Neuroscience, continuing a program initiated by the Foundation in 2009 that has supported 170 fellows in neuroscience.
This highly regarded postdoctoral program supports exceptional young researchers across the five boroughs of New York City as they pursue innovative neuroscience research and advance their careers toward becoming independent principal investigators. Nine scholars were competitively selected for a three-year term from a broad pool of applications from more than a dozen ...
The once-welcomed Rohingya refugees now face hostility from the hosts in Bangladesh
2024-05-29
The number of refugees has sharply increased in recent decades, reaching 37.8 million in 2022. Amidst this surge, host communities—locals residing in areas where refugee camps are situated—are also positively and negatively impacted by the refugee influxes. The negative impacts include competition over scarce resources and in the unskilled labor market. While the international media and aid organizations put the spotlight on assisting refugees, the challenges faced by host communities are frequently sidelined.
In 2017, over ...
Improving air quality increases forest fires
2024-05-29
If we want cleaner air, fewer forest fires, and less severe climate change, a new UC Riverside study shows we must reduce aerosol pollution and greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide at the same time.
The study found that boreal forests in the northern hemisphere are particularly vulnerable to negative effects of cleaning up aerosol pollution. This includes forests in Canada, Alaska, northern Europe, and northern Russia.
Aerosols are small particles like dust and sea salt as well as airborne chemicals produced by fossil fuel combustion. They are responsible for poor air quality. The UCR study, published in the journal ...
[1] ... [1147]
[1148]
[1149]
[1150]
[1151]
[1152]
[1153]
[1154]
1155
[1156]
[1157]
[1158]
[1159]
[1160]
[1161]
[1162]
[1163]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.