Clues to mysterious disappearance of North America’s large mammals 50,000 years ago found within ancient bone collagen
2024-05-31
50,000 years ago, North America was ruled by megafauna. Lumbering mammoths roamed the tundra, while forests were home to towering mastodons, fierce saber-toothed tigers and enormous wolves. Bison and extraordinarily tall camels moved in herds across the continent, while giant beavers plied its lakes and ponds. Immense ground sloths weighing over 1,000 kg were found across many regions east of the Rocky Mountains.
And then, sometime at the end of the Last Ice Age, most of North America’s megafauna disappeared. How and why remains hotly contested. Some researchers believe the arrival of humans was pivotal. Maybe the animals were hunted and eaten, or maybe humans just altered ...
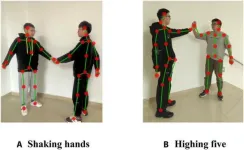
Revolutionizing interaction recognition: The power of merge-and-split graph convolutional networks
2024-05-31
In a significant advancement for robotics and artificial intelligence, researchers at Chongqing University of Technology, along with their international collaborators, have developed a cutting-edge method for enhancing interaction recognition. The study, published in Cyborg and Bionic Systems, introduces the Merge-and-Split Graph Convolutional Network (MS-GCN), a novel approach specifically designed to address the complexities of skeleton-based interaction recognition.
Human interaction recognition plays a crucial role in various applications, ranging from enhancing human-computer interfaces ...
Do shape-memory alloys remember past strains in their life?
2024-05-31
Endowed with the power of memory, certain alloys can magically return to their original shape when heated or deformed. However, the repeated back-and-forth between the original and new configuration may leave permanent imprints on the alloy’s microscopic features, which could then impact its ability to reversibly transform shape. Thus, unraveling the impact of the strain history on these alloys’ functionality is essential to improving predictive capabilities, but it has not received enough attention.
To fill this knowledge gap, the National Science Foundation ...
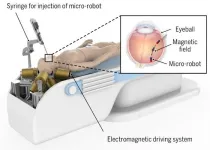
A novel electromagnetic driving system for 5-DOF manipulation in intraocular microsurgery
2024-05-31
The electromagnetic driving systems are proposed for the flexible 5-DOF magnetic manipulation of a micro-robot within the posterior eye, enabling precise targeted drug delivery. A research team has presented a novel electromagnetic driving system that consists of eight optimized electromagnets arranged in an optimal configuration and employs a control framework based on an active disturbance rejection controller (ADRC) and virtual boundary.
The team published their findings in Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Mar 23, 2024.
Intraocular microsurgery has witnessed a transition from the utilization of conventional handheld surgical tools to the adoption of robot-assisted surgery, owing ...
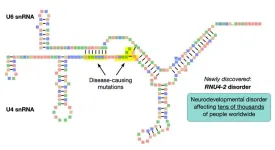
Researchers identify a genetic cause of intellectual disability affecting tens of thousands
2024-05-31
New York, NY [May 31, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and others have identified a neurodevelopmental disorder, caused by mutations in a single gene, that affects tens of thousands of people worldwide. The work, published in the May 31 online issue of Nature Medicine [DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03085-5], was done in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Bristol, UK; KU Leuven, Belgium; and the NIHR BioResource, currently based at the University of Cambridge, UK.
The findings will improve clinical diagnostic ...
EMBARGOED: Nearly one-third of US adults know someone who’s died of drug overdose
2024-05-31
Losing a loved one to drug overdose has been a common experience for many Americans in recent years, crossing political and socioeconomic divides and boosting the perceived importance of the overdose crisis as a policy issue, according to a new survey led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
A nationally representative survey of more than 2,300 Americans, fielded in spring 2023, suggests that 32 percent of the U.S. adult population, or an estimated 82.7 million individuals, has lost someone they know to a fatal drug overdose. ...
Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of all-cause mortality in women
2024-05-31
About The Study: Higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% lower risk of all-cause mortality in this cohort study. This inverse association was partially explained by multiple cardiometabolic factors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shafqat Ahmad, Ph.D., email shafqat.ahmad@medsci.uu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14322)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Traumatic brain injury strikes 1 in 8 older Americans
2024-05-31
Some 13% of older adults are diagnosed with traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to a study by UC San Francisco and the San Francisco VA Health Care System. These injuries are typically caused by falls from ground level.
Researchers followed about 9,200 Medicare enrollees, whose average age was 75 at the start of the study, and found that contrary to other studies of younger people, being female, white, healthier and wealthier was associated with higher risk of TBI.
The study publishes in JAMA Network Open on May 31, 2024.
The researchers, ...
Stem cells shed new light on how the human embryo forms
2024-05-31
A new study using stem cell-based models has shed new light on how the human embryo begins to develop, which could one day benefit the development of fertility treatment.
The study led by at the University of Exeter Living Systems Institute has revealed how early embryo cells decide between contributing to the foetus or to the supporting yolk sac.
Understanding this decision is important because the yolk sac is essential for later development in the womb. Producing the right number of yolk sac forming cells may be critical for infertility treatment using in vitro fertilised (IVF) embryos.
Only limited research ...
BU study finds policy makers’ use of in-hospital mortality as a sepsis quality metric may unfairly penalize safety-net hospitals
2024-05-31
EMBARGOED by JAMA Network Open until 11 a.m., ET May 31, 2024
Contact: Maria Ober, mpober@bu.edu
BU Study Finds Policy Makers’ Use of In-Hospital Mortality as a Sepsis Quality Metric May Unfairly Penalize Safety-net Hospitals
(Boston)—Sepsis is a leading cause of death and disability and a key target of state and federal quality measures for hospitals. In-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis is frequently measured for benchmarking, both by researchers and policymakers. For example, in New York, sepsis regulations mandate reporting of risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality, and hospitals with lower or higher than expected in-hospital ...
Mediterranean diet tied to one-fifth lower risk of death in women
2024-05-31
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital identified and assessed underlying mechanisms that may explain the Mediterranean diet’s 23 percent reduction in all-cause mortality risk for American women
The health benefits of the Mediterranean diet have been reported in multiple studies, but there is limited long-term data of its effects in U.S. women and little understanding about why the diet may reduce risk of death. In a new study that followed more than 25,000 initially healthy U.S. women for up ...
Relieving a fear of public speaking
2024-05-31
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research - If you dread public speaking you are not alone. It is a leading social phobia, one that can cause a state of anxiety that reduces otherwise articulate people to nervous incoherence.
A strong fear of public speaking is known as glossophobia. Academic studies estimate it affects 20 per cent of the population, but depending on the sample and methodology, the figure could be as high as 40 per cent.
As American writer and humourist Mark Twain said, ...
Innovating learning with ChatGPT-based Prompt Tutor
2024-05-31
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research – “Giving students immediate and frequent feedback makes online learning more effective,” Associate Professor Ouh Eng Lieh told the Office of Research.
However, based on how most online lessons are designed, questions could not be answered nor doubts clarified until students meet their instructor in the following face-to-face class.
The time delay of a few days to a few weeks can impede student learning as it might make it difficult for students to catch up and understand the subsequent topics in the course.
Learning also ...
Moving beyond cubicles: How an active workplace design can drive workers’ behaviors
2024-05-31
Ishikawa, Japan -- Physical inactivity and sitting for prolonged hours are highly prevalent among office-based workers, known to be resulting in various health risks and economic constraints. However, to reduce sedentary time and increase physical activity, health promotion interventions alone are insufficient. The design of workplaces should also be considered to promote interactive behavior among workers.
Many models, such as the socio-ecological model, show how multiple factors interact to influence workers' active and sedentary behaviors. These models specifically magnify the impact of workplace environments in shaping these behaviors. Several studies ...
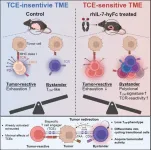
Breakthrough in using bispecific antibodies for solid tumors
2024-05-31
Professor Seung-Woo Lee and PhD candidate Kun-Joo Lee from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), in collaboration with NeoImmuneTech Director Donghoon Choi and Professors Dae Hee Kim and Sun Shim Choi from Kangwon National University, have revealed a groundbreaking method to significantly enhance the efficacy of bispecific antibody therapies in treating solid tumors. Their findings were published on May 13 in “Cell Reports Medicine”, an international journal of healthcare research.
Bispecific antibodies, which can simultaneously bind to two different ...
Fjords are effective carbon traps regardless of oxygen levels
2024-05-31
The fjords on Sweden’s west coast act as effective carbon traps regardless of whether the bottom water is oxygen-rich or not. This is the conclusion of a new study with researchers from the University of Gothenburg.
Large quantities of plant parts sink to the bottom of fjords on the Swedish west coast where they form sediment. This buries organic carbon, which would otherwise contribute to ocean acidification and the greenhouse effect. When the plant parts are exposed to oxygen and other substances, the organic carbon begins to decompose into inorganic carbon, which can be dissolved into carbonic acid in the water. Research ...
Korea University College of Medicine’s team predict hearing conditions in vestibular schwannoma patients using radiomics
2024-05-31
Korea University College of Medicine’s Team Predict Hearing Conditions in Vestibular Schwannoma Patients Using Radiomics
A recent study demonstrates that radiomics imaging analysis can effectively forecast the hearing status of patients with vestibular schwannoma patients. Since treatment methods, such as surgery or active surveillance, vary for these patients based on tumor size and hearing condition, predicting hearing status is crucial in planning and determining the appropriate treatment.
The research team led by Professor June Choi from the Department ...
European Academy of Sciences honors Rice’s Pol Spanos with prestigious award
2024-05-31
HOUSTON – (May 31, 2024) – For his “exceptional contributions to the field of dynamics,” Pol Spanos, the Lewis B. Ryon Professor of Mechanical and Civil Engineering at Rice University, has been awarded the 2024 Blaise Pascal Medal in Engineering by the European Academy of Sciences.
Spanos, who joined the Rice faculty in 1984, was recognized for his “theoretical insights, ranging from equivalent linearization to statistical quadratization, which have significantly advanced our understanding of structural behavior. These insights have not only led to more accurate predictions but have also empowered engineers ...
Rice’s Jamie Padgett wins Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award
2024-05-31
HOUSTON – (May 31, 2024) – Jamie Padgett, the Stanley C. Moore Professor in Engineering and chair of civil and environmental engineering at Rice University, has received the 2024 Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE).
Padgett was recognized for her “contributions to fragility, risk and resilience modeling of multimodal transportation systems and their infrastructure components when subjected to earthquakes and other hazards.”
Her ...
Sleep moderates the link between bullying and suicide in teens
2024-05-31
DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2024 annual meeting found that sleep duration significantly moderates the association between bullying and suicide attempts among adolescents in the U.S.
The study revealed that 15% of adolescents reported they were bullied at school, and 16% were bullied electronically; 10.2% reported they had attempted suicide during the past year; and 77.3% did not adhere to sleep duration recommendations. Adolescents who reported 4 hours of sleep or less per night were two times as likely to attempt suicide, and sleep duration significantly moderated the association between bullying ...
AI-controlled stations can charge electric cars at a personal price
2024-05-31
As more and more people drive electric cars, congestion and queues can occur when many people need to charge at the same time. A new study from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden shows how AI-controlled charging stations, through smart algorithms, can offer electric vehicle users personalised prices, and thus minimise both price and waiting time for customers. But the researchers point to the importance of taking the ethical issues seriously, as there is a risk that the artificial intelligence exploits information from motorists.
Today's commercial ...
The world’s most powerful anti-fungal chemistries cause fungal pathogens to self-destruct
2024-05-31
Scientists have discovered that the most widely-used class of antifungals in the world cause pathogens to self-destruct. The University of Exeter-led research could help improve ways to protect food security and human lives.
Fungal diseases account for the loss of up to a quarter of the world’s crops. They also pose a risk to humans and can be fatal for those with weakened immune systems.
Our strongest "weapon" against fungal plant diseases are azole fungicides. These chemical products account for to a quarter of the world agricultural ...
Could the world famous Roman Baths help scientists counter the challenge of antibiotic resistance?
2024-05-31
The world-famous Roman Baths are home to a diverse range of microorganisms which could be critical in the global fight against antimicrobial resistance, a new study suggests.
The research, published in the journal The Microbe, is the first to provide a detailed examination of the bacterial and archaeal communities found within the waters of the popular tourist attraction in the city of Bath (UK).
Scientists collected samples of water, sediment and biofilm from locations within the Roman Baths complex including the King’s Spring (where the waters reach around 45°C) and the Great Bath, where the temperatures ...
Fast charging electric vehicles with stable high-energy density lithium-ion batteries
2024-05-31
A research team led by Dr. Choi Jeong Hee at the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) Battery Materials and Process Research Center, in cooperation with a Hanyang University team mentored by Professor Lee Jong-Won and a Kyunghee University team mentored by Professor Park Min-Sik, developed a core technology to ensure the charging/discharging stability and long-life of lithium-ion batteries under fast-charging conditions.
A crucial prerequisite for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is the enhancement of lithium-ion battery performance in terms of driving ...
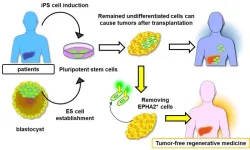
Tackling the hurdle of tumor formation in stem cell therapies
2024-05-31
Ikoma, Japan – Pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) are a type of stem cells capable of developing into various cell types. Over the past few decades, scientists have been working towards the development of therapies using PSCs. Thanks to their unique ability to self-renew and differentiate (mature) into virtually any given type of tissue, PSCs could be used to repair organs that have been irreversibly damaged by age, trauma, or disease.
However, despite extensive efforts, regenerative therapies involving PSCs still have many hurdles to overcome. One being the formation of tumors (via ...
[1] ... [1141]
[1142]
[1143]
[1144]
[1145]
[1146]
[1147]
[1148]
1149
[1150]
[1151]
[1152]
[1153]
[1154]
[1155]
[1156]
[1157]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.